![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the roughened ridge on the posterior middle 1/3 of the femur bone called?
|
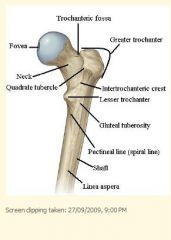
Linea aspera
|
|
|
Adductor tubercle - where is it, and which muscle attaches to it?
|
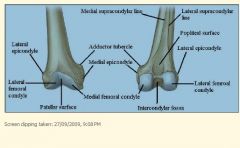
It is posteriosuperior to medial epicondyle.
The adductor magnus attaches to it. |
|
|
Where is the tibial tuberosity?
|
A prominence located on the anterior aspect of the proximal end.
|
|
|
Where is the Gerdy's tubercle, and what attaches to it?
|
It is on the lateral tibial condyle, and it gives attachment to the iliotibial tract.
|
|
|
Which nerves form the lumbar plexus?
|
L1-L4
1. Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh 2. Femoral nerve 3. Obturator nerve |
|
|
Laternal cutaneous nerve of the thigh - innervation and function?
|
* L2-L3
* supplies skin on the anterolateral side of thigh |
|
|
Femoral nerve - innervation and function?
|
* L2,3,4
* thigh extensor muscles * pectineus muscle (adductor) * anterior and medial skin of thigh * branches into saphenous nerve, the longest sensory branch of the femoral nerve. This innervates medial side of leg and foot to medial side of big toe. |
|
|
Obturator nerve - innervation and function?
|
* L2,3,4
* medial compartment of thigh (adductors). * hip and knee joints. |
|
|
Course of the great saphenous vein
|
Start at dorsum of foot, anterior to medial malleolus, along medial side of leg and knee. At upper thigh, it passes through deep fascia and opens into femoral vein.
|
|
|
Course of the small saphenous vein
|
Lateral side of foot, posterior to lateral malleolus, up posterior leg, drains into the popliteal vein.
|
|
|
What is the scientific name of the deep fascia of the thigh?
|
Fascia lata
|
|
|
Thigh anterior compartment contains extensor muscles. But there is an exception - what is it?
|
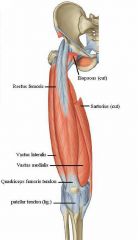
The sartorius muscle flexes hip and knee joints. But it is still innervated by the femoral nerve.
|
|
|
Thigh medial compartment contains adductor muscles. They are all innervated by the obturator nerve. But there are two exceptions - what are they?
|
The hamstring part of the adductor magnus, which is attached to the ischial tuberosity, is innervated by the sciatic nerve.
The pectineus is innervated by the femoral nerve. |
|
|
What is the name of the structure derived from fascia lata, that divides the thigh into three compartments?
|
Intermuscular septae
|
|
|
Name all the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh.
|
Psoas major
Iliacus Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Vastus lateralis Rectus femoris Sartorius |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the psoas major muscle?
|
Anterior rami of L1,2,3.
Hip flexion. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the iliacus muscle?
|
Femoral nerve.
Hip flexion. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the rectus femoris muscle?
|
Femoral nerve.
Knee extension. Hip flexion. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the sartorius muscle?
|
Femoral nerve.
Knee flexion Hip flexion. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of vastus medialis, intermedius and lateralis?
|
They are all innervated by the femoral nerve, and they all mediate knee extension.
|
|
|
Name the muscles contained in the medial compartment of the thigh.
What purpose do they serve? |
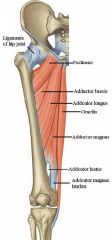
Gracilis
Pectineus Adductor longus Adductor brevis Adductor magnus They adduct the hip. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the gracilis muscle?
|
Obturator nerve.
Hip adduction. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the pectineus muscle?
|
Femoral nerve.
Hip adduction and flexion. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the adductor longus muscle?
|
Obturator nerve.
Hip adduction. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the adductor brevis muscle?
|
Obturator nerve.
Hip adduction. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the adductor magnus muscle?
|
Adductor part - obturator nerve, hip adduction.
