![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
129 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The limb bud is pliable, grows not only in ____ but also with ____. contorting and dragging neurovascular structures distally as it assumes a more mature attitude. These changes are important in accomplishing a ___, a uniquely human trait. |
length torsion bi-pedal gait |
|
|
The positions of the developing upper and lower extremities develop during which weeks of prenatal development? |
5th,6th, and 7th week |
|
|
at the ___ week the hand and foot plates are visible and the longitudinal axes of the limbs lie nearly perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the trunk. By the ___ week digital rays are visible in the hands but not in the feet (superiorly) By the end of the __ week the digital rays in the feet are now present and the extremities have begun their rotation. |
5th 6th 7th |
|
|
the ___ extremity rotate laterally, the ___ extremity rotate medially. the elbows face the ___ direction and the knees face the ___ direction during the end of the 7th week |
upper lower caudally cranially |
|
|
The lower extremity girdle (part of the appendicular skeleton) is formed by what three fused bones?
The ___ exhibit 8 centers of ossification that do not ultimately fuse until the age of 25 years |
pubis, ilium, ischium
os coxae |
|
|
___ is a region to produce good quality autogenous cortico-cancellous bone graft
___ can be used as a landmark to assess pelvic position and limb lengths |
iliac crest anterior superior iliac spine |
|
|
The ____ closes off the greater sciatic foramen. this foramen has what 3 important components?
The ___ closes off the lesser sciatic foramen. |
shorter scarospinous ligament internal pudendal vessels, pudendal nerve, and nerve to obturator internous
sacrotuberous ligament *(pudendal nerve, internal pudendal vessels, and nerve to obturator internus)* |
|
|
What does the greater sciatic foramen consist of ?
What does the lesser sciatic foramen consist of ? |
The superior gluteal vessels and nerves, the inferior gluteal vessels and nerves, internal pudendal vessels and nerve, sciatic nerve, post. femoral cutaneous nerve, nerve to the obturator internus, and nerve to the quadratus femoris
pudendal vessels and nerve, nerve to obturator internus, and tendon of obturator internus |
|
|
___ is the longest bone of the body (24-33% of your total weight)
The ___ is the angle formed by the long axis of the femoral head and neck and the long axis of the femur. About __ degrees in the infant then __ degrees as an adult |
femur angle of inclination 135 120 |
|
|
the ___ is the angle formed by the transverse axis of the femoral condyles and the long axis of head and neck. it normally demonstrates what? |
torsion angle of the femur/angle of declination 12 degrees on anterversion in the adult |
|
|
Muscles that attach to the ___ will usually abduct and laterally rotate the hip
____ is dense vertically oriented bone that originates in posteromedial portion of femoral shaft. it radiates laterally toward the posterior aspect of the greater trochanter and reinforces the femoral neck posteroinferiorly |
greater trochanter
calcar femorale |
|
|
The __ is a sesamoid bone that is constantly present in patients. Sesamoid bones develop with in the ____. which tendon? where is the tendon enveloped? |
patella tendon quadraceps femoris
|
|
|
Surface anatomy: ___ aka rim of the ilium us located at L4. it can be palpated to facilitate spinal taps and spinal anesthesia. It is often a place to harvest autogenous bone graft ____ - if you trace the iliac crest anteriorly and posteriorly this feature can be palpitated. it is a landmark for measuring limb length |
Iliac crest ASIS |
|
|
Surface anatomy: ___ is 5-6 cm posterior to ASIS (L5) ___ is difficult to palpate but easy to locate, corresponds to dimple 4 cm lateral to midline Sacral dimples are located where? The coccyx and sacral hiatus is located proximal to which cleft?
