![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
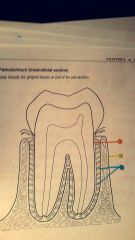
1.? 2.? 3.? |
1. Cementum 2. Alveolar bone 3. Periodontal ligament |
|
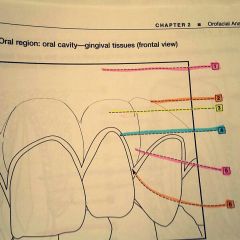
1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? 5.? 6.? |
1. Alveolar bone 2. Mucogingival junction 3. Attached gingiva 4. Marginal gingiva 5. Interdental gingiva 6. Sulcus |
|
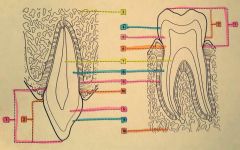
1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Anatomical crown 2. Clinical crown 3. Maxillary alveolar process 4. Enamel |
|
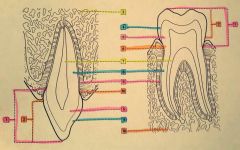
5.? 6.? 7.? |
5. Dentin 6. Cementoenamel junction 7. Pulp cavity |
|
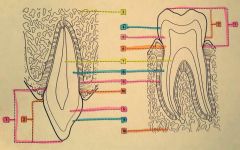
8.? 9.? 10.? |
8. Dentin 9. Cementum 10. Mandibular alveolar process |
|
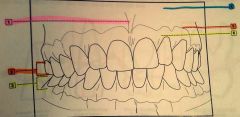
1.? 2.? 3.? |
1. Labia frenum 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular teeth |
|

4.? 5.? 6.? |
4. Alveolar bone 5. Mucogingival junction 6. Attached gingiva |
|
1.? 2.? 3.? |
1. Cementoenamel junction 2. Root 3. Crown |
|
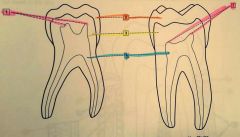
1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Pulp horns 2. Enamel 3. Dentin 4. Pulp cavity |
|
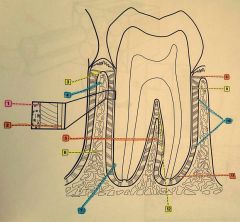
1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Sharpey's fibers within alveolar bone 2. Sharpey's fibers within cementum 3. Alveolar crest 4. Alveolar bone |
|
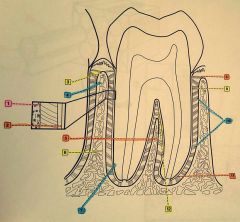
5.? 6.? 7.? 8.? |
5. Interradicular septum 6. Interdental bone 7. Cementum 8. Alveolar crest group |
|
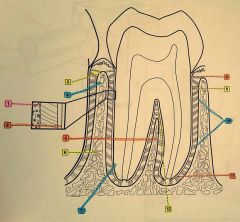
9.? 10.? 11.? 12.? |
9. Horizontal group 10. Oblique group 11. Apical group 12. Interradicular group |
|
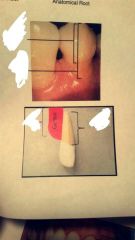
Top? Lower top? Lower left? Lower right? |
Top: anatomical crown Lower top: clinical crown Lower left: clinical root Lower right: anatomical root |
|

Pink? Purple? Green? Yellow? Red? Orange? |
Pink: alveolar mucosa Purple: Mucogingival junction Green: attached gingiva Yellow: gingival margin Red: Interdental papilla Orange: Interdental papilla |
|

1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Crown 2. Root 3. Enamel 4. Dentin |
|
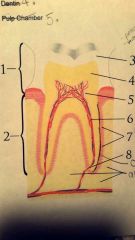
5.? 6.? 7.? 8.? |
5. Pulp chamber 6. Pulp/root canal 7. Periodontal ligament 8. Apex |
|
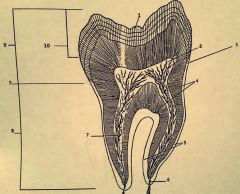
1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Enamel 2. Pulp horn 3. Cementoenamel junction 4. Dentin |
|

