![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
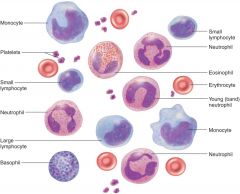
Blood Smear histology
|
4-6 liters (serum = plasma – fibrinogen) -- Plasma (yellowish-50%--water) -- Electrolytes: Na+ (extracellular compartment) -- Proteins – albumins, globulins and fibrinogen -- Nutrients-- Hormones (free or bound) -- Gases (CO2 and N3) -- Formed Elements – enclosed in a membrane with definite structures --- Erythrocytes ---
Leukocytes -- Granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) and Agranulocytes (lymphocytes, monocytes) --- Platelets (clotting, formed from megakaryocytes |
|
|
Components
|
Blood Proteins (liver) --- Albumins – colloid pressure, transport, viscosity, pH ---- Globulins – alpha (Hb), beta (Fe), gamma (IgG) ----- Fibrinogen – fibrin portion of blood clots
|
|
|
Viscosity - resistance to flow:
|
Increase in protein and blood cells and Dehydration increases viscosity
|
|
|
Osmolarity
|
total amount of solutes in blood which cannot diffuse out of capillaries -----
|
|
|
Colloid osmotic pressure – (oncotic pressure) set by amount of proteins in blood - nonpenatrated solutes
|
Used to determine filtration rates of capillaries
|
|
|
Hemopoiesis – production of blood (RBC, WBC and platelets
|
Begins with a Pluriopotent Stem Cell (PPSC) ---- Tissues:
Yolk Sac – blood islands produce stem cells which migrate during development to tissue sites ----------- Liver – stops production at birth -------- Bone Marrow – produces all 7 types ---- Spleen – after birth produces only lymphocytes ----- Thymus ----- Lymphoid tissues – thymus, tonsils, spleen, nodes: produce lymphocytes |
|
|
PPSC -- Pluriopotent Stem Cell --
|
– potential to develop into multiple mature cell types
|
|
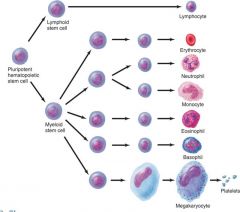
Myeloid vs Lymphoid hemopoiesis (Colony forming unit) -- need hormone to become a specific kind of cell
|
production in lymphoid tissues
vs bone marrow ( need growth-stimulating factor) |
|
|
Myeloid Stem Cells – multiply slowly
|
Colony forming units – differentiated into a specialized cell for each type of formed element
|
|
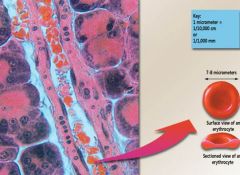
Erythrocytes
|
most abundant-- Carry O2 -- Bi-concave disc -- no nucleus or mitochondria -- Highly specialized cytoskeleton: spectrin and actin give flexibility -- Cytoplasm – 33% hemoglobin ---- Carbonic anhydrase – important enzyme for gas transport and blood pH
|
|
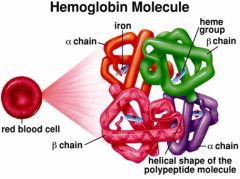
Hemoglobin – gas transport
|
HbA – 2a, 2b chains with heme groups – 4 chains bind O2 --- 98 % of O2 carried on Hb --- 5% CO2 carried on Hb --- HbF – fetal hemoglobin -- 2g chains instead of
Increased affinity for O2 allows transfer between mothers blood and fetus --- HbA2 – 2delta chains instead of b - increased in certain anemias and delta-thalassemia Structure --- Porphyrin ring cages iron – red color of blood ---- Heme group binds Fe2+ (iron) – 4X |
|
|
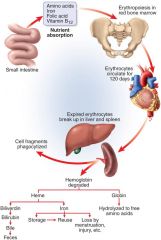
Erythropoiesis – production of red blood cells
|
3-5 days for production ---- Increase cell number --- Synthesis of hemoglobin ---- Loss of organelles
Hormonal Regulation – Erythropoietin (EPO) |
|
|
Hypoxemia –vs Emphysema (destructed lung disease) –
|
Low O2 in blood – stimulates EPO release from kidney tubule --- result in polycythemia (not that rbc not woeking but the LUNG)
|
|
Required for erythropoiesis:
|
Iron --- Folic Acid – essential for thymine synthesis, DNA
B12 – required for the action of folic acid (B9)--- Copper – Hb synthesis, transport - ceruloplasmin -- |
|
|
B12 – absorption
|
Requires – R-proteins (saliva) and Intrinsic Factor (stomach)
Absorption – receptor mediated endocytosis in ileum Transcobalamin transport in blood Deficicency – Pernicious anemia (megaloblastic) |