|
Iliac tubercles PSIS S2 (landmark for some anesthesia techniques) natal/intergluteal cleft |
|
|
____ gives rise to the subcostal nerve (1/2 of the population of the lumbar plexus). the lateral branches of this nerve serve the skin in the proximal thigh, inferior, and lateral to ASIS
__ gives rise to the iliohypogastric nerve |
T12 L1 |
|
|
___- a scant region of skin is innervated by cutaneous branches of this nerve in the superior medial region of the thigh _____ gives rise to the lateral femoral nerve. the cutaneous nerve that serves the skin on the anterior and lateral thigh ___ gives rise to the genitofemoral nerve. which will split into two cutaneous branches, and the femoral branch will serve the proximal anterior thigh centrally |
L1 (ilioguinal nerve) L2 and L3 L1,L2 |
|
|
___ gives rise to the femoral nerve. which produces cutaneous and muscular branches which serve structures in the anterior hip and thigh regions ____ gives rise to the obturator nerve. which produces cutaneous and muscular branches which serve structures in the medial thigh What gives rise to the accessory obturator in approximately 30% of the population? |
L2, L3, and L4 L2, L3, and L4 L3, L4
|
|
|
Does the lumbosacral trunk contribute to the sacral plexus? is it a branch of the lumbar plexus? |
yes no |
|
|
____ is dense vertically oriented bone that originates in the postmedial portion of femoral shaft. it radiates laterally toward the posterior aspect of the greater trochanter, and reinforces the femoral neck posteroinferiorly |
Calcar Femorale |
|
|
the head of the navicular bone articulates with what? what three bones make up the ankle?
|
three different cuneiform bones (ant, post, and intermediate) navicular, cuboid, and cuneiform |
|
|
What makes up the medial longitudinal arch of the foot? what makes up the lateral longitudinal arch of the foot? What makes the transverse arch of the foot? |
Calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuneiforms, and the medial three metatarsals
calcaneus, cuboid, and two lateral metatarsals
navicular, cuneiforms, cuboid, and the five metatarsals |
|
|
where do you insert a venous catheter? |
cut down to great saphenous vein anterior to medial malleous |
|
|
where do the nerves of the lumbar and sacral plexuses originate from?
The ___ plexus of nerves is formed anterior to the lumbar transverse processes, within the proximal attachment of a muscle which inserts into the thigh, the psoas major The__ plexus is formed anterior to the sacrum and is a pelvic structure |
the ventral rami of the spinal nerves the lumbar plexus the sacral plexus |
|
|
What vertebra levels make up the lumbosacral trunk?
What makes the lumbosacral plexus? |
L4-L5
lumbosacral trunk and the sacral plexus |
|
|
What is the terminal branch of the femoral nerve? Where is the saphenous nerve located What does the saphenous nerve run with in the leg? what does the saphenous nerve mainly innervate? what are the branches of the saphenous nerve? |
saphenous nerve femoral triangle and adductor canal saphenous vein supplies the skin of the medial side of the leg and foot to the knee joint, subsartorial plexus, patellar plexus
|
|
|
what gives off the medial and lateral circumflex femoral artery? what is considered the main blood supply to the thigh because of the numerous perforating muscular branches of the anterior and posterior and medial compartments of the thigh? |
deep femoral artery deep femoral artery/ profundus femoral |
|
|
the aorta bifuricates into an anterior the what? the internal iliac splits into an anterior and posterior division which are the ____ and ___ respectively
the ___ artery becomes the femoral artery inferior to the inguinal ligament. what is the external iliac artery largest branch? |
obturator artery, and the superior and inferior gluteal arteries external iliac artery deep femoral artery |
|
|
what gives rise to the medial and lateral plantar arteries? what becomes the plantar arch (which anastomoses with the 1st perforating artery from the DP)? |
posterior tibia artery lateral plantar artery |
|
|
Surface anatomy: ____ is located at the midline, it is difficult to palpate, covered with fat. This is the location of articulation between the right and left ischiopubic rami. What is the boney angle inferior to the ischiopubic rami? Can the angle be estimated during a pelvic exam? |
Pubic symphysis sub pubic angle yes but only in females |
|
|
what is the site for difficult decubuti (bed sores)/decubiti ulcers?
The fascia lat is a portion of which part of the body?
What is the deep fascia called in the leg? |
ischial tuberosity and the greater trochanter of the humerus
Deep fascia
crural fascia |
|
|
Where can you find the opening of the saphenous vein?
The roof of the fascia opening is fenestrated and is called the what?
what is the function of the deep fascia in the lower limb? ___ is a disease caused in part due to the deep fascia |
fascia latae cribiform fascia allows for more efficient proximal flow of blood in the deep venous system Volkmanns contraction (compartment syndrome) |
|
|
___ is a thick lateral portion of the fascia lata. What insertion does the iliotibial tract provide for? what is the main function of the iliotibial tract? |
iliotibial tract the gluteus maximus and tensor fascia latae muscles help stabilize the knee in extension |
|
|
what are the boudries of the femoral triangle? what are the contents of the femoral triangle?