Hamstring part - sciatic nerve, hip adduction. |
|
|
What is the adductor hiatus?
|
Opening in the aponeurosis of the adductor magnus muscle leading from the anterior compartment of the thigh into the popliteal fossa. It transmits the femoral vessels.
|
|
|
What is the femoral triangle's boundaries?
What is its apex continuous with? What is contained in it? |
Boundaries - sartorius, adductor longus, inguinal ligament.
Apex is continous with adductor canal, which ends in the adductor hiatus. Contains (from medial to lateral) - femoral vein, artery, nerve. |
|
|
Femoral artery is the continuation of the...
|
External iliac artery.
|
|
|
What is the course of the femoral artery?
|
Under inguinal ligament, through femoral triangle, through the adductor canal, adductor hiatus, and becomes the popliteal artery.
|
|
|
What is another name for the deep artery of the thigh?
|
Profunda femoris artery.
|
|
|
Name the main branches of the deep artery of the thigh.
|
* lateral circumflex femoral artery
* medial circumflex femoral artery * perforating branches - they perforate the adductor magnus and supply back of thigh. |
|
|
What structure does the lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries form?
|
The cruciate anastomosis, around the femur under the greater trochanter.
|
|
|
Where does the obturator artery originate from, and what does it supply?
|
* from internal iliac artery.
* supplies tissues around obturator foramen, and head of femur. |
|
|
What's the name of the fibrocartilaginous rim that attaches to margin of acetabulum, and what is its purpose?
|
Labrum.
Makes the mouth of acetabulum narrower, which helps to hold the head of femur in place. |
|
|
Name the 3 capsular ligaments around the hip joint.
|
Iliofemoral, pubofemoral, ischiofemoral ligaments.
|
|
|
What is another name for the round ligament of the head of the femur?
|
Ligamentum teres femoris.
|
|
|
What is the name of the ligament on the medial side of the knee joint, and what does it attach to?
|
Tibial (medial) collateral ligament.
* Extends from medial epicondyle to the medial surface of the shaft of tibia. * There is a bursa between this ligament and the joint capsule. |
|
|
What is the name of the ligament on the lateral side of the knee joint, and what does it attach to?
|
Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament.
* Extends from lateral epicondyle to the head of the fibula. |
|
|
What are the attachment points of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
|
* From anterior part of intercondylar region on the tibia, to the lateral condyle of the femur.
|
|
|
What are the attachment points of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)?
|
* From the posterior part of intercondylar region of the tibia, to the medial condyle of the femur
|
|
|
What is the attachment of the medial meniscus?
|
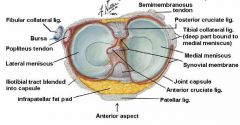
* medial meniscus is semicircular, and its peripheral margin is adherent to the deep part of the MCL.
|
|
|
What is the attachment of the lateral meniscus?
|
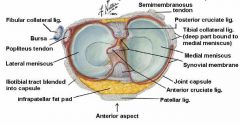
* lateral meniscus is nearly circular.
* tendon of the popliteus muscle and capsule separate it from the LCL. Therefore it is more mobile than the medial meniscus. |
|
|
What is a bursa?
Name 3 bursae in the knee area. |
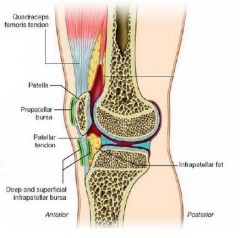
* a sac of fluid in areas where muscles or tendons tend to rub against bone.
* prepatellar bursa * superficial infrapatellar bursa * deep infrapatellar bursa |
|
|
What is the innervation of the knee and hip joints?
|
Articular branches of different nerves, including the obturator nerve.
|
|
|
Name all of the superficial gluteal muscles.
|
Gluteus maximus, medius, minimus.
|
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the gluteus maximus?
|
* Inferior gluteal nerve
* Hip extension |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the gluteus medius?
|
* Superior gluteal nerve
* Hip abduction |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the gluteus minimus?
|
* Superior gluteal nerve
* Hip abduction |
|
|
Name all of the deep gluteal muscles.
|
Piriformis
Superior gemellus Obturator internus Inferior gemellus Quadratus femoris Obturator externus Tensor fascia lata (it migrates laterally during development though, but is still considered a deep gluteal muscle) |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the deep gluteal muscles (excluding the tensor fascia lata)?
|
* Sacral plexus.
