![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What specialized cells are capable of contraction?
|
Myoepithelial cells (glands)
Pericytes (precapillary) Myofibroblasts (wound contraction) Muscle cells (muscles) |
|
|
How do skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle differ?
|
Arrangement of myofibrils
Capacity for regeneration Neural regulation |
|
|
What are the traditional (3) groups of muscle?
|
Skeletal
Smooth Cardiac |
|
|
Basic Idea of Skeletal muscle:
|
striated
controlled voluntarily Multinucleated |
|
|
Basic Idea of smooth muscle:
|
which is non-striated and involuntary in action
|
|
|
Basic Idea of cardiac muscle:
|
multinucleated
striated involuntary |
|
|
What intracellular things allow for contraction to occur?
|
intracellular contractile filaments, composed primarily of actin and myosin
|
|
|
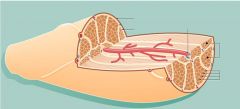
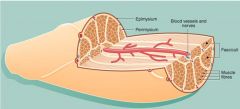
What is the epimysium?
|
Epimysium surrounds the entire muscle
|
|
|
What is the perimysium?
|
Perimysium surrounds the bundles
|
|
|
What is the endomysium?
|
Endomysium surrounds individual muscle fibers
|
|
|
Muscle fibers are composed of many cells. What are they called?
|
Myoblasts
|
|
|
What are the satellite cells in muscle tissue?
|
cells that lie under the basement membrane represent stem cells held in reserve.
|
|
|
Within the muscle, what are the myofibrils?
|
Myofibrils are intracellular contractile elements running longitudinally within the muscle fiber, and it is the registration of adjacent myofibrils that gives skeletal muscle its striated (banded) appearance.
|
|
|
Are skeletal muscle fibers directly innervated?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
What is the basic unit of contraction in muscle fibers?
|
Sarcomere
|
|
|
Describe the A Band:
|
dark staining, bisected by an H band. Except for the H band, it contains both thick and thin filaments. The thick filaments are composed of myosin.
|
|
|
Describe the I Band:
|
light staining, bisected by a thin Z line. The I band contains only thin filaments composed of actin, tropomyosin and troponin.
|
|
|
Describe the Z line:
|
contains alpha-actinin and vinculin, that anchor the actin filaments.
A sarcomere runs from one Z line to the next. "Ze 'Z' line seperates Ze sarcomeres" |
|
|
In a sarcomere what are the thick and thin filaments?
|
Thick - Myosin
Thin - Actin |
|
|
What is a motor endplate?
|
The region where the motor neuron terminates at the muscle fibers.
|
|
|
What is a motor unit?
|
A motor nerve and all muscle fibers it innervates.
|
|
|
What is released at the motor end plate and where is it released?
|
Acetylcholine is released into the sarcolemma (muscle plasma memrane) and then spread to the T-tubules
|
|
|
What are the T-tubules?
|
Depolarization spreads through the T-tubules to reach the inner fibers.
The depolarization causes Ca release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. |
|
|
What is muscle tone?
|
The continous balance between relaxed and contracted. No muscle is ever completely relaxed.
|
|
|
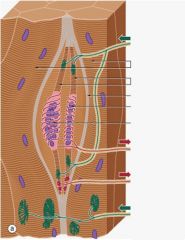
What do muscle spindles do?
|
Provide information that leads to maintanence of muscle tone.
They are particularely heavy in units requiring fine motor control. |
|
|
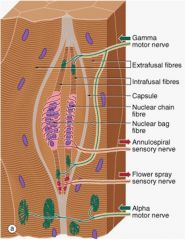
What are muscle spindles composed of?
|
Modified skeletal fibers called intrafusal fibers
|
|
|
Describe nuclear chain vs. nuclear bag fiber:
|
Bag - Centrally located nucleous
Chain - Spread out nucleous |
|
|
Describe how muscle spindles work:
|
Sensory nerve endings continuously monitor the degree of stretching of these muscle fibers, and as they lengthen, i.e. they stretch because the main muscle mass is relaxing, impulses are relayed to the spinal cord. These impulses lead to the reflex activation of alpha motor neurons in the ventral horn that cause the main muscle to contract. This is also the physiological mechanism involved in the "stretch reflex".
