![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Drugs causing rhabdomyolysis ? |
Alcohol,heroine,cochise, acetomenophin,statins, glucocorticoids. |
|
|
Drugs causing auto immune myopathy resembling polymyosities? |
D pencillamine |
|
|
Drug producing mitochondria myopathy with red ragged fibres? |
Zidovidine |
|
|
Drugs causing painless myopathies +autophagi vacuoles? |
Amidorne, hydrochloroquine. |
|
|
Causes of small fibre neuropathy? |
1.DM 2.leprosy 3.amyloidosis 4.tangeris ds 5.fabrys 6.HIV 7.vasculitis 8.sle 9. Arsenic poisoning |
|
|
Causes of large fibre neuropathy? |
1.B12 def,pyrodoxine toxicity 2.cisplatin nd taxanes 3.fredrichs ataxia 4.paraneoplastic |
|
|
Causes of ganglionapathy ? |
1.sjogren 2.paraneoplastic |
|
|
Para neoplastic ganglonapathy |
Anti hu antibody, small cell CA of lung |
|
|
Combined small nd large fibre neuropathy seen in? |
1.carcinomatous 2.DM 3.primary biliary cirrhosis 4.hereditary |
|
|
Autonomic predominant condtns? |
1.gbs -AIBDP 2.DM 3.amyloidosis 4.porphyria 5.Paraneoplastic 6. Vincristin, cisplatin, amidorone |
|
|
Pattern in AIDP? |
Symmetrical proximal nd distal weakness with sensory loss |
|
|
Pattern in axonal small fibre neuropathy? |
Symmetrical distal sensory loss with or without weakness |
|
|
Pattern of ganglionapathy? |
Assymetrical propioceptive loss, without weakness nd with out length dependent |
|
|
Pattern of radiculopathy? |
Asymmetrical distal weakness with sensory loss, and pain along the distribution. |
|
|
Lenox-gastaut syndrome |
1.multiple seizure type 2.slow spike nd wave pattern on EEG 3.impaired cognitive function. |
|
|
Muscle presentation? |
Symmetrical weakness without sensory loss. |
|
|
H reflex is equal to? |
S1 of ankle jerk. |
|
|
Hereditary motor sensory neuropathy + upper limb postural tremors are seen in?? |
Roussy le`vy syndrome |
|
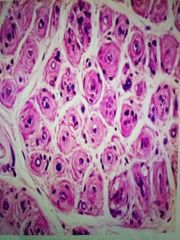
Wt is this nd where is it seen? |
Onion bulb formation seen in Charcot marry tooth ds mainly type 1 |
|
|
PS cavus +inverted champagne leg app +onion bulb formation on biopsy Diagnosis? |
Charcot merry tooth ds |
|
|
AR /ATP binding casette protein def ,assymetrical mono neuropathy, orange tonsils, axonal degenertn Ds diagnosis? |
Tangier's ds |
|
|
Peripheral neuropathy +RP +cerebral ataxia ds diagnosis? |
Refsum ds |
|
|
Phytanic axis oxidase def ,α oxidation of fatty acids is affected ds ? |
Refsum ds |
|
|
fabrys ds? |
AR, α galcatose def. |
|
|
HIV + poly radiculopathy is seen in? |
CMV infectn |
|
|
HIV + mono neuritis multiplex is seen in? |
Small vessel vasculitis |
|
|
Wt are betz cells? |
Giant pyramidal cells in layer 5 of motor cortex |
|
|
3 things to remember abt partial simple seizures ? |
1.todds palsy 2.epilepsy partialis continua 3.jacksonian march |
|
|
A kinetic Mutism or abulia is due to? |
B/l occlusion of ACA, leading to b/l ant cingulate gurus syndrome |
|
|
Gait apraxia is seen in? It is also called as? |
B/l frontal lobe lesions, also called as ignition foot phenomenon |
|
|
Which part of brain is affected in grestmann syndrome? |
Angular gurus in dominant lobe of parietal lobe |
|
|
What is grestmann syndrome? |
1.tactile agnosia 2.acalculia 3.finger agnosia 4.rt nd left disoriented 5.agraphia with alexia |
|
|
Wt is seen in b/l temporal lobe lesions ?? |
1.kluver bucy syndrome 2.deafness 3.korsakoffs amnestic state |
|
|
Wt is kluver bucy syndrome ? |
Seen in b/l temporal lobe lesion 1.increased aggression 2.loss of fear 3.increased sexual drive 4.loss of satiety 5.loss of goal-oriented behaviour |
|
|
Things to remember abt parvo cellular pathway? |
1.small receptive fields 2.color vision 3.no response to moving stimuli 4.stereopsis or depth |
|
|
Lesion of u/l occipital lobe? |
C/l homonemous macular sparring congrous hemi anopia 2.color agnosia 3.prosapagnosia |
|
|
Syndromes seen in b/l occipital love lesion? |
1.anthon's 2.balints syn |
|
|
Balints syndrome |
1.optic ataxia 2.occulomotor apraxia. 3.simultagnosia |
|
|
Anton's syn |
Denial of blindness, cortical bliness + presence of pupilary reflex |
|
|
Types of sensory aphasia? |
1.nominal aphasis 2.conduction aphasia 3.trans cortical sensory aphasis 4.wernickes aphasia |
|
|
Dementia + hallucination in Parkinsonism is called as? |
Dementia with lewy bodies |
|
|
2nd mcc of dementia? |
Vascular dementia |
|
|
Wt are shadow plaques in multiple sclerosis? |
Remyelinating axons in cns |
|
|
The auto reactive T lymphocytes are directed against wt in multiple sclerosis? |
Myelin basic protein nd myelin oligo dendrocyte glycoprotein. |
|
|
Lhermitt sign |
Electric shock like sensation frm back radiating to thigh seen in multiple sclerosis |
|
|
Uhthoff phenomenon? |
Unilaterally visual burning during hot showers or exercises ,sign of exacerbating symptoms in multiple sclerosis |
|
|
Which nutritional toxicity has parkinsonism like picture? |
Manganese |
|
|
Absent swallow tail sign seen in? |
Parkinsonism |