* Hip lateral rotation. |
|
|
Where do you give IM injections in the gluteal region?
|
Upper lateral quadrant of the gluteal region, where there is no danger of injury to sciatic nerve.
|
|
|
What is Trendelenburg's sign? Which muscles does it test?
|
Ask a patient to stand on one leg, and their hip on the opposite side will fall because of weak abductor muscles (gluteus medius and minimus).
|
|
|
Which muscles' tendons comprise the pes anserinus?
|
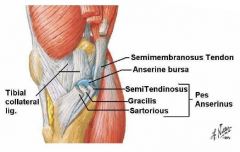
Say Grace before Tea
Sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus muscles attach to the medial proximal tibia in a three-pronged pattern. The combined tendons of insertion is named pes anserinus. |
|
|
Name all of the muscles in the posterior thigh compartment.
|
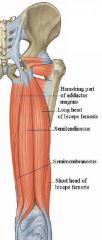
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus Biceps femoris |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the semitendinosus muscle?
|
* sciatic nerve (tibial branch)
* knee joint flexion * hip joint extension |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the semimembranosus muscle?
|
* sciatic nerve (tibial branch)
* knee joint flexion * hip joint extension |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the biceps femoris?
|
* Short head: sciatic nerve (common fibular/peroneal branch)
* Long head: sciatic nerve (tibial branch) * knee joint flexion * hip joint extension |
|
|
What spinal levels contribute to the sciatic nerve?
What is the course of the sciatic nerve? What does it innervate? |
* L4,5, S1, 2, 3
* Passes through the greater sciatic foramen, enters gluteal region, back of thigh at the lower border of the gluteus maximus, runs all the way down to popliteal fossa, and divides into the tibial and common fibular/peroneal nerves. * Innervates posterior thigh muscle, except for the short head of biceps femoris which is innervated by the common fibular nerve, and long head which is innervated by the tibial nerve. |
|
|
Which spinal levels form the sacral plexus?
What are the main branches of the sacral plexus? Which spinal levels form the lumbosacral trunk? |
* Sacral plexus - formed by the lumbosacral trunk, and the ventral rami of S1,2,3, and part of S4
* Lumbosacral trunk - formed by part of ventral ramus of L4, and entire ventral ramus of L5. * Main branches are the sciatic nerve (L4-S3), pudendal nerve (S2-4), superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1), inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2), and nerve branches for the deep gluteal muscles. |
|
|
Which spinal levels contribute to the superior gluteal nerve?
What is its course? What does it supply? |
* a branch of sacral plexus (L4-S1).
* enters gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen, passing above the piriformis along with the superior gluteal artery. * supplies gluteus medius and minimus, as well as the tensor fascia lata. |
|
|
Which spinal levels contribute to the inferior gluteal nerve?
What is its course? What does it supply? |
* a branch of the sacral plexus (L5-S2).
* enters the gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen, passing below the piriformis along with the inferior gluteal artery. * supplies the gluteus maximus muscle. |
|
|
What is the origin of the superior gluteal artery?
Which muscles does it supply? |
* branch of the internal iliac artery.
* supplies the gluteus medius and minimus, as well as superior part of gluteus maximus. |
|
|
What is the origin of the inferior gluteal artery?
What muscles does it supply? |
* branch of the internal iliac artery.
* supplies the lower part of gluteus maximus, and all of the deep gluteal muscles. |
|
|
What arteries supply the anterior part of the posterior thigh?
|
The perforating branches of the deep femoral artery.
|
|
|
What are the boundaries of the popliteal fossa?
|
superior borders:
* biceps femoris (laterally), semimembranosus and semitendinosus (medially). Inferior borders: * lateral head of gastrocnemius and plantaris (laterally), medial head of gastrocnemius (medially). Roof of the fossa is covered by deep fascia, and superficial fascia contains the small saphenous vein. |
|
|
What are the main contents of the popliteal fossa?
|
* popliteal artery (and its genicular branches) and vein.