|
Hemolysis factors
|
Bilirubin -- Urobilogen --- Jaundice
|
|
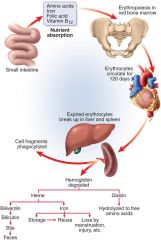
Hemolysis – spectrin gradually deteriorates
|
Membrane releases hemoglobin
Hemoglobin – macrophages cause release of Heme and Fe2+ Heme becomes biliverdin then bilirubin which binds to albumins Bilirubin to liver and enters bile Colonic bacteria convert to urobilinogen (brown) Jaundice – yellowing of skin and whites of eyes Hemolytic – too many RBC rupture Liver/Bile obstruction |
|
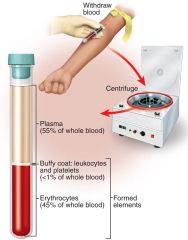
Hematocrit - % of whole blood composed of RBC’s (packed cell volume)
|
Males: 45- 52 % --- Females: 37- 48 % --- Why? -- Menus -- Hormones -- Body fat -- Dehydration – increases, but blood volume less
|
|
|
Blood Doping
|
Transfusion – elevated hemoglobin and hct
|
|
|
Recombinant EPO (1980’s)
|
Darbepoietin
Epogen Procrit |
|
|
Not all bad – treat anemia associated with cancer, kidney disease and AIDS
|
Increased number of reticulocytes
Risks of polycythemia |
|
|
Polycythemia – increased number of RBC’s
|
Primary – cancer of bone marrow cells --- Secondary – dehydration, emphysema, altitude, exercise, ↑ EPO --Risks – ↑ blood pressure, ↑ viscosity – clots
|
|
|
Anemia – decrease number of RBC’s
|
↓ Erythropoiesis (kidney, iron , B12, folic issues) --- ↑ Hemolysis ---Hypoblastic – decline in number of RBC’s ---- Aplastic – cessation of erythropoiesis
|
|
|
Thalassemia
|
abnormal hemoglobin – genetic alteration of globulins, geographical (, )
|
|
|
Symptoms of anemia
|
Decreased O2 delivery to tissues – hypoxia
Reduced blood osmolarity – edema Decrease blood viscosity – decreased blood pressure and faster heart beat |
|
|
Types of anemia
|
Hemolytic – increased hemolysis, hereditary
Microcytic – smaller than normal RBC – iron deficient anemia, bleeding Megaloblastic – larger than normal RBC – inability to divide, vitamin deficient |
|
Sickle Cell Anemia
|
1.3 % African Americans
Hemoglobin defects – HbS Single amino acid substitution RBC’s clump together Homozygous sickle cell, heterozygous resistant to malaria Symptoms: clots, pain, fatigue Treatment: management Pain killers Folic Acid Hydroxyurea Antibiotics for infections |
|
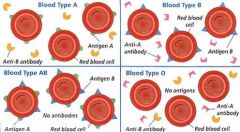
Blood Typing
|
ABO System Type O – universal donor – no antigens to agglutinate ------ Type AB – universal recipient – no antibodies
|
|
Rh Factor – reactions to antigen D
|
Rh+ has antigen D
Anti-D antibodies not normally present, form only when exposed to Rh+ blood |
|
|
Transfusions
|
first transfusion of an Rh- with Rh+ will lead to antibodies being produced (second transfusion must type)
|
|
|
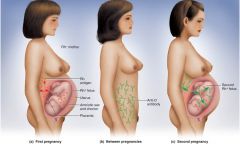
Pregnancy – Mom Rh-
|
First child Rh+ - at birth blood may mix and mom (Rh-) will produce antibodies
Second child Rh+ - then mom’s antibodies will attack Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) RhoGAM – binds to fetal D-antigens so Mom does not produce immune response HDN – infants anemic and jaundice, treat with phototherapy to degrade bilirubin |
|
|
Erythropoietin (EPO) was first isolated from the urine of anemic patients who had high circulating levels of the hormone.
|
Where is EPO produced in the body and what is the stimulus for release?
Although these patients had elevated levels of EPO, they were still anemic and unable to produced functional RBC’s. What are some possible reasons for this condition? How would these patients be treated? |
|
|
Blood smear
|
RBC-Platelet-WBC-Agran (Large mono- small leuko)-Granu (Baso-Neutro-Eosio
|
|
|
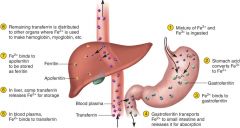
Fe3+ to Fe2+
|
gastroferitin -- transferitin (intestine) - aopferitin - Feritin (liver)
|

