![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the transpyloric plane (TPP)?
|
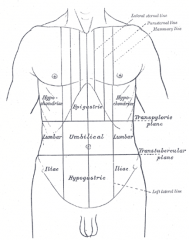
Halfway b/e the jugular notch and upper border of symphysis, this line crosses the tips of 9th costal cartilages anteriorly and 1st lumbar vertebra posteriorly
|
|
|
What is the transtubercular plane (TTP)?
|
The imaginary plane at the level of the iliac tubercles that crosses L5 posteriorly.
|
|
|
What is the subcostal plane?
|
The lowest point of the costal margin (margin of the 10th costal cartilage on each side. Lies at the level of the intervertebral disc b/e L2 and L3
|
|
|
What is the supracrestal (supracristal) plane?
|
L4; b/e the highest points of the iliac crests at L4 spinous process
|
|
|
What is the interspinous plane?
|
The sacral promontory: Connects the right and left ASIS (anterior superior ilial spines)
|
|
|
What are the layers of the abdominal wall?
|
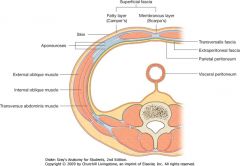
"Savage Surgeons Should Always Make Plans To Eat People"
1. Skin 2. Superficial fascia "Camper's fascia" - contains fat 3. Superficial fascia "Scarpa's fascia" - membranous layer 4. Anterior rectus sheath 5. Muscular layer (External oblique, Internal oblique, transversus abdominis) 6. Posterior Rectus sheath 7. Transversalis fascia 8. extraperitoneal fascia 9. parietal peritoneum |
|
|
What muscle tendon divides into two to envelop the Rectus abdominus muscle?
|
Tendon of Internal oblique
|
|
|
What fascial layer continues inferiorly into the peritoneal region to become the superficial perineal fascia (Colles' fascia)?
|
deep membranous layer (scarpa's fascia)
|
|
|
What fascial layer lines the deep surface of the transversus abdominus muscle?
|
Transversalis fascia
|
|
|
What separates the perietal peritoneum from the transversalis fascia?
|
Extraperitoneal fat
|
|
|
Which way do the fibers for external oblique and internal oblique run?
|
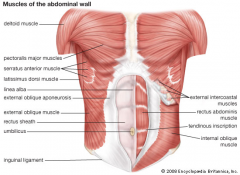
External oblique; fibers run diagonally antero-downward (like putting your hands into your front pockets)
Internal oblique; fibers run diagnoally postero-downward (like putting your hands into your back pockets) |
|
|
Which direction do the fibers of the transversus abdominus run?
|
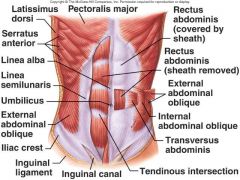
transversely across the abdomen
|
|
|
Where does the external oblique become aponeurotic?
|
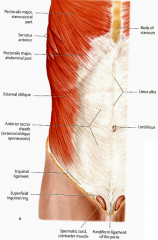
At the midclavicular line
|
|
|
Where do the fibers of the external oblique decussate?
|
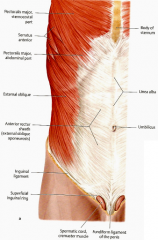
At the linea alba
|
|
|
What tendon forms the inguinal ligament?
|
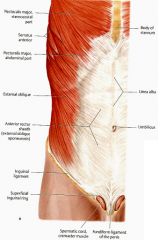
The inferior border of the aponeurosis of the external oblique
|
|
|
What muscles does the external abdominal oblique interdigitate with?
|
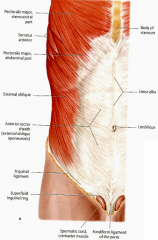
External surfaces of ribs 5-12 and interdigitates w/ the serratus anterior and the pectoralis major
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the external oblique?
|
1. Intercostal nerves from T7 to T11
2. subcostal nerve (T12) |
|
|
What muscles work together to bring the right shoulder toward the left hip?
|
Right external oblique and left internal oblique
|
|
|
What is the lacunar ligament?
|
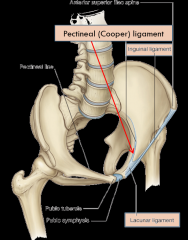
The ligament that connects the inguinal ligament to the pectineal (cooper's) ligament
|
|
|
What muscle contributes to the rectus sheath?
|
Internal abdominal oblique
|
|
|
B/e what layers of the anterior abdominal wall are the neurovascular contained?
|
B/e the internal abdominal oblique and the transversus abdominis muscle
|
|
|
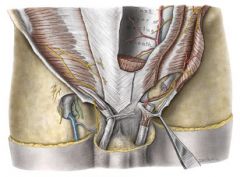
What muscle forms the falx inguinalis? What does this structure do?
|
The lower part of the transversis abdominis; this structure forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal.
|
|
|
What muscle forms the conjoint tendon?
|
The internal oblique and the transversis abdominis
|
|
|
Through what triangle would a hernia pass through if it was below the 12th right, medial to the internal oblique, lateral to the quadratus lumborum/erector spinae?
|
The lumbocostal/superior lumbar/Gryndfeldt triangle
|
|
|
Through what triangle would a hernia pass through if it was inferior to the latissimus dorsi, superior to the iliac crest and medial to the external oblique?