* tibial nerve and its branches * common fibular/peroneal nerve and its branches * popliteal lymph nodes and fat |
|
|
What is the segmental innervation of the knee joint?
|
|
|
|
What is the segmental innervation of the knee joint?
|
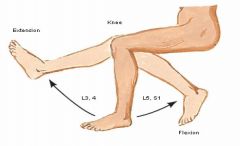
|
|
|
What is the segmental innervation of the hip joint?
|
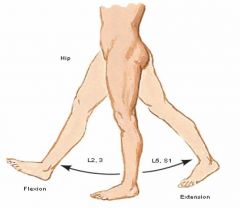
|
|
|
What is the segmental innervation of the lateral ankle movement?
|
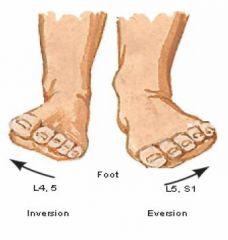
|
|
|
What is the segmental innervation of vertical ankle movement?
|
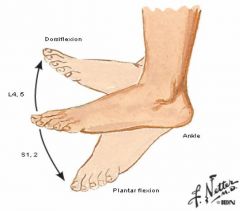
|
|
|
What is the soleal line, and what muscle attaches to it?
|
* Rough ridge on the upper part of the posterior surface of the tibia.
* Soleal muscle attaches to it. |
|
|
What is the medial malleolus?
|
* The medial surface of the distal end of the tibia.
|
|
|
What is the fibular notch?
|
* The lateral aspect of the distal tibia, with which the lower end of the fibula articulates.
|
|
|
What does the inferior surface of the distal tibia articulate with?
|
* The superior trochlear surface of the talus.
|
|
|
What is the lateral malleolus?
|
* Distal end of the fibula.
|
|
|
What is the proximal tibio-fibular joint?
|
* small synovial joint between flat facet on head of fibula, and small facet on the lateral condyle of the tibia.
|
|
|
What is the middle tibio-fibular joint?
|
* fibrous joint formed by the interosseous membrane connecting the bodies of the tibia and fibula.
|
|
|
What is the distal tibio-fibular joint?
|
* a syndesmosis uniting the lower ends of the tibia and fibula. Connected by a very strong interosseous ligament.
|
|
|
What are the 3 parts of the tarsus?
Which bones are in each of the 3 parts? |
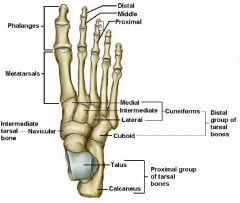
Proximal group
* talus * calcaneus Intermediate group * navicular Distal group * Cuboid * 3 cuneiforms (lateral, intermediate, medial) |
|
|
What are the 3 parts of the talus?
|
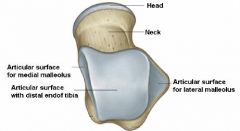
* head, neck, body.
|
|
|
What bones does the talus articulate with?
|
* tibia, fibula (medial malleolus), calcaneus
|
|
|
What bones does the calcaneus articulate with?
|
* talus superiorly, cuboid anteriorly.
|
|
|
What is the shelf-like projection on the medial surface of the calcaneus called?
|
* sustentaculum tali
|
|
|
What at the anterior end of the inferior surface of the calcaneus?
What attaches to it? |
* Calcaneal tubercle.
* Short plantar ligament attaches to it. |
|
|
What is at the posterior surface of the calcaneus?
What attaches to it? |
* Calcaneal tuberosity.
* Attachment of the calcaneal tendon. |
|
|
What are the main joints in the foot?
|
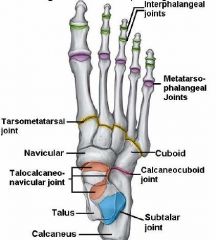
* interphalangeal joints (DIP and PIP)
* metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP) * tarsometatarsal joints * intertarsal joints * talocalcaneonavicular joint * calcaneocuboid joint * subtalar joint, or talocalcaneal joint |
|
|
What is the purpose of the intertarsal joints?
|
* inversion and eversion
|
|
|
What are the motions that the MTP joints are responsible for?
|
* flexion, extension, abduction, adduction of the toes.
|
|
|
What are the motions that the PIP and DIP joints are responsible for?
|
* flexion and extension.
|
|
|
What is the deltoid ligament?
