![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The unifying characteristics of all life on the planet |
Cell |
|
|
|
The simplest form structure that possesses all the characteristics of life |
Individual cell |
|
|
|
Composite cell general anatomy of a cell includes 3 regions |
Cell membrane (skin of cell Cytoplasm (everything else Nucleus ( contains DNA |
|
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Flexible but sturdy barrier that defines t he limit of the cell |
|
|
|
The movement of materials between the cells and it's environment is strictly regulated and referred to as |
Selective permeability |
|
|
|
Plasma membrane description |
Selective permeability Phospholipids Amphipathic |
|
|
|
The material between the plasma membrane and the nucleus |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
|
2 parts of cytoplasm |
Cytosol the fluid and dissolved substances Organelles inclusions that have a specific shape and function within the cell |
|
|
|
Endoplasmic reticular ER |
A series of membranes that are continuous with the nuclear envelope |
|
|
|
2 forms of ER |
Rough ER glycoprotein and phospholipids Smooth ER fatty acid and steroid synthesis, detoxification of certain drugs, calcium storage |
|
|
|
Ribosome |
Granules composed of DNA The site of protein synthesis May be bound to a membrane or free floating in cytosol |
|
|
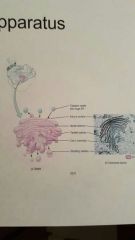
Golgi apparatus |
A series of membranes that further process package proteins produced by the roughER for secretion as secretory vesicles |
|
|
|
Lysosomes |
Secretory vesicles from the Golgi apparatus that contain digestive enzymes The enzymes are responsible for recycling of worn out Organelles and programmed cell death |
|
|
|
Peroxisomes |
Vesicles within the cell that contain powerful oxidizing enzymes Neutralize toxic chemicals within the cell |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
Organelles that contain enzymes that drive aerobic cellular respiration Produce ATP |
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Network of proteins that provide the structural framework of the cell |
Microfilaments (actin Intermediate filaments Microtubules (tubulin |
|
|
Cilia and flagella |
Plasma membrane that move the entire cell or generate a current over the cell |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Contains the DNA The control center of the cell DNA is the nucleic Acid that stored the genetic information of the cell The information stored in the DNA regards of specific proteins and rhe replication of the cell itself |
|
|
|
Chromatin |
Not actively dividing |
Decondensed |
|
|
Chromosomes |
When DNA is wound up |
Condenses |
|
|
Amphipathic |
Molecules that loves and hates water |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Hate water |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic |
Love water |
|
|
|
Microvilli |
Tight junctions between cell |
|
|
|
Centrosome |
Two rod shaped centrioles bodies that lie at right angles to one another |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of a solute from a high concentration to a low solute concentration Does not require a membrane protein |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water |
Membrane is impermeable to the solute and concentration gradient exist |
|
|
Passive movement |
Filtration by which water salutes are forced through a membrane by hydrostatic pressure |
|
|
|
The life cycle ( cell cycle) |
Composed of to parts Interphase Mitoic phase |
|
|
|
During Interphase |
G1, S (synthesis a second set), G2 The cell grows and prepares for the next cell division |
Majority |
|
|
During Mitoic phase |
The cell divides producing two identical daughter cells |
|