What is the abdominal opening of the femoral canal? |
inguinal ligament (superiorly), sartorius (laterally), and the adductor longus (medially) femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein, empty space than lymph, and the femoral canal
femoral ring |
|
|
__ lies medial to the femoral vein in the femoral sheath. What does the femoral canal contain? What can happen in the femoral canal? (clinically) |
femoral canal fat, areolar connective tissue, and lymph nodes femoral herniation |
|
|
What is the femoral sheath formed by? What does the femoral sheath contain? |
by a prolongation of the transversalis fascia in the thigh the femoral artery and vein, and the femoral canal. (the nerve is NOT in the femoral sheath but lies laterally to it) |
|
|
Where do femoral hernias lie? Sac is formed by the ____ femoral hernia passes through the _____ from the abdomen and into the ____ More common in females or males? |
lateral to the pubic tubercle and deep to the inguinal ligament femoral ring, femoral canal females |
|
|
Where does the adductor canal begin? where does it end what does the adductor canal occupy? The adductor canal lies between the ___ muscle and the ____ muscle and is covered by the ___ and ____ what does the adductor canal contain? |
apex of the femoral triangle, ADDUCTOR HIATUS middle 1/3 of the thigh adductor longus, vastus medialis, sartorius and fascia femoral vessels, saphenous nerve and vastus medialis nerve |
|
|
___ is the aperture in the tendon of insertion of the adductor magnus. What does the adductor hiatus allows? What is the main scheme of the adductor hiatus? |
adductor hiatus of the femoral vessal into the popliteal fossa femoral vessels (in the adductor canal) then the adductor hiatus, and then the vessels become the popliteal vessals once in they're in the popliteal fosssa |
|
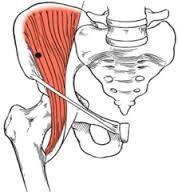
name the muscle, function, innervation? |
iliacus flexes thigh (with psoas major) femoral nerve
|
|
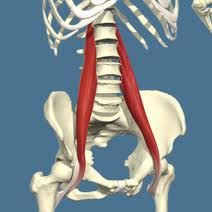
|
psoas flexes thigh (with iliacus) femoral nerve |
|
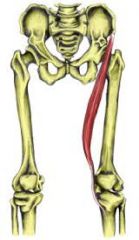
|
sartorius flexes, abducts, and rotates the thigh. laterally flexes the leg (tailors position) femoral nerve
|
|
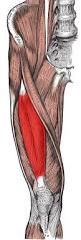
|
Rectus femoris flexes thigh, extends leg (knee) femoral nerve |
|
|
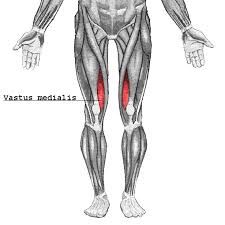
vastus medialis extends leg (knee) femoral nerve |
|
|
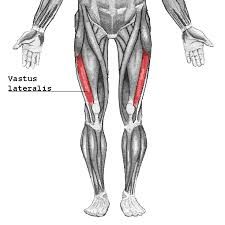
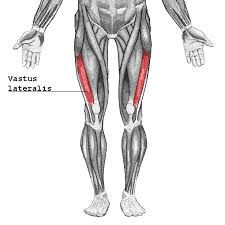
vastus lateralis extends leg (knee) femoral nerve |
|
|
vastus intermedius extends leg (knee) femora nerve |
|
|
what joins to form the iliopsoas muscle? What forms the quadriceps femoris muscle? Knee jerk/patellar reflex occurs when the ___ is tapped resulting the contraction of the quadriceps fermoris muscle. what are the innervation? What does damage to the femoral nerve cause? |
iliacus and the psoas muscle Vastus lateralis, medialis, and intermedius
patellar ligament (tendon), L2-L4
paralysis of the quadriceps muscle so impaired flexion of the hip and impaired extension of the leg, and diminished or absent patellar reflex |
|
|
All the muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh are supplied by the femoral nerve at L_to L_ The ___ extends the leg and controls its flexion The __ flexes the thigh and extends the leg, together with the ___ they form the kicking muscle of the leg. What are the quads important for?
