![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
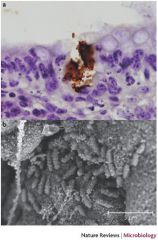
E. COLI EHEC (here colonising terminal rectum of calf) |
Note: Another name for E. coli O157, "EHEC" = Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli.
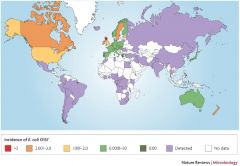
Host range:Cows Geo range: detected in most regions globally Transmission: Eating Beef, salad, dairy |
|
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever
|
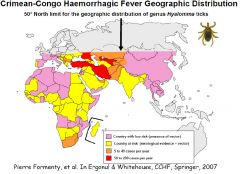
Pathogen: Bunyaviridae in RNA viruses
Vector: Hyolomma ticks Host Range: wide range of wild and domestic animals such as cattle, sheep and goats, ostriches Geo range: many countries in Eurasia and Africa up to 50 deg North (these ticks dont live there) Transmission: Hyolomma ticks |
|

Mycoplasma gallisepticum
|
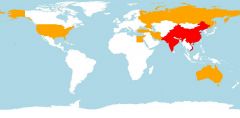
Pathogen: Mycoplasma (bacterium without a cell wall)
Host Range: Birds Disease: chronic respiratory disease (CRD) in chickens and infectious sinusitis in turkeys, chickens, game birds, pigeons, and passerine birds of all ages. Geo range: maybe global - map is EID2 map. Transmission: transovarian, or by direct contact with birds, exudates, aerosols, airborne dust and feathers, and to a lesser extent fomites |
|

Tularemia
|
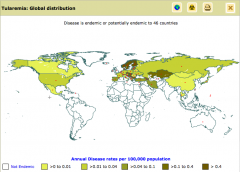
Pathogen: Francisella tularensis
Host Range: Rabbits, Rodents, beavers, squirels, ticks, mosquitoes, horseflies Disease: Skin lesions, death, Bone infection (osteomyelitis), Infection of the sac around the heart (pericarditis), Meningitis, Pneumonia Geo range: Northern hemisphere Transmission: bites by infected insects; contact with infected rodents, aerosolised infection (mowing over dead animals) Treatment / Prevention: Antibiotics / Vaccine Mortality rate: Humans: 5% if untreated. Causes mass dieoffs in rabbits. |
|
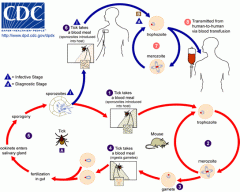
Theileria
|
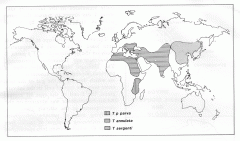
Theileria annulata
Theileria electrophori Theileria equi Theileria microti Theileria orientalis Theileria parva Theileriae are protozoan parasites carried by ticks. When ticks carrying theileriae feed on cattle, the parasites get into their bloodstream and enter red blood cells. In some animals, sufficient red blood cells are destroyed to cause anaemia, a reduction in the red blood cell numbers. This reduces the ability of blood to carry oxygen and makes the animal ill. There are 2 clinical syndromes: 1. An anaemia, abortion/stillbirth syndrome (usually with no observable lymphadenopathy [swollen lymph nodes], a highly significant clinical issue), in adult cattle originating from a parasite- (and often also tick vector-) free region when moved to an infected region, or conversely, in adult cattle within a hitherto unaffected tick vector-infested region, apparently after movement of carrier livestock from an endemically affected region; and 2. A severe, highly non-responsive, acute anaemia syndrome in calves (usually 2-6 months of age or older) in tick vector and parasite endemic areas, particularly when seasonal calving and calf-hood coincide with the highest risk period for tick vectors (late winter through to mid summer). |
|

