![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gross anatomy deals with tissues that are ______ in size.
|
0.1mm; visible to the naked eye
|
|
|
ventral?
|
toward the abdomen
|
|
|
rostral
|
toward the mouth
|
|
|
dorsal
|
toward the back
|
|
|
caudal
|
toward the butt
|
|
|
ventral
|
toward the abd
|
|
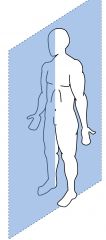
Plane?
|
sagittal/median
|
|
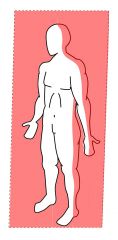
plane?
|
coronal/frontal
|
|
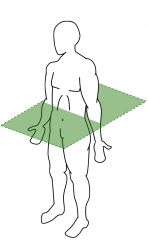
plane?
|
transverse/horizontal
|
|
|
Vertebral column consists of ____ vertebrae and intervertebral
|
33-34
are 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 4-5 coccygeal vertebrae in human |
|
|
disks make up _______ of length of vertebral column
|
20-25%
|
|
|
number of cervical nerves?
|
8
|
|
|
Location of Cervical nerve 1? C8?
|
C1 n. = between base of skull and C1
C8 n. = between C7 and T1 |
|
|
Location of Thoracic nerve 1?
|
Below T1
|
|
|
In CSF glucose is down, WBC count is increased, fluid is turbid/hazy/unclear, increased protein =?
|
bacterial meningitis
bacteria uses glucose, creates waste (protein and color), and immune system responds (wbcs) |
|
|
Osteophytes cause? symptom?
|
bony processes from arthitis of uncovertebral joints (superior process on cervical body) that may compress the vertebral artery and spinal nerve = chronic neck pain
|
|
|
"Spinal cord appears pink because it Is covered by the_____ and the actual color is_____"
|
pia mater
creamy/white-yellow |
|
|
Contents of the
vertebral canal? |
spinal cord and its blood
vessels plus the meninges and cerebro-spinal fluid. |
|
|
myelography?
|
injection of contrast medium followed by x-ray to detect pathology of spinal cord.
|
|
|
contrast medium used to study
the internal covering layer (mucous membrane) of the digestive tract with radiography? |
Barium sulfate
|
|
|
CT can be enhanced by?
|
Iodine contrast
|
|
|
______ is absolutely safe and better
differentiates between the white and gray matter than the CT gray matter contains more ______ |
MRI
gray matter contains more water |
|
|
PET is used to assess
|
functional blood flow to the brain
and heart. |
|
|
shaft of long bone = ?
ends of long bone = ? |
shaft of long bone = diaphysis
ends of long bone = epiphysis |
|
|
_____ bones are roughly cube-shaped
_____ bones are thin and flattened, usually curved |
Short bones: roughly cube-shaped
Flat bones: thin and flattened, usually curved |
|
|
Compact bone?
Spongy (cancellous) bone? |
Compact bone: dense outer layer of bone
Spongy (cancellous) bone: internal network of bone |
|
|
Membranes of the long bones?
|
periosteum, Sharpey’s fibers, and endosteum
|
|
|
Intramembranous ossification? Two notable bones that form this way?
|
Bones are directly ossified without any pre-existing cartilage
Skull bones and the clavicle are formed directly from mesenchyme |
|
|
Endochondral ossification?
|
Bones develop from a pre-existing cartilage
Most bones develop initially from hyaline cartilage |
|
|
_________ at the top of stacks
divide quickly and pushes the epiphysis away from the diaphysis; this lengthens the long bone |
Chondroblasts
|
|
|
produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates epiphyseal plates
|
Growth hormone
|
|
|
ensures that the skeleton retains proper proportions
|
Thyroid hormone
|
|
|
Promote bone growth, later induce closure of epiphyseal plates
|
Sex hormones
|
|
|
bones are inadequately mineralized = ?
|
osteomalacia
|
|
|
rickets? cause?
|
occurs in children, analogous to osteomalacia, weakened and bowed legs, malformation of the head and ribs
caused by dietary Vit D and calcium phosphate deficiency |
|
|
Paget's disease?
|
characterized by excessive rate of bone deposition but reduced mineralization leading to bone thickening.
bones are thicker but actually weaker |
|
|
Achondroplasia?
|
congenital (genetic disease), defective cartilage growth and defective enchondral ossification leading to Dwarfism.
|
|
|
Muscles make up about ______% of the body's mass; skeletal muscle accounts for ____%
|
Muscles make up about 50% of the body's mass; skeletal muscle accounts for 40%
|
|
|
do bones function to store triglycerides?
|
yes
|
|
|
_______ build up bone by secreting minerals/matrix materials?
|
osteoblasts
|
|
|
______ break down bown and release calcium/minerals
|
osteoclasts
|
|
|
cleidocranial dysostosis/dysplasia (CCD)?
Gene involved? |
rare autosomal disorder with defective ossification, delayed bone/tooth growth, and craniofacial abnormalities
RUNX2 (aka CBFA1) |
|
|
A bands contain
|
both thick and thin filaments
|
|
|
I bands contain
|
contain only thin filaments
|
|
|
H bands ?
|
center of the A band with no thin filament overlap.
|
|
|
M lines
|
center of sarcomere
|
|
|
During contraction what zones move?
|
H zone and I band narrow
Z lines move closer together |
|
|
thick filaments contain what protein?
|
myosin
|
|
|
thin filaments contain?
|
actin, tropomyosin, and troponin
|
|
|
__________ blocks the myosin binding site on actin
|
Tropomyosin
|
|
|
calcium binds to _____ and moves tropomyosin so myosin and actin can bind
|
troponin C
|
|
|
What are they "hybrid muscles?"
|
Muscles innervated by more than one nerve:
Trapezius Biceps femoris (long and short head) Adductor magnus iliopsoas pectineus m. |
|
|
Adductor magnus innervation?
|
linea aspera = obturator n
adductor tubercle = tibial n |
|
|
iliopsoas
|
iliacus = femoral n
psoas = lumbar plexus |
|
|
pectineus
|
femoral n. and obturator n.
|
|
|
MRI's show _________ as white and x-rays and CT scans show _________ as white.
|
MRI's show soft tissue as white and x-rays and CT scans show bones as white.
|
|
|
does the thumb rotate?
|
no it does circumduction
|
|
|
Why do bones appear white on negative film
|
bones absorb the x-rays
|
|
|
Epiphyseal plate osiffies and becomes ?
|
epiphyseal line
|
|
|
Intramembranous ossification
|
No cartilage -> mesenchyme is invaded by osteoblasts -> become osteocytes
|