|
2-4 quadriceps rectus femoris climbing, running, jumping, rising from a sitting position, and walking up and down the stairs |
|
|
Pes Anserinus (goose foot) is the insertion of what three muscles into the medial aspect of the knee capsule? |
Sartorius (anterior), Gracilis (medial), and the semitendinosus (posterior) |
|
|
the medial thigh musculature comprises the adductors of the __ joint. They generally originate from the ___ and insert onto the ____
The obturator externus is innervated by the ___ division of the obturator nerve from the lumbar plexus (t or F) pectineus is comprised of a superficial and deep component. for the pectineus the __ nerve will flex and the __ nerve adduct |
hip pelvis anteriorly and inferiorly medial posterior femor posterior true femoral obturator nerve |
|
|
The obturator nerve exits through the front door of the ___, and leaves the psoas region medially. Damage to the obturator nerve cause what? obturator artery originates from the __ artery what runs with the obturator nerve? Obturator nerve is L_ to L_ what supplies the bloody supply of the pelvic muscles, ilium, head of femur and proximal portion of adductors |
obturator canal weakness of adduction and a lateral swinging of the limb during walking because of unopposed abductors internal iliac artery small obturator artery 2-4 obturator artery |
|
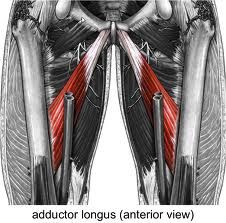
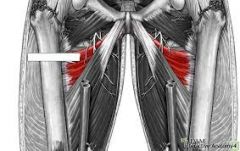
name the muscle, innervation and function |
adductor longus obturator nerve adducts thigh (hip) |
|
|
adductor brevis obrturator nerve adducts thigh (hip) |
|
|
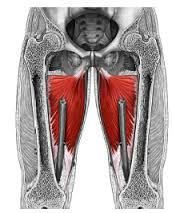
Adductor magnus Obturator nerve and sciatic adducts the thigh (hip) |
|
|
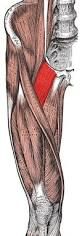
Pectineus obturator and femoral Adducts and flexes thigh (anterior) |
|
|
gracilis obturator nerve adducts thigh, flexes leg (knee)
|
|
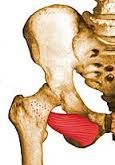
|
obturator externus obturator nerve rotates thigh laterally |
|
|
___ muscle will flex the hip and knee ___ muscle will flex the hip and extend the knee ___ muscle will adduct the hip and flex the knee |
sartorius rectus femoris gracilis |
|
|
All the muscles of medial compartment of the thigh are supplied by the __ divison of the obturator nerve except which muscles? (extensor portion =tibial nerve, adductor portion= posterior division of obturator nerve) |
anterior division pectineus and the adductor magnus |
|
|
___ artery supplies the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh. obturator artery gives a branch ___ to the hip joint Obturator nerve arises from the ___ and has the root value of ____. (t or F) the nerve is medial to the psoas major and divides into an an anterior and posterior branches before it exits the obturator foramen. |
obturator acetabular branch lumbar plexus l2-l4 little from l5 |
|
|
___ division of the obturator nerve, innervates the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh and branches to the hip joint. It has sensory to the medial side of the thigh and sometimes the leg. it is a branch of the knee joint __ division innervates the obturator externus and branch to the knee, and innervates the adductor magnus (adductor portion) |
anterior posterior |
|
|
__ nerve has a root value of L2-L4 and emerges from the medial side of the psoas major muscle. it communicates with the anterior branch of the anterior obturator nerve and supplies the pectineus muscle and the hip joint |
accessory obturator nerve |
|
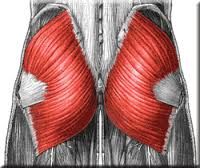
Name the muscle, innervation and functuon |
gluteus maximus inferior gluteal extends the hips (thigh) and stabilizes the knee in extension |
|
