![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do B and T lymph recognize antigens?
|
antigen-specific receptors on surface: BCR and TCR
|
|
|
What is an antigen? List examples of soluble molecule and molecules belonging to whole cells:
|
-molecules that are recognized and responded to by cells
-soluble: proteins, polysaccharides, glycoproteins, nucleoproteins -whole cells: bacteria, protozoa, tumor, virus-infected cells |
|
|
what are two names of the small molecular names to which the cells of adaptive system bind?
|
-epitopes or antigenic determinants
|
|
|
What is a difference between a B and a T cell? (Also, what KIND of antigens can T cells only recognize?)
|
-B cell recognize antigen by itself; T cell need MHC
-T cell only recognize protein antigens |
|
|
What are the three types of APC's:
|
-dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells
|
|
|
Draw a CTL:APC cell interaction and draw a Th:APC interaction
|
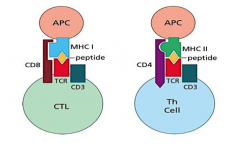
|
|
|
Where do APC's and T cells meet?
|
secondary lymph organs (lymph nodes)
|
|
|
How do you know that DC is maturing?
|
-upregulation of MHC molecules and expression of costimulation molecules such as B7
|
|
|
Define MHC (HLA) and define the 6 types of loci amongst the two classes. Where is class I found and where is class II found?
|
Major histocompatibility complex: human leukocyte antigen complex:
-1: (on all nucleated cells): HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C -2: (on APC's): HLA-DP; HLA-DQ; HLA-DR / only found on antigen presenting cells |
|
|
What are the properties of MHC molecules and genes? (3):
|
1.) co-dominant expression (both parental alleles of each are expressed)
2.) polymorphic genes (many diff. alleles are present in population) 3.) MHC expressing cell types: class II: professional APCs, macrophages, B cells and class I: all nucleated cells |
|
|
MHC Structure : Draw a picture of MHC1 and show where the CD8 bind and indicate how many aa can fit in between alpha 1/ alpha 2:
|
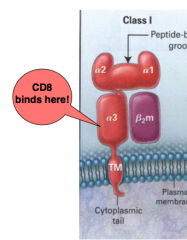
8-11 aa
|
|
|
MHC Structure : Draw a picture of MHC2 and show where the CD4 bind and indicate how many aa can fit in between alpha 1/ beta 1:
|
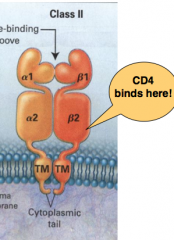
10-30 aa
|
|
|
What is the name of processing of intracellular antigens: (2)
List/ draw steps that involve Class I MHC being loaded with intracellular peptides: |
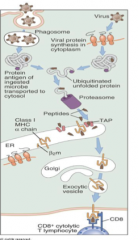
-cytosolic or endogenous pathways
-ubiquitinated unfolded protein -transfer to the ER via TAP (transporter associated with antigen processing, TAP) -the MHC class I chain is in the ER: has the alpha and beta chain / form stable complexes than transporter to the golgi and then via exocytic vesicle to the membrane |
|
|
What is the name of processing of extracellular antigens? (2)
List the steps involved with a class II MHC being loaded with extracellular peptides: |
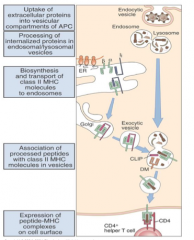
-endocytic or exogenous
-exogenous proteins taken in are fragmented by proteases in ENDOSOME -endosome fuses with lysozome -The alpha and beta chains of MHC class II (with invariant chain) synthesized in ER and taken to golgi then exocytic vesicle; --> THEN fuse with lysosome -invariant chain digested to leave CLIP (class-II associated invariant chain protein) -HLA-DM takes clip out of the MHC-II |
|
|
What is infection defined as and can it be both extracellular and intracellular?
|
-attachment and entry of pathogen to host
-yes; both intracellular and extracellular |
|
|
Why the separation of class I and class II pathways of antigen processing?
|
-to establish the different versions of T cell effector responses for extracellular and intracellular hosts
|