|
|
|
What motor neurons regulate the spindle fibers?
|
gamma motor neurons
|
|
|
Describe the smooth muscle cell:
|
spindle shaped
smaller than skeletal fiber single, central nucleous no orderly arrangement of fibrils (no striations due to random placement of actin and myosin 'threads') |
|
|
What can smooth muscle secrete?
|
Smooth muscle cells also synthesize and secrete collagen, elastin and proteoglycan
|
|
|
Can smooth muscle divide?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Can Skeletal Muscle divide?
|
i dunno...can it?
|
|
|
Can cardiac muscle divide?
|
No
|
|
|
In smooth muscle, does contraction require innervation?
|
No, self regulation or drone via autonomic
No direct innervation and no T-tubules |
|
|
In smooth muscle, how is the signal for contraction spread from cell to cell?
|
gap junctions
|
|
|
How is smooth muscle contraction initiated?
|
Via Ca flux.
Differs than skeletal and cardiac |
|
|
How many nuclei do cardiac cells have?
|
(2) or more
|
|
|
How are cardiac cells joined together?
|
a branching network via intercalated discs
|
|
|
What (3) types of junctions exist at the intercalated disks?
|
Desmosomes that transmit tension from one cell to the next.
Adhering junctions that are similar to the zonula adherens between epithelial cells. Gap junctions that provide electrical continuity between adjacent cells. |
|
|
Why is cardiac muscle striated?
|
Less so in comparison to skeletal.
Myofibrils contribute a striated appearance to this muscle, although the striations are less distinct than in skeletal muscle. A and I bands and Z lines can be seen and the mechanism of contraction is similar to that of skeletal muscle. |
|
|
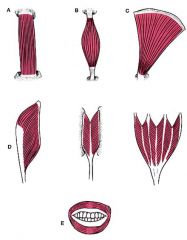
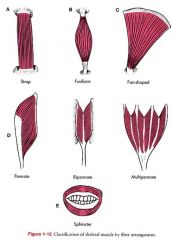
What are the two parts of a muscle?
|
Fleshy Fascia
and Tendon |
|
|
Within a muscle, what are the two attachment ends called?
|
origin
and insertion |
|
|
What protein in muscles is the cause of muscular distrophies?
|
Dystrophin holds actin to the cytoskeletal elements and is missing in some diseases
|
|
Label
|
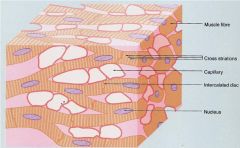
Good
|
|
Label
|
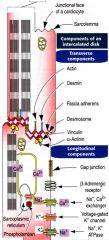
Good
|
|
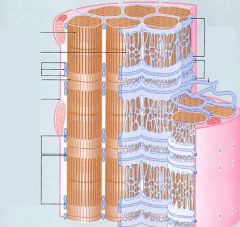
Label
|
Good
|
|
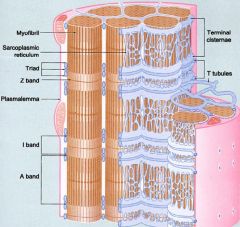
Label
|
Good
|
|
Label
|
Good
|
|
Label
|
Good
|
|
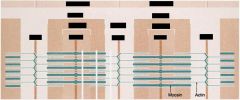
Label
|
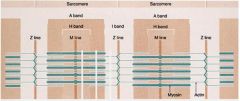
Good
|
|
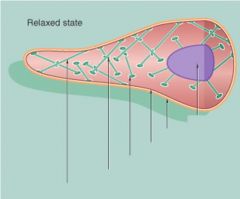
Label items within smooth muscle cell
|
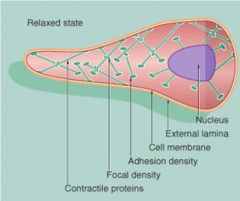
Good
|