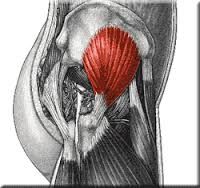
|
gluteus minimus superior gluteal internal rotation hip (thigh) |
|
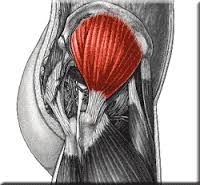
|
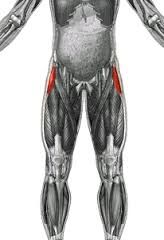
gluteus medius superior gluteal abducts the hip (thigh) |
|
|
tensor fasciae latae superior gluteal flexes, abducts hip (thigh) and stabilizes the knee in extension |
|
|
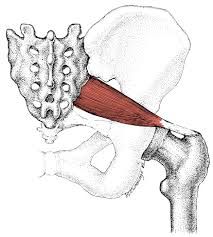
piriformis sacral (S1-S2) rotates the thigh (hip) laterally |
|
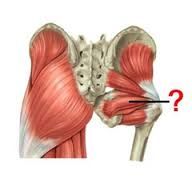
name the obturator internus, superior and inferior gemellus. what is the innervation and fucntions of these muscles? |
nerve to obturator internus, except inferior gemellus (nerve to quadratus femoris) rotates thigh ((hip) laterally |
|
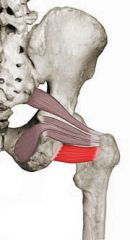
|
quadratus femoris nerve to quadratus femoris rotates thigh (hip) laterally |
|
|
Gluteal gait is a waddling gait, characterized by the pelvis falling on the unaffected side side at each step due to paralysis of the __ muscle. this muscle functions to stabilize the ___ when the opposite foot is off the ground. |
gluteal medius pelvis |
|
|
A __ gait is seen with lesions to the inferior gluteal nerve. the anterior thigh muscles will overpower the weak gluteus maximus and hamstring muscle, this results in what? |
gluteus maximus extension of the spine in order to shift the center of gravity posteriorly |
|
|
All the muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh are supplied by the tibial portion of the sciatic nerve except what? what innervates it?
what are the general actions of the posterior thigh muscles? |
short head of biceps femoris, common peroneal nerve flexion of the leg at the knee joint, and extension of the thigh at the hip joint |
|
|
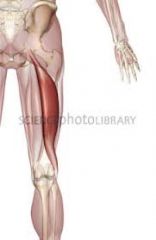
what are the actions of the hamstring muscles? what are the muscles of the hamstrings |
extend hip and flex knee (frequently inflammed in athletes) semitendinosus, semimembranosus, bicep femoris |
|

Name the muscle, innervation, and function |
semitendinosus tibial portion of sciatic nerve extends thigh, flexes leg (knee) |
|

|
semimembranosus tibial portion of sciatic nerve extends thigh, flexes leg (knee) |
|
|
bicep femoris tibial portion of sciatic nerve (long head) and common perineal (short head) division of the sciatic nerve extends thigh and flexes leg (knee) |
|
|
what is the deep tendon reflex of the calcaneal reflex? what is the fascia of the leg? anterior of the leg= lateral part of the leg= posterior part of the leg= |
tibial nerve s1 crural fascia extensor peroneal flexor |
|
|
Athlectic pain: ___ is entrapment syndromes, radiculopathy ___ is ischemia, DVT ___ are strains, tears, herniations, tendinitis, tendinosis ___ is periostitis or tears ___ is stress fractures |
nerve vascular muscle fascia osseous |
|
|
____ is description of non specific exertional leg pain syndrome. it is inflammation of the Interosseous membrane or periosteum covering the tibia and fibula. ___ refers to the ischemic and entrapment pains associated with swelling of muscles with in the non distendible structures (deep fascia , IO membrane, and bone) which contain a compartment of muscles |
shin splints compartment syndrome |
|
|
___ keeps the tendons from bow stringing at the ankle, the crural fascia thickens to form bands called retinacula What muscles make up the tendons of the lateral compartment? __ dives deep at the base of the 1st metatarsal |
superior extensor retinaculum peroneus longus and brevis peroneus longus |
|
|
compression of the _ nerve can impair dorsiflexion of the ankle leading to a high steppage gait and foot slap on heel strike. this can occur following trauma to the what? ____ innervates sensation between 1st and second toe pararlysis of __ causes foot drop |