What are its parts? |
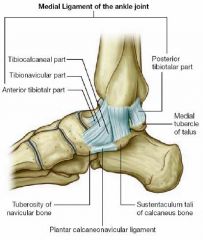
The ligaments of the medial side of ankle.
* tibionavicular ligament * tibiocalcaneal ligament * anterior tibiotalar ligament * posterior tibiotalar ligament |
|
|
Name the parts of the lateral ankle ligament.
|
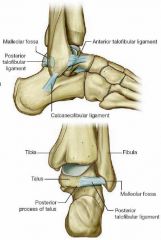
* anterior talofibular ligament
* posterior talofibular ligament * calcaneofibular ligament |
|
|
What are the three compartments of the leg, divided by intermusclar septae?
|
Anterior, posterior and lateral compartments.
Note that the posterior compartment is further divided into deep and superficial compartments. |
|
|
What are retinacula?
Name the location of three retinacula in the ankle area. |
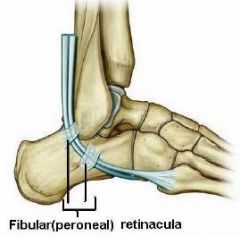
They are thickened deep fascia, used to hold tendons in place.
* Anterior ankle - there are extensor retinacula. * Lateral ankle - there are fibular/peroneal retinacula. * Posteromedial ankle, there is flexor retinacula. |
|
|
What is the only muscle on the dorsum of the foot?
What is the most medial part of the muscle called? |
* Extensor digitorum brevis.
* Extensor hallucis brevis. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of extensor digitorum brevis muscle?
|
* Deep fibular nerve..
* Extension of medial four toes. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the extensor hallucis brevis muscle?
|
* Deep fibular nerve.
* Extension of the great toe. |
|
|
Name all of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg.
|
* tibialis anterior
* extensor hallucis longus * extensor digitorum longus * fibularis (peroneus) tertius |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the tibialis anterior muscle?
|
* deep fibular nerve.
* dorsiflexion of ankle * inversion of foot |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the extensor hallucis longus muscle?
|
* deep fibular nerve
* extension of great toe |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the extensor digitorum longus muscle?
|
* deep fibular nerve
* extension of lateral four toes |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the fibularis (peroneus) tertius?
|
* deep fibular nerve
* dorsiflexion of ankle * eversion of foot Note that some people do not have this muscle. |
|
|
Name all of the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg.
|
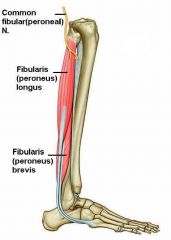
* Fibularis (peroneus) longus.
* Fibularis (peroneus) brevis. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the fibularis longus muscle?
|
* Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve.
* Eversion of foot. |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the fibularis brevis muscle?
|
* Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve.
* Eversion of foot. |
|
|
What root levels comprise the common fibular (peroneal) nerve?
What is the course of the common fibular nerve? What other nerves does it give rise to? |
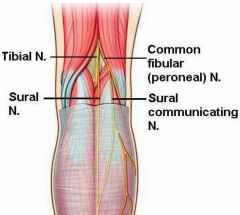
* L4, 5, S1, 2
* Starts as a branch of the sciatic nerve. It extends from superior angle of popliteal fossa to the lateral side. It winds around neck of fibula, and gives rise to deep and superficial fibular nerves. Gives rise to: * sural communicating branch * deep fibular nerve * superficial fibular nerve |
|
|
What does the superficial fibular nerve innervate?
|
* Lateral compartment of the leg. This includes fibularis longus and brevis. Also, the skin of the dorsum of the foot, except for the first interdigital cleft.
|
|
|
What does the deep fibular nerve innervate?
|
* Anterior compartment of the leg, and dorsum of the foot.