5.? 6.? 7.? |
5. Cementum 6. Apical foramen 7. Pulp canal |
|
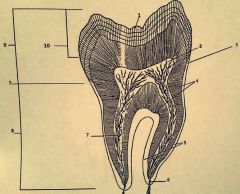
8.? 9.? 10.? |
8. Root 9. Anatomical crown 10. Clinical crown |
|
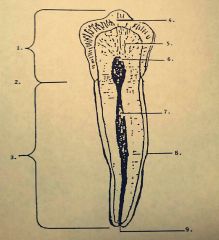
1.? 2.? 3.? |
1. Anatomical crown 2. Cementoenamel junction 3. Root |
|
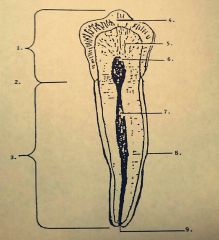
4.? 5.? 6.? |
4. Enamel 5. Dentin 6. Pulp chamber |
|
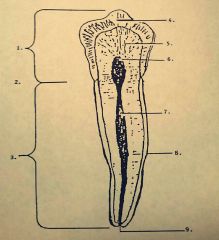
7.? 8.? 9.? |
7. Pulp canal 8. Cementum 9. Apex |
|
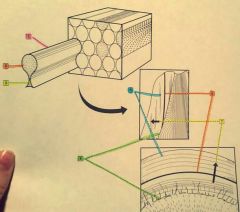
1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Enamel rod 2. Head portion 3. Tail portion 4. Dentinoenamel junction |
|
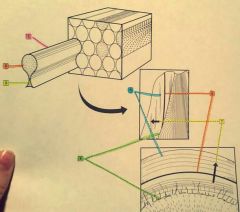
5.? 6.? 7.? |
5. Lines of retzius 6. Neonatal line 7. Direction of enamel rod |
|