Lumpy skin disease
|
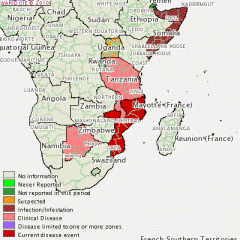
Pathogen: Poxviridae, Neethling virus / LSDV
Host Range: cattle and zebus, giraffes, African buffalo, and impalas, Oryx, springbok Symptoms: fever, discharge from the eyes and nose, nodular, necrotic skin lesions, edema of the limbs, and swollen lymph nodes Geo range: Endemic in some African countries, now also found in Egypt, turkey, Israel, palestine, jordan, arab peninsula, iraq Transmission: biting insects, perhaps mosquitoes (e.g. Culex mirificens and Aedes natrionus) and flies (e.g. Stomoxys calcitrans and Biomyia fasciata) Could also be other mechanisms of transmission. Treatment / Prevention: Two vaccines: live attenuated versions of Neethling virus and sheeppox virus. Mortality rate: low (up to 10%) |
|
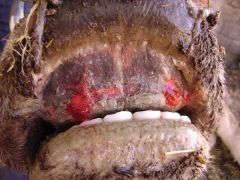
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease (cow with "erosive lesion")
|
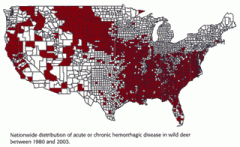
Pathogen: Reoviridae, Orbivirus, EHDV (ww) / Ibaraki virus (Japan, Korea, and Taiwan)
Note: Bluetongue is also an orbivirus Host Range: most wild and domestic ruminants (particularly white-tailed deer) Ibaraki virus causes diseases in cattle Symptoms: appetite loss, no fear of people, weakness, excessive salivation, rapid pulse, rapid respiration rate, fever (lying in bodies of water to reduce temperature), unconsciousness, blue tongue. : indistinguishable from bluetongue, foot and mouth disease in deer Geo range: North America, Australia, Asia, and Africa. Emerging in Europe in cattle (4 mediterranean countries) Transmission: Culicoides variipennis mainly Treatment / Prevention: live attenuated Ibaraki disease vaccine used in Japan Mortality rate:s 90% in white tailed deer; varies between strains etc |
|

American foulbrood (Field test) |
Pathogen: Bacterium; Paenibacillus larvae (european FB; Melissococcus plutonius)
Symptoms: larvae die before cells are closed Geo range: Transmission: robber bees stealing honey from infected hives, apiarists Treatment / Prevention: Kill bees and burn hives and equipment Mortality rate: |
|
Porcine epidemic diarrhea |
Pathogen: Porcine epidemic diarrhea Virus, Coronavirus, RNA.
Transmission: faecal/oral Treatment / Prevention: Mortality rate: much higher in unweaned piglets (can be 100%) |
|
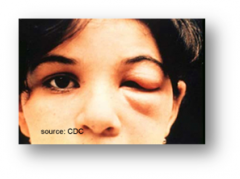
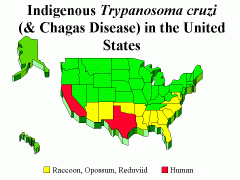
Chagas Disease (Trypanosomiasis)
|
Pathogen: Trypanosoma cruzi
Symptoms: heart disease, megaesophagus, and megacolon host range: humans, dogs and cats, pigs, goats, lagomorphs, rodents, marsupials, bats, xenarthra (anteaters, armadillos, and sloths), non-human primates, opossums armadillos, raccoons, coyotes, rats, mice, squirrels, dogs, and cats Vector / transmission: triatomine bugs, or "kissing bugs." "assassin bugs." (130 species); bite or ingestion (dogs) Treatment / prevention: Reduviid Bug control in house; Antiparasitic treatment (most effective early, before irreversible damage occurs to the heart or gastrointestinal tract) |
|
Venezuelan hemorrhagic fever
|
PATHOGEN: Guanarito virus (Yellow fever is also haemorrhagic in the area) arenavirus; |
|

Canine distemper (“hard pad disease”) |
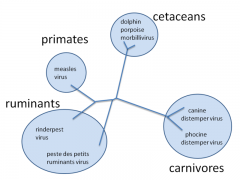
Pathogen: Canine distemper virus; Morbillivirus; Paramyxoviridae (close relative of the paramyxoviruses measles and rinderpest) |
|
Hepatitis E |
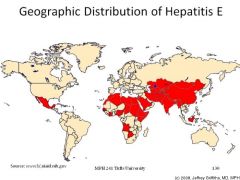
Hep E viruses are single stranded RNA viruses in the Hepeviridae family. They are orally transmitted from eating infected meat or contaminated water in e.g. refugee camps. Host range includes lagomorphs, pigs (liver) chickens. Besides swine and chickens, recently strains of HEV have been |
|

Australian Bat Lyssavirus |
Lyssaviruses: This group of RNA viruses includes the rabies virus traditionally associated with the disease. it's a dangerous zoonosis. |

