![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chemical level |
Atoms combine to form molecules |
|
|
Cellular level |
Cells are made up of molecules |
|
|
Tissue level |
Tissues consist of similar types of cell |
|
|
Organ level |
Organs are made up of different organs that work closely together |
|
|
Organismal level |
The human organism is made of many organ systems |
|
|
Urinary/renal organ system |
2 kidneys->2 ureters->1 bladder->1 urethoe |
|
|
Gastrointestinal/digestive organ system |
Esophagus->stomach->small intestine->large intestine( colon) Small intestine- duodenum, jejinum, ileum (DJI) |
|
|
What is the primary source of vitamin D? |
The skin |
|
|
The purpose of the skeletal system |
Protects & supports body organs, helps to move, blood cells are formed within the bones, bones store minerals |
|
|
The purpose of the muscular system |
Gives you the ability to move when the muscles contract |
|
|
The purpose of the nervous system |
Responds tho internal & external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands |
|
|
The purpose of the endocrine system |
Glands that produce hormones for growth, reproduction, and nutrient use ( metabolism) by body cells. Thyroid, thymus, pineal gland, pituitary gland, adrenal ( sits on top of the kidneys), pancreas, ovaries,& testes |
|
|
Cardiovascular |
Blood vessels transport blood which caries oxygen, carton dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc. The heart pumps the blood & veins carry blood. |
|
|
Lymphatic system |
Immunity- picks up fluid that's of excess & gives it back to the veins to be recirculated. Disposes of debris, houses white blood cells. Lymphatic vessels, red bones marrow, thymus, theocratic duct, spleen, lymph nodes. |
|
|
Respiratory system |
Constantly supplies blood with oxygen & removes carbon dioxide. The gaseous exchanges occur through the wall's of the air sacs of the lungs. Oxygen exchange takes place at the bronchioles alreoli. |
|
|
What are the accessory glands of the digestive system? |
Liver, gall bladder, & the pancreas |
|
|
Itis |
Inflammation |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Equilibrium- balance within the body despite surrounding changes |
|
|
Homeostatic control mechanisms |
The nervous & endocrine systems accomplish the communicating via nerve impulses & hormones |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
President of the endocrine system- sends signals to pituitary which is secondary & adrenal. |
|
|
Components of a control mechanism |
- Receptors ( sensors):monitor the environment, respond to stimuli- Afferent signals= messages arriving to the brain (CNS- central nervous system) - Control center:receive input from receptor, determines appropriate response- Efferent signals= messages exiting the brain -Effector |
|
|
Negative feedback |
Brain sends signals to endocrine system-> hypothalamus |
|
|
Positive feedback |
Only during pregnancy or during labor. Milk production, labor contractions because of oxytocin. |
|
|
Coagulate |
Thinning blood |
|
|
Homeostatic imbalance |
Increase risk of heart disease, aging, allows destructive positive feedback mechanisms to take over ex. Heart failure |
|
|
Body planes |

Median (midsagittal), frontal (coronal), transverse. |
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
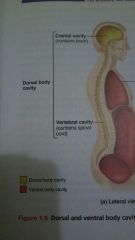
Cranial (brain), vertebral (spinal cord) |
|
|
Ventral body cavity |
Thoracic, abdominopelvic |
|
|
2 major divisions of the body |
1. Axial- head, neck, & trunk 2. Appendicular- limbs |
|
|
Serius membrane |
Fluid around the heart- viseral is the inner layer, parietal is the outer layer, pericardial is in between. |
|
|
Abdominopelvic quadrants |
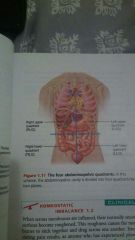
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic regions |
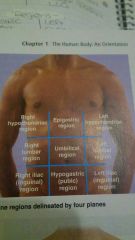
|
|
|
Energy |
Kinetic- energy in action, potential- stored energy that is inactive but has potential to do work but isn't doing so at the moment |
|
|
Atoms |
Smallest part of any element. |
|
|
Major elements of the human body |
-Carbon. C -Hydrogen. H -Oxygen. O -Nitrogen. N -Other traces-> calcium |
|
|
Types of chemical bonds |
An attraction between molecules. Ionic, covalent, hydrogen |
|
|
Synthesis reaction |
Making- A+B= AB - always involves bond formation -anabolic- making, building up |
