![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
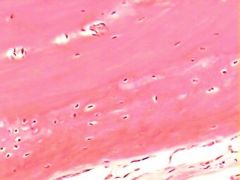
What is this? |
Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Where is fibrocartilage found? |
vertebral discs and knee joints |
|
|
What does fibrocartilage do? |
It acts as a shock absorber |
|
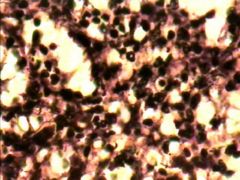
What is this? |
Reticular Connective Tissue |
|
|
Where is Recticular Connective Tissue? |
lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and liver |
|
|
What does Recticular Connective Tissue do? |
It provides framework for soft organs |
|
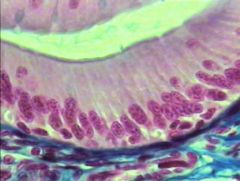
What is this? |
Simple Non-ciliated Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Simple Non-ciliated Columnar Epithelium located? |
Found in lining of digestive tract |
|
|
What does Simple Non-ciliated Columnar Epithelium do? |
It provides protection, absorption, and secretion |
|
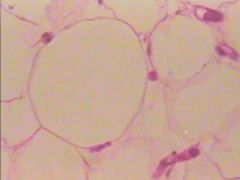
What is this? |
Adipose Connect Tissue |
|
|
Where is Adipose Connective Tissue located? |
Found around the heart, kidneys, bone marrow, behind eyeball, under skin |
|
|
What does Adipose Connective Tissue do? |
It provides insulation, energy reserve, support, and protection |
|
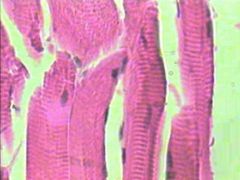
What is this? |
Skeletal Muscle |
|
|
Where is the Skeletal Muscle located? |
Located attached to the bone |
|
|
What does the Skeletal Muscle do? |
Provides voluntary movement |
|
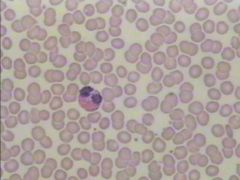
What is this? |
Blood |
|
|
Where is Blood located? |
In the blood vessels |
|
|
What does Blood do? |
Provides transportation of nutrients and wastes to the body |
|
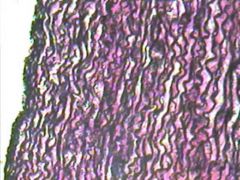
What is this? |
Elastic Connective Tissue |
|
|
Where is Elastic Connective Tissue located? |
Found in walls of arteries, bronchial tubes, lungs, vertebral ligaments, suspensory ligaments of penis, and vocal cords |
|
|
What does Elastic Connective Tissue do? |
Provides elasticity |
|
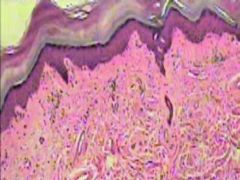
What is this? |
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium located? |
Found in the top layer of skin |
|
|
What does Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium do? |
Provides waterproofing protection |
|
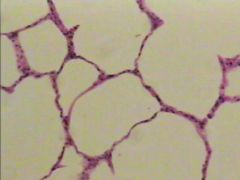
What is this? |
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Simple Squamous Epithelium located? |
Found in capillary walls, filtration membranes in kidneys, walls of alveoli, heart lymph, blood vessels and body cavity lining |
|
|
What does Simple Squamous Epithelium do? |
Provides surface for diffusion or filtration |
|
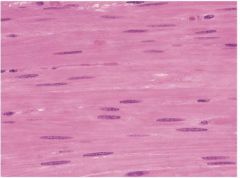
What is this? |
Smooth Muscle |
|
|
Where is Smooth Muscle located? |
found in iris of eye, digestive organs, walls of blood vessels |
|
|
What does Smooth Muscle do? |
Provides involuntary movement |
|
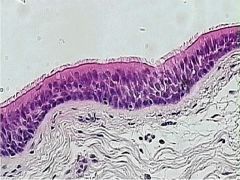
What is this? |
Pseudostratified Ciliatied Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Pseudostratified Ciliatied Columnar Epithelium located? |
Found in respiratory tract, ducts of large glands, part of urethra, lining of trachea |
|
|
What does Pseudostratified Ciliatied Columnar Epithelium do? |
Provides secretion and propulsion of mucus |
|
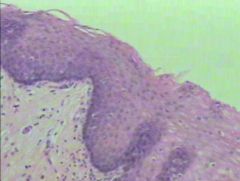
What is this? |
Stratified Squamous Non-keratinized Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Stratified Squamous Non-keratinized Epithelium located? |
Found on tongue, lining esophagus, mouth, anus, and vagina |
|
|
What does Stratified Squamous Non-keratinized Epithelium do? |
Provides protection without waterproofing |
|
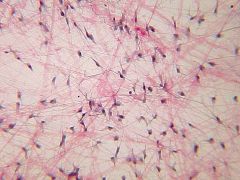
What is this? |
Loose Aerolar Connective Tissue |
|
|
Where is Loose Aerolar Connective Tissue located? |
Found separating muscles, wraps small vessels, surrounds glands, attaches skin to underlying tissue, found in all mucous membranes |
|
|
What does Loose Aerolar Connective Tissue do? |
Provides a reservoir for water and salts |
|
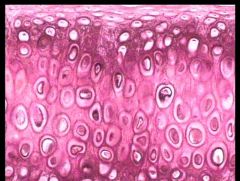
What is this? |
Elastic Cartilage |
|
|
Where is Elastic Cartilage located? |
Found in Epiglottis, pinna of ear, eustachian tubes |
|
|
What does Elastic Cartilage do? |
Provides strength and shape |
|
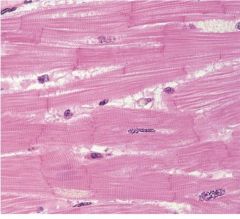
What is this? |
Cardiac Muscle |
|
|
Where is Cardiac Muscle located? |
Found in heart |
|
|
What does Cardiac Muscle do? |
Provides pumping movement of heart |
|

