![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The female reproductive system is made up of |
The female genital tract is made up of : A. i. the external genitalia (vulva) ii. Internal reproductive organs(vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries) OR B. i. Lower(Vulva & vagina) II.Upper(cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries) |
|
|
|
Components of the vulva |
Components: 1. Mons pubis 2. Clitoris 3. Urethral orifice 4. Labia majora and minora 5. Vestibule *Vaginal orifice or introitus *Hymen *Greater vestibular gland Blood supply is from the internal pudendal artery Nerve- ilioinguinal and genital branch of genitofemoral. |
|
|
|
Another name for the bartholin' gland is? |
Greater vestibular gland |
|
|
|
Bartholin' is homologue to what in male |
Homologue of the Cowper’s (bulbourethral) gland in the male. |
|
|
|
Bartholin' gland is a.... Organ, located? Shape? Size? |
Paired gland each located posterior to the bulb of the vestibule. Oval in shape and the size of a pea. |
|
|
|
Describe the duct of the bartholin' gland 1. Size? 2. Opening 3. Position |
Duct is about 2cm and opens at the introitus below the hymen but above the fourchette. |
|
|
|
Bartholin gland is lined by? Secretes? Function? |
1. The gland is lined with columnar or cuboidal epithelium. 2. Secretes mucoid substance for lubrication. Bartholin’s cyst(obstruction without infection). Bartholin’s abscess (if there is infection). |
|
|
|
Bartholin’s cyst Vs Bartholin’s abscess |
Bartholin’s cyst - obstruction without infection Bartholin’s abscess (if there is infection). |
|
|
|
What is the Mons pubis |
It is a fibro-fatty pad, covered by hair bearing skin that covers the bony pubic ramus |
|
|
|
Glands in the labia majora |
1. Sebaceous glands 2. Sweat glands 3. And a few specialized apocrine glands |
|
|
|
Labium minora , anteriorly Vs posteriorly |
Anteriorly, they decide in 2 to form the prepuce and frenulum of the clitoris ( clitoral hood) Posteriorly, They decide to form a fold of skin called fourchette at the back of the vagina introitus |
|
|
|
Which of the labrium is engorged during sexual arousal |
Both the labia minora and labia majora |
|
|
|
What is the clitoris? Measures? |
It is an erectile structure , measures approximately 0.5 - 3.5 cm in length. |
|
|
|
What makes of the body of the clitoris |
Paired column of erectile tissue and vascular tissue called corpora cavernoma... These become the courage at the bottom of the clitoris and run deeper and laterally |
|
|
|
Vestibule is? Contains? |
Is the cleft between the labia minora. It contains opening of the 1. Vagina ( opening or introitus) , 2. urethra, 3. bartholin gland Hymen |
|
|
|
Remaining tags of hymen ( after rupture during sex) is called |
Carunculae myrtiformes |
|
|
|
Vagina anatomy - definition, measurement , relation ? Shape? Epithelium? |
1. A fibromuscular canal extending from the vestibule to the uterus. 2. About 7cm anteriorly and 9cm posteriorly. 3. Anteriorly related to the urethra and the bladder. Posteriorly related to the rectum. 4. H-shaped and has transverse ridges called rugae. 5. Stratified squamous epithelium Cervix dips into it superiorly to form the fornices. |