* This includes all the muscles in the anterior compartment. * Also, extensor digitorum brevis on the dorsum of the foot. * As well as the skin adjoining the first interdigital cleft. |
|
|
What is the course of the popliteal artery?
What artery does it originate from? |
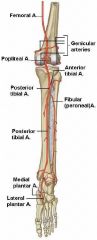
* Continuation of the femoral artery.
* Begins at the opening of adductor hiatus. Runs through popliteal fossa, and divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries. * Also gives off genicular branches in the popliteal fossa, which supply the knee joint. |
|
|
What is the course of the anterior tibial artery?
What does it supply? |
* Originates from the popliteal artery. Enters the anterior compartment of the leg by passing through opening in upper part of interosseus membrane. Runs down to a point between the two malleoli, where it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery.
* Supplies the anterior compartment of the leg. |
|
|
What is the course of the dorsalis pedis artery?
What does it supply? |
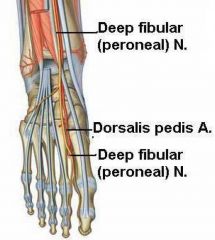
* Continuation of the anterior tibial artery. Begins in front of the ankle, between the two malleoli. Continues along the medial side of the dorsum of the foot to reach proximal end of 1st intermetatarsal space. Here it dips downward between the two heads of the 1st dorsal interosseous muscle, and ends in the sole, completing the plantar arterial arch.
* Supplies the dorsum of the foot by giving off some branches. |
|
|
What are the nerve roots of the sural nerve?
What is its course? What does it innervate? |
* L5,S1,2
* Cutaneous branch of the tibial nerve, joins the sural communicating nerve (a branch of common fibular nerve), pierces deep fascia in middle of leg to become superficial. * Innervates posterolateral side of leg, and lateral side of foot. |
|
|
Where is the flexor retinaculum?
|
It is on the medial side of the ankle.
|
|
|
What are the structures in the tarsal tunnel, starting from anterior to posterior?
|
Tom Dick And Not Harry
* Tendon of tibialis posterior * Tendon of flexor digitorum longus * Posterior tibial artery * Tibial nerve * Tendon of flexor hallucis longus |
|
|
Name the muscles in the superficial group of posterior leg muscles.
|
* Gastrocnemius
* Plantaris * Soleus |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the gastrocnemius muscle?
|
* tibial nerve
* plantar flexion of foot * flexion of knee |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the plantaris muscle?
|
* tibial nerve
* plantar flexion of foot |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of soleus muscle?
|
* tibial nerve
* plantar flexion of foot |
|
|
Name the muscles in the deep group of posterior leg muscles.
|
* Popliteus
* Flexor hallucis longus * Flexor digitorum longus * Tibialis posterior |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the popliteus muscle?
|
* Tibial nerve
* Unlocks knee joint (laterally rotates femur on fixed tibia). |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the flexor hallucis longus?
|
* Tibial nerve
* Great toe flexion (DIP) |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the flexor digitorum longus?
|
* Tibial nerve
* Lateral four toe flexion (DIP) |
|
|
What is the innervation and function of the tibialis posterior muscle?
|
* Tibial nerve
* Inversion and plantar flexion of foot. |
|
|
What are the 3 most important ligaments of the foot?
|
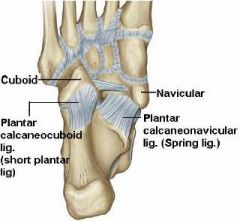
* Spring ligament (calcaneonavicular ligament)
* Short plantar ligament (calcaneo-cuboidal ligament) * Long plantar ligament |
|
|
Which points of the sole is body weight transferred to?
|
* Heel
* 1st MTP joint * 5th MTP joint |
|
|
How is the integrity of the bony arches of the foot maintained? Name 4 points.
|
1. Shape of interlocking bones
2. Stretch of plantar ligaments 3. Plantar aponeurosis 4. Action of muscles through bracing action of their tendons |
|
|
What is the latin name for "buneon"?
|
Hallux valgus
|
|
|
What is the thickened central part of the deep fascia of the sole called?
|
Plantar aponeurosis.