What is this? |
Bone |
|
|
What does the Bone do? |
Provides strength and reservoir for minerals |
|
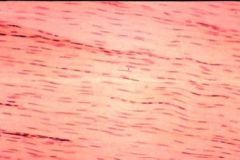
What is this? |
Dense Regular Connective Tissue |
|
|
Where is Dense Regular Connective Tissue located? |
Found in tendons, ligaments, membrane of hear, kidneys, testes, fasicles around muscle |
|
|
What does Dense Regular Connective Tissue do? |
Provides strength |
|
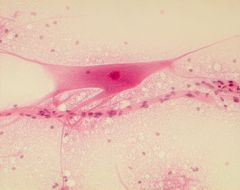
What is this? |
Neural Tissue |
|
|
Where is Neural Tissue located? |
brain, spinal cord, and nerves |
|
|
What does Neural Tissue do? |
Conducts electricity |
|
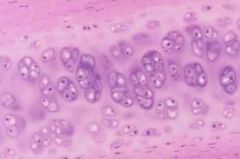
What is this? |
Hyaline Cartilage |
|
|
Where is Hyaline Cartilage located? |
joints of long bones, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchial tubes, nose, embryonic skeleton |
|
|
What does Hyaline Cartilage do? |
Provides flexible support |
|
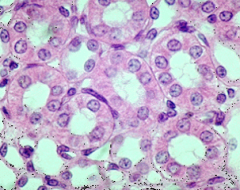
What is this? |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Simple Cuboidal Epithelium located? |
ovaries, tubules of kidneys, ducts of salivary glands, liver, and pancreas |
|
|
What does Simple Cuboidal Epithelium do? |
Provides secretion and absorption |
|
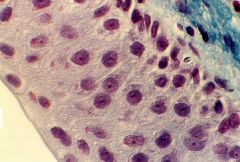
What is this? |
Transitional Epithelium |
|
|
Where is Transitional Epithelium located? |
Found in walls of ureter and urinary bladder |
|
|
What does Transitional Epithelium do? |
Provides protection from distention |
|
|
What are the four main types of tissue? |
Connective, muscle, neural, epithelial |
|
|
Study of tissue is called... |
Histology |
|
|
A collection of specialized cells and cell products that perform a specific function is called... |
Tissue |
|
|
Simple means |
one layer |
|
|
stratified means |
many layers |
|
|
squamous means |
flat |
|
|
cuboidal mean |
cube-like |
|
|
columnar means |
tall |
|
|
How many layers of cells would be found in areas where little mechanical protection is needed and absorption/diffusion is very high? |
one layer |
|
|
How many layers of cells would be found in areas where mechanical and chemical stress would be very high? |
many layers |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Loose tissues? |
Adipose, Aerolar, Reticular |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Dense tissues? |
elastic, dense regular, dense irregular |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Cartilage Connective Tissues? |
Hyaline, Fibrocartilage, Elastic |
|
|
What is the most common type of cartilage? |
Hyaline |
|
|
The __________ of connective tissue is made up of fibers and a ground substance. |
Matrix |
|
|
What is the least common type of connective tissue? |
Aerolar |
|
|
Damaged cartilage heals slowly because it is.... |
avascular |
|
|
What are 3 basic components of all connective tissue types? |
1. Specialized cells 2. Solid extracellular protein fibers 3. Fluid extracellular ground substance |
|
|
Where is mucous located? |
digestive, respiratory, reproductive tract |
|
|
What are 3 serous membranes? |
1. Pleura- covers lungs 2. Peritoneum- covers abdominal organs 3. Pericardium- covers heart |
|
|
What is Synovial? |
line moving, articulating joint cavities, producing synovial acid, protect ends of bones, lack epithelium |
|
|
What is Cutaneous? |
skin, covers the surface of the body |
|
|
Which above communicates with the exterior of the body? |
Mucous |
|
|
Loose areolar tissue of mucous membrane is called? |
Lamina propria |
|
|
Endocrine glands |
secretion are discharged directly into the interstitial fluid and blood |
|
|
Exocrine glands? |
Produce secretion onto epithelial surfaces through ducts |
|
|
Merocrine |
exocytosis- sweat glands |
|
|
Apocrine |
shedding cytoplasm- mammary glands |
|
|
Holocrine |
cell bursting, gland cells replaced by stem cells- sebaceous glands |
|
|
What are 3 types of muscles? |
Skeletal, smooth, cardiac |
|
|
What muscles are involuntary? |
Smooth |
|
|
Which muscle type have inter calculating discs? |
Cardiac |
|
|
Which muscle type is non striated? |
Smooth |
|
|
What are two major types of cells in Neural tissue? |
Neurons and Neuroglia |
|
|
What are the supporting cells in the Neural tissue? |
Neuroglia |
|
|
What happens to tissues in general as one ages? |
repair declines, cancer rate increases |
|
|
Osteoporosis is most common in... |
women |
|
|
Restoring Homeostatis after tissue injury involves what two processes? |
Inflammation and regeneration |