|
|
|
Cervix and vagina |
Cervix dips into the vagina superiorly to form the fornices. |
|
|
|
Epithelium of the vagina |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
Blood supply to 1. Vulva 2. Vagina 3. Uterus 4. Ovaries |
1. Vulva - Blood supply is from the internal pudendal artery. Nerve- ilioinguinal and genital branch of genitofemoral.
2. Vagina - Blood supply- vaginal artery, branches of the uterine, branches of the internal pudendal, middle and inferior rectal arteries. Lymphatics to inguinal nodes, internal iliac, obturator and sacral nodes. 3. Uterus 1. Blood supply from uterine and ovarian arteries. 2. Venous drainage to pampiniform plexus in the broad ligament, uterine vein, ovarian vein, vaginal plexus and vertebral plexus. 3. Lymphatics: paracervical plexus, external and internal iliac nodes, obturator and sacral nodes. Ovaries . Blood supply from the ovarian and the uterine arteries2. Venous drainage by the pampiniform plexus, ovarian and uterine veins.3. Lymphatics by aortic nodes, external iliac nodes. |
|
|
|
What is the rugae of the vagina |
These are transverse ridges in the vagina |
|
|
|
The vagina walls are usually in ? Except? |
Apposition Except at the vault where they are separated by the cervix |
|
|
|
The vault of the vagina is divided into how many fornices? |
4 fornices - posterior, anterior , and 2 lateral |
|
|
|
Mid vagina Vs lower vagina |
Mid vagina is a transverse slit while the lower vagina is an H-shape in transverse section |
|
|
|
Does the vagina has glands? |
No. The vagina has NO glands and is kept moist by secretions from the uterine and cervical glands And by transudation from its epithelial lining |
|
|
|
Epithelium is? |
Thick and rich in glygogen , which increases in the postovulatory phase of the cycle |
|
|
|
When is the vagina devoid of glycogen and why |
Before puberty And After menopause Because of the lack of estrogen |
|
|
|
The bacteria that has protective role |
Doderlein's bacillus, a normal Commensal of the vaginal flora, breaks down glycogen to form lactic acid, producing a pH of 4.5 |
|
|
|
Measurements of the uterus |
Pear- shaped and measures 1. 9cm in length, 2. 6cm transversely, 3. 4cm in AP. 4. Wall is 1-2 cm thick. |
|
|
|
Uterus anatomy 1. Shape, measurements 2. Position 3. Cavity shape 4. Wall? 5. Relations |
1. Pear- shaped and measures 9cm in length, 6cm transversely, 4cm in AP. Wall is 1-2 cm thick. 2. Anteverted and anteflexed. 3. Cavity is triangular in shape. 4. Wall is 1-2 cm thick. Wall has serosa, myometrium and the endometrium. 5. Anteriorly related to the bladder and posteriorly to the coils of the intestine. |
|
|
|
Parts of the uterus |
Has the 1. fundus, 2. body, 3. isthmus and 4. the cervix. Cervix is different in structure and function. |
|
|
|
Isthmus lies? Forms ? |
Isthmus lies between the histological os and the Anatomical os. Isthmus forms the lower uterine segment. |
|
|
|
How many internal os ? |
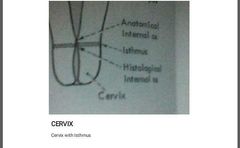
Internal os:Anatomical internal os and histological internal os. Isthmus lies between the histological os and the Anatomical os. The site of the Histologic os is where the mucus membrane of the isthmus becomes that of the cervix |