|
|
Decomposition reaction |
Breakdown- - Catabolic - glycogen- the storage form of glucose ° is broken down to release glucose ° is kept in the liver |
|
|
Glucose energy |
ATP(highest form of energy) is never used. AMP(lowest form of energy) what is being used. ADO is on reserve& goes back to APT. |
|
|
Amaylase |
Enzyme that is in our mouths to help break down the carbs we eat. |
|
|
Inorganic compound |
-water, salts, & many acids & based -do not contain carbon |
|
|
Organic compounds |
-carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acid- CHO in common -contain carbon, usually large & covalently bonded |
|
|
Acids |
-electrolyte -proton (hydrogen ion) donor & acceptor Ex. HCl- made for enzyme formation, to kill bacteria |
|
|
Bases |
Also called alkaline -electrolyte -hydroxide donor & acceptor or the treatment Ex. Bicarbonate ion & ammonia are important in the body |
|
|
pH |
Power of hydrogen- The negative logarithm of (H+) in moles per liter. -always 7.4 in blood -regulated by buffers-kidneys & lungs -slight change in pH can be fatal -pH change interferes with cell foundation & may damage living tissue |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Group of molecules that includes sugar & starches. Contain CHO. Classified according to size & solubility. Major source of cellular fuel. -monosaccharide:1 sugar ex. glucose, fructose, galactose, deoxyribose, ribose -disaccharide:2 sugars, too large to pass through cell mambranes ex. Sucrose, lactose, metose -polysaccharide:polymers of simple sugars, for storage, not soluable ex. glycogen, starch |
|
|
Lipids OH |
Fat/glycerides contain CHO has fatty acids & glycerol Main purpose- energy, insulation & protection. -monoglyceride -diglyceride -triglyceride:neutral fat |
|
|
Amino acids |
Building blocks of proteins. 20 common types. Amine & organic acid group. Can either be a base (proton acceptor) or an acid (proton donor). EAA are the one the body doesn't produce. EAA- histadine, isoleucine, leucine, Celine NEAA- methonine, arginine Changes are called mutations. |
|
|
Sickle cell trait/anemia |
An amino acid, disease of the Hemoglobin, C shaped cell. At the 6th position in the cell there is glutamine. In sickle cell, glutamin is kicked out & Celine replaces it. Cells cannot carry oxygen. It is hereditary & is in the X chromosome which means the father has to carry it as well as the mother. If only 1 parent has it then it is only the trait. |
|
|
4 major compounds |
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, & nucleic acid. |
|
|
Fibrous proteins |
Structured-Strandlike, water insoluble ex. keratin, collagen |
|
|
Globular protiens |
Functional-compact ex. antibodies, hormones, enzymes |
|
|
Enzymes |
Biological catalysts, in the presence of an enzyme you conserve energy. The pancreas produce all the enzymes we need. |
|
|
Holoenzymes |
Functional enzyme- consist of- -apoenzyme(protein) -cofactor (metal ion) or coenzyme (vitamin) |
|
|
Nucleic acid |
In DNA & RNA- largest molecule in the body. Contains CHON & P. |
|
|
Nucleotide |
Building block, composed of N- containing base, a pentose sugar, & phosphate group. |
|
|
DNA |
Double helix, contains Adenosine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine. Pairs are always A-T, G-C. Never contains Uracil. The most important part of a cell. |
|
|
RNA |
Single helix, contains Adenosine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil. Never contains Thymine. Always paired with A-U, G-C. It's the messenger- carries the messages that DNA gives. 1)messenger 2)transfer 3)ribosomal |
|
|
3 Phosphates |
ATP-highest form of energy ADP-middle form of energy AMP-lowest form of energy |
|
|
Cells |
The basic unit of life, over 200 different types of human cells. 3 parts- -plasma membrane: flexible outer boundry. -cytoplasm/cytosol: intracellular fluid containing organelles. (blood of the cells) -nucleus: most important structure in a cell |
|
|
Organelles |
-Mitochondria: APT is made, provide cells with power (conEd) -Lysosome/Lysozyme: Breaks down old cells, digestive enzyme -Endoplasmic reticulum: smooth is for detoxification, rough have ribosomes & they make protein |
|
|
Golgi apparatus/Golgi bodies |
The post office- picks up proteins that are being produces, arranges, & ships them. |