* it fixes the skin at the sole * it protects deep structures * it helps maintain the longitudinal arches of the foot |
|
|
Name the muscles in the first layer of the sole.
|
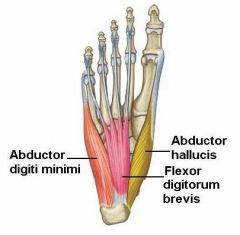
* Abductor hallucis
* Flexor digitorum brevis * Abductor digiti minimi |
|
|
Name the components of the second layer of the sole.
|
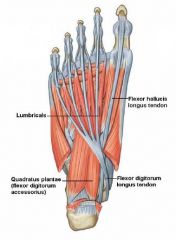
* Tendon of flexor hallucis longus
* Tendon of flexor digitorum longus * Quadratus plantae * Lumbricals |
|
|
Name the muscles in the third layer of the sole.
|
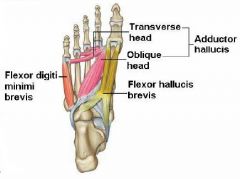
* Flexor hallucis brevis
* Adductor hallucis * Flexor digiti minimi brevus |
|
|
Name the muscles in the fourth layer of the sole.
|
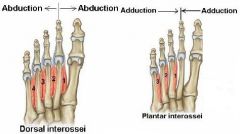
* Four dorsal interossei muscles.
* Three plantar interossei muscles. |
|
|
What is the function of the quadratus plantae muscle?
|
* Pulls tendon of flexor digitorum longus towards the midline.
* Also called the flexor digitorum accessorius. |
|
|
What is the function of the lumbricals muscles?
|
* Flexion of the metatarsophalangeal joints and extension of the interphalangeal joints.
|
|
|
What is the function of the dorsal interossei muscles?
|
* Abduction of the toes.
|
|
|
What is the function of the plantar interossei muscles?
|
* Adduction of the toes.
|
|
|
What is the nerve supply of the posterior leg?
|
Tibial nerve.
|
|
|
What are the root levels of the tibial nerve?
What is its course? |
* L4,5,S1,2,3
* Branch of sciatic nerve. * Situated in middle popliteal fossa. Enters back of leg by passing through the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. Passes deep to soleus muscle, down to back of medial malleolus. Then divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves. |
|
|
What is the arterial supply for the posterior leg?
|
* Posterior tibial artery.
|
|
|
What is the course of the posterior tibial artery?
|
* Branch of the popliteal artery. Begins at lower border of popliteus muscle, and is located between superficial and deep muscles in posterior leg. Passes behind medial malleolus to enter sole of foot, and divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries.
* A branch of it, the fibular artery, supplies the lateral compartment of the leg. |
|
|
What is the arterial supply for the lateral leg compartment?
|
* Fibular artery, a branch of the posterior tibial artery.
|
|
|
Lateral plantar nerve supplies all muscles of the sole of the foot, except which ones?
|
Medial plantar nerve supplies these:
* 1st layer: FDB, ABH * 2nd layer: first lumbrical muscles * 3rd layer: FHB |
|
|
The skin of which toes are innervated by which nerve?
|
* Medial 3 1/2 toes - medial plantar nerve.
* Lateral 1 1/2 toes - lateral plantar nerve. |
|
|
Which artery in the sole gives off the plantar arch?
|
* Lateral plantar artery.
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the ASIS?
|
Sartorius
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the AIIS?
|
Rectus femoris
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the ischial tuberosity?
|
Long head of biceps femoris
Semimembranosus Semitendinosus |
|
|
What ligament attaches to the fovea capitis?
|
Head of the femur ligament.
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the greater trochanter?
|
Gluteus medius
Gluteius minimus Piriformis |
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the lesser trochanter?
|
Iliopsoas tendon.
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the linea aspera?
|
Hip adductor muscles.
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the adductor tubercle?
|
Adductor magnus
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the tibial tuberosity?
|
Patellar tendon
|
|
|
What muscle(s) attach to the head of the fibula?
|
Biceps femoris
|