|
|
|
Ligaments of the uterus |
1. Round ligament, 2. ovarian ligament, 3. broad ligament.
|
ROB |
|
|
About cervix 1. Shape & length 2. Cervix canal has? 3. Epithelium? |
Endometrium and to a lesser extent the myometrium show cyclical histological and functional changes related to menstruation. 1. Cervix is barrel- shaped and about 3cm long. Supravaginal and portio vaginalis. Internal os and external os. 2. Cervical canal (endocervix) has arbor vitae. 3. Vaginal cervix is lined by squamous epithelium while the endocervix is columnar. |
|
|
|
Cervix epithelium |
Vaginal cervix is lined by squamous epithelium while the endocervix is columnar. |
|
|
|
Layers of the endometrium |
Endometrium has single layer of cuboidal or columnar ciliated cells on a cellular stroma. a. Stratum compactum b. Stratum spongiosum c. Stratum basalis a anb b = stratum functionalis |
|
|
|
Uterus 1. Blood supply 2. Venous drainage 3. Lymphatics |
1. Blood supply from uterine and ovarian arteries. 2. Venous drainage to pampiniform plexus in the broad ligament, uterine vein, ovarian vein, vaginal plexus and vertebral plexus. 3. Lymphatics: paracervical plexus, external and internal iliac nodes, obturator and sacral nodes. |
|
|
|
Non pregnant uterus is situated in? |
Entirely within the pelvis |
|
|
|
Weight of adult uterus |
Approximately 70g |
|
|
|
The area of insertion of each Fallopian tube is? |
Cornu |
|
|
|
What is parametrium |
A cellular connective tissue lying lateral to the cervix |
|
|
|
What is the endocervix ? |
The endocervix is the cervical canal |
|
|
|
What is the arbour vitae |
The mucus membrane of the endocervix ( cervical canal ) has anterior and posterior columns from Which folds radiate out, the arbour vitae |
|
|
|
The cervix has numerous deep glandular follicles that? |
Secrete clear, alkaline mucus . The main component of physiological vaginal discharge |
|
|
|
Linings of the cervix |
The epithelium of the endocervix is columnar and also ciliated in its upper two-thirds. This changes to stratified squamous epithelium around the region of the external Os and the junction of these two types of epithelium is called the squamocolumnar junction |
|
|
|
About Fallopian tubes 1. Attached? 2. Length 3. Opens into? 4. Parts? How many? Length? |
1. Attached to the cornua and lies in the free upper border of the broad ligament. 2. about 10 cm in length and tortuous. 3. Opens into the peritoneal cavity and the uterus. Site of fertilization (and tubal gestation). 4.Has 4 parts viz: intestitial (1-2cm), isthmus (2-3cm), ampulla (5cm), and infundibulum. |
|
|
|
List the parts of the Fallopian tube and their length |
A. Has 4 parts viz: 1. intestitial (1-2cm), 2. isthmus (2-3cm), 3. ampulla (5cm), 4. and infundibulum or fimbrial portion |
|
|
|
Relation to the Fallopian tube |
1. Superiorly related to the coils of the intestine and omentum. The appendix and caecum on the right and the pelvic colon on the left. 2. Inferiorly are the broad ligament and its contents. The epoophoron, paroophoron and Gartner’s duct- Remnants of mesonephric duct. 3. Posteriorly are the ovary and the POD. 4. Anteriorly is the top of the bladder. Lined by ciliated columnar epithelium (endosalpinx ) with thin stroma. Epithelium thrown into a complex arborescence in the ampulla. Muscular wall. |
|
|
|
Epithelium of the Fallopian tube |
Q. Lined by ciliated columnar epithelium (endosalpinx ) with thin stroma. Epithelium thrown into a complex arborescence in the ampulla. Muscular wall. |
|
|
|
List the activities of the Fallopian tube and what controls them |
Both the muscular and secretory activities are under the influence of the ovarian hormones. |
|
|
|
Ovary 1. Shape 2. Measures? 3. Weight 4. Which side is larger 5. Attachments |
1. Solid ovoid structure 2. measures 3.5cm in length and 1.5- 2.5 cm in thickness. 3. Each weighs 4-8g. 4. Right tends to be larger than left 5. Attached to the back of the broad ligament by the mesovarium and suspended from the cornu by the ovarian ligament. |
|
|
|
List the only pelvic structure not covered by peritoneum |
Ovary |
|
|
|
Ovary 1. .......... transmits the vessels and nerves. |
Hilum transmits the vessels and nerves. |
|
|
|
Structure of the ovary |
STRUCTURE 1. Cortex (outer zone) and the medulla (inner zone). Both have connective tissue stroma which contains the vessels, nerves and follicles. |
|
|
|
adnexium (plural adnexa) or the appendage is? |
The tube and the ovary and their mesenteries are so closely related anatomically that they are collectively called the adnexium (plural adnexa) or the appendage. Their position varies greatly |
|
|
|
What takes place in the ovary |
Steroidogenesis and follicular development take place in the ovary. |
|
|
|
Blood supply of the ovary |
1. Blood supply from the ovarian and the uterine arteries 2. Venous drainage by the pampiniform plexus, ovarian and uterine veins. 3. Lymphatics by aortic nodes, external iliac nodes. |
|