1.? 2.? 3.? 4.? |
1. Anatomical crown 2. Root 3. Clinical crown 4. Periodontal ligament |
|
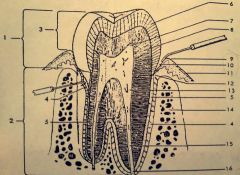
9.? 10.? 11.? 12.? |
9. Gingival margin 10. Gingival Sulcus 11. Attached gingiva 12. CEJ |
|
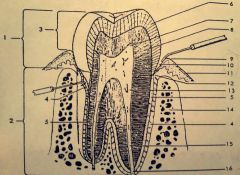
5.? 6.? 7.? 8.? |
5. Cementum 6. Enamel 7. Pulpal horn 8. Dentin |
|
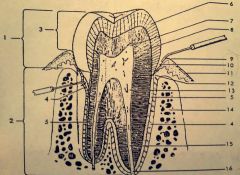
13.? 14.? 15.? 16.? |
13. Pulp 14. Alveolar bone 15. Root canal 16. Apical foramen |
|
|
What is enamel comped of? |
96% inorganic |
|
|
What are the positive aspects of enamel? |
-no nerve tissue -very durable |
|
|
What are the negative aspects of enamel? |
-prone to break because it's too hard -can't repair itself |
|
|
What is the function of enamel? |
-protect the inner tooth structure -withstand the forces of chewing and biting |
|
|
Where is enamel located? |
-anatomical crown: part of toothr covered by enamel -clinical crown: part of tooth that is visible |
|
|
What forms enamel? |
Ameloblasts |
|
|
What does enamel appear like microscopically? |
Crystal enamel rods |
|
|
What is the composition of dentin? |
-70% inorganic - elastic and porous |
|
|
What are the positive aspects of dentin? |
Can restore itself |
|
|
What are the negative aspects of dentin? |
-can cause sensitivity if exposed -if exposed it is considered carious |
|
|
What is the function of dentin? |
-insulates the inner tooth -provides another layer of protection for the tooth |
|
|
Where is the dentin located? |
-below the enamel in the crown of the tooth -below the cementum in the root of the root |
|
|
What forms dentin? |
Odontoblasts |
|
|
What does dentin appear luke microscopically? |
Hollow tubes (inside the tubes are Tomes dentinal fibers, which help to provide thermal sensitivity and act as pain sensors) |
|
|
What triggers the process of reparative dentin? |
Irritation |
|
|
What is formed when dentin is irritated? |
Secondary reparative dentin |
|
|
What cells form reparative dentin? |
Odontoblasts |
|
|
What does reparative dentin look like? |
Thin, hard, dense layer of new dentin |
|
|
Where is reparative dentin formed? |
Over the pulp |
|
|
What is cementum composed of? |
50% inorganic |
|
|
What are the positive aspects of cementum? |
-continuously repairs itself -not sensitive |
|
|
What are the negative aspects of cementum? |
-it can wear and when it does it can become sensitive -if exposed it is considered carious |
|
|
What is the function of cementum? |
Attaches teeth to the alveolar bone |
|
|
Where is cementum located? |
Covers the anatomical root |
|
|
What forms cementum? |
Cementoblasts |
|
|
What does cementum appear like microscopically? |
As layers |
|
|
What does DEJ stand for? |
Dentin and enamel junction |
|
|
What does CEJ stand for? |
Cementum and enamel junction |
|
|
What is the pulp also referred to as? |
The nerve |
|
|
What is the pulp composed of? |
-nerves -blood vessels -odontoblasts -connective tissue |
|
|
Where is the pulp located? |
Anatomical crown -pulp chamber -pulp horn Radicular portion -pulp or root canals -apex root tip -Apical foreman |
|
|
What is the function of the pulp? |
-receive and transmit pain (nerve) -defend the tooth from bacteria (blood vessels) -moisture and nutrition for the dentin |
|
|
What cells make up pulp? |
Nerve and blood cells (pulp will bleed if penetrated because it has blood cells) |
|
|
Where is the PDL located? |
Between cementum and jaw bone |
|
|
What makes up PDL? |
- continuous connective tissue with gun tissue -Sharpey's fiber bundles |
|
|
What is the width of the PDL? |
.1 to .4mm (very thin) |
|
|
What are the main functions of the PDL? |
-anchor tooth in the jaw bone -shock absorber -cushions tooth in the bone |
|
|
What is a process? |
A bony extension or projection |
|
|
Where is the alveolar process located? |
Is the jawbone surrounding the tooth root. It starts at the apex and ends at the alveolar crest in a healthy mouth |
|
|
What is the function of the alveolar process? |
To support and hold the terth in a functional position |
|
|
What two bones make up the alveolar process? |
Compact bone and cancellous bone |
|
|
What is the compact bone? |
Dense, found on the outside of bones, very strong protection |
|
|
What is the cancellous bone? |
Found in the center of bonr, sponge like or Web like |
|
|
What is the alveolus? |
A single tooth's bony socket |
|
|
What is the Lamina dura? (In the alveolar process) |
Compact bone thay lines the alveolus |
|
|
What is the alveolar crest? (Alveolar process) |
High point of the alveolar bone found between adjacent teeth |
|
|
What is the Interdental septum? (Alveolar process) |
Alveolar bone located between adjacent tooth roots |
|
|
What is the interradicular spetum? (Alveolar process) |
Located in a multirooted tooth onlh. The bone that is located between the tooth's root |
|
|
What is the oral mucosa (gingival unit)? |
Oral mucosa - soft tissue in the oral cavity thay is moist with saliva |
|
|
Where is oral mucosa (gingival unit) located? |
-lines the cheek -floor of the mouth -soft palate and inner lips |
|
|
What are the properties of the oral mucosa (gingival unit)? |
-thin -delicate -Freely moveable |
|
|
What color is the oral mucosa (gingival unit)? |
Pink to dull red |
|
|
Where is the gingiva located? |
Lines or covers the hard palate and alveolar bone |
|
|
What color is the gingiva? |
Pink if healthy |
|
|
What is free gingiva? |
Unattached, surrounds the tooth, loose |
|
|
What is gingival margin? |
Edge of gingiva around tooth |
|
|
What is gingival sulcus? |
1-2mm space between the tooth and free gingiva |
|
|
What is the gingival papilla? |
Triangular gingiva between the tooth and the free gingiva |
|
|
What is the attached gingiva? |
Firmly attached to the alveolar bone. Located from the bottom of the free gingiva and top of the Mucogingival border |
|
|
What is the Mucogingival border? |
Deep red line where the attached gingiva meets the alveolar mucosa |
|
|
What is the alveolar mucosa? |
From the bottom of the Mucogingival border to the bottom of the vestibule |
|
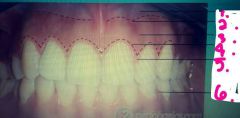
1.? 2.? 3.? |
1. Alveolar mucosa 2. Mucogingival junction 3. Attached gingiva |
|
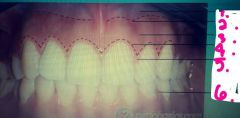
4.? 5.? 6.? |
4. Free gingival groove 5. Free gingiva 6. Interdental gingiva |
|
|
What causes bone loss, periodontal disease? |
-bacteria |
|
|
What is the proper protocol for gingivitis? |
Floss |
|
|
What is the first stage of periodontal disease? |
Gingivitis |
|
|
What does a periodontal probe measure? |
Gingival sulcus |
|
|
What is the 3 step process for dentin? |
1. Irritation 2. Odontoblasts form 3. Becomes secondary reparative dentin |
|
|
Dentin is less or more dense than enamel? |
Dentin is less dense than enamel |
|
|
What causes dentin to be sensitive? |
Dentin tubules |
|
|
Is cementum less or more dense than bone? |
Less dense than bone |
|
|
What is the use of fluoride? |
Hardens enamel and cementum |