|
The inferior lumbar (petit) triangle
|
|
|
What triangle could a herniated kidney pass through?
|
Superior lumbar (Gryndfeldt) triangle
|
|
|
What are the contents of the rectus sheath?
|
1. Rectus abdominis muscle
2. Pyramidalis muscle 3. Superior Epigastric vessels 4. Inferior epigastric vessels 5. thoracoabdominal nerves |
|
|
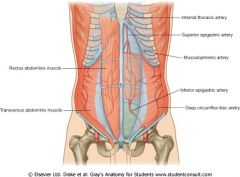
What does the superior epigastric vessel originate from?
|
Internal thoracic artery
|
|
|
What does the inferior epigastric artery originate from?
|
External iliac artery
|
|
|
What is the action of the rectus abdominis?
|

1. helps in respiration by depressing ribs
2. flexes and laterally rotates spine 3. assists in defecation, micturition, parturition, vomiting and coughing |
|
|
What is the origin of the iliohypogastric nerve? ilioinguinal nerve?
|
First lumbar nerve (L1)
|
|
|
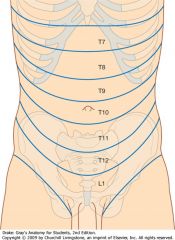
What nerve supplies the dermatome around the umbilicus?
|
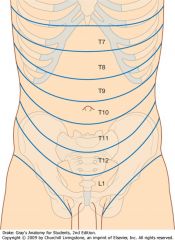
T10
|
|
|
What nerves supply the dermatomes from the xiphoid process to just above the umbilicus?
|
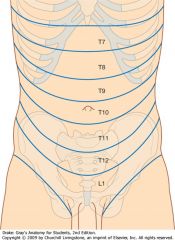
T7-T9
|
|
|
What nerves supply the dermatomes just below the umbilicus to the pubic region?
|
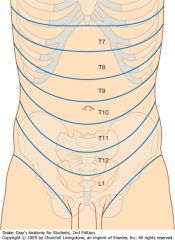
T11-L1
|
|
|
What does the ilioinguinal nerve supply?
|
the anterior surface of the scrotum/labia majora, and sends a small cutaneous br. to the thigh
|
|
|
What nerves pierce the rectus sheath?
|
T7-T12
|
|
|
What nerve pierces the internal abdominal oblique in front of the anterior superior iliac spine?
|
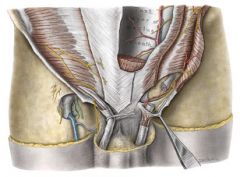
iliohypogastric nerve
|
|
|
What nerve pierces the external oblique aponeurosis above the superficial inguinal ring?
|
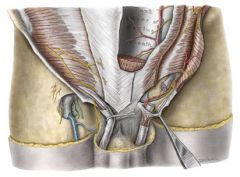
Iliohypogastric nerve
|
|
|
What does the iliohypogastric nerve terminate as?
|
The lowest anterior cutaneous branch of the abdomen/root of the penis
|
|
|
What nerves are the distal abdominal parts of the anterior rami of the inferior six spinal nerves?
|
thoracoabdominal nerves
|
|
|
What nerve supplies the area of the mons pubis?
|
Ilioinguinal nerve
|
|
|
What nerves supplies the area overlying the iliac crest
|
Iliohypogastric nerve
|
|
|
What does the ilioinguinal nerve supply?
|
1. skin of lower inguinal region
2. mons pubis 3. anterior scrotum/labium majora 4. adjacent medial thigh |
|
|
What nerve becomes cutaneous at the superficial inguinal ring?
|
Ilioinguinal nerve
|
|
|
What nerve pierces the internal oblique and runs along the inguinal canal?
|
Ilioinguinal nerve
|
|
|
What is the origin of the inferior epigastric artery?
|
External iliac artery
|
|
|
What is the origin of the deep circumflex iliac artery?
|
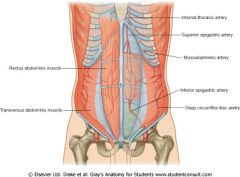
External iliac artery
|
|
|
What is the origin of the superifical epigastric artery?
|
Femoral artery
|
|
|
What is the origin of the superficial circumflex iliac artery?
|
Femoral artery
|
|
|
What is the venous drainage of the anterior abdominal wall superior to the umbilicus?
|
Drains to the SVC via the thoracoepigastric veins
|
|
|
What is the venous drainage of the anterior abdominal wall inferior to the umbilicus?
|
Drains to the IVC via the superficial epigastric vein
|
|
|
What is the venous drainage of the anterior abdominal wall in the umbilical region?
|
Drains to the hepatic portal system via the periumbilical veins
|
|
|
What connects the SVC and IVC superficially?
|
The thoracoepigastric vein
|
|
|
What is the lymphatic drainage of the region superior to the transumbilical plane?
|
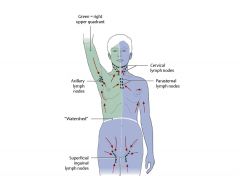
Drains to axillary lymph nodes w/ a few going to the parasternal nodes
|
|
|
What is the lymphatic drainage of the region inferior to the transumbilical plane?
|
Drains to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes
|
|
|
What is the lymphatic drainage of the deep tissues of the anterior abdominal wall?
|
1. External iliac nodes
2. Lumbar (aortic) nodes 3. Mediastinal nodes |