common peroneal nerve (superficial) proximal fibula or result of poor positioning of unconscious pt during surgery deep peroneal nerve tibialis anterior (deep peroneal nerve) |
|
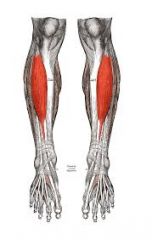
Name the muscle, innervation, and function |
anterior tibialis anterior deep peroneal nerve dorsi flexion of ankle and inverts foot |
|
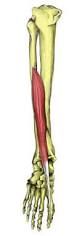
|
extensor hallucis longus deep peroneal nerve extends great toe
|
|

|
extensor digitorum longus deep peroneal nerve extends lateral toes |
|

|
peroneus tertius deep peronealnerve dorsiflexion of ankle and everts the foot |
|
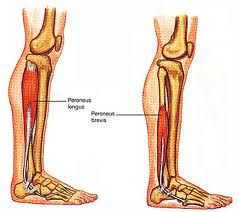
|
peroneus longus and brevis superficial peroneal nerve everts foot and plantar flexion of the ankle
|
|
|
___ muscle will insert medially into the calcaneus, and some people are missing this muscle
what is the quadriceps reflex?
what muscle will contract during a ankle jerk? Normal reflex of the ankle jerk suggest what? |
Plantaris tendon (freshmen nerve) L2-L4 gastrocnemius and the soleus intact of S1 ventral rami and tibial nerve |
|
|
All of the muscles of the leg (superficial and deep) and all of the foot muscles with the exception of extensor digitorum brevis are innervated by what?
__ muscle will bring blood supply for achilles tendon tears |
tibial nerve flexor hallucis longus |
|
|
What muscles enter the tarsal tunnel? |
Tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus (occupied with nerve, artery, and vena commutantes) and flexor hallucis longus |
|
|
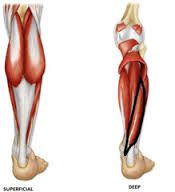
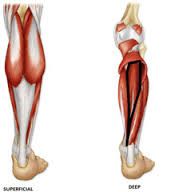
What are the deep muscles of the posterior leg? what are the superficial muscles of the posterior leg? |
gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris
popliteus, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior |
|

Name the muscle, innervation, and function |
gastrocnemius tibial nerve flexes the knee, and plantar flexes the ankle |
|
|
Soleus tibial nerve plantar flexes the ankle |
|

|
Plantaris Tibial nerve flexes leg, plantar flexes ankle |
|
|
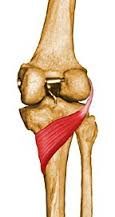
popliteus tibial nerve rotates femur laterally, unlocks the knee |
|
|
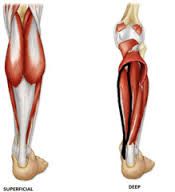
flexor hallucis longus tibial nerve flexes great toe |
|
|
flexor digitorum longus tibial nerve flexes lateral four toes
|
|
|
tibialis posterior tibial nerve plantar flexes ankle and inverts foot |
|
|
_ to __ is the tibial nerve The tibial nerve is the branch of ___ in the gluteal and thigh regions What is the tibial nerve superficial too and deep to what? The tibial nerve travels behind the ___ and is covered by _____? |
L4-S3 sciatic nerve popliteus muscle gastrocnemius soleus medial malleolus flexor retinaculm |
|
|
The anterior tibila artery runs with what nerve?
At the level of the ankle joint line the anterior tiibial artery becomes what? |
deep peroneal nerve dorsalis pedis (DP) artery distally |
|
|
The popliteal artey begins at the ___ and biruficates at the inferior border of the __ muscle. what are the branches of the popliteal artey? the anterior tibial artery will send branches to the ___ muscle. The __ artery is a branch of the posterior tibial artery, and is in close association with the flexor hallucis longus muscle. The peroneal artery wil give branches to what two muscles? |
adductor hiatus popliteal muscle anterior and posterior tibial arteries peroneus longus peroneal peroneus longus and brevis |
|
|
What does the posterior tibial artery run with?
At the distal end, theposterior tibial artery lies deep to what?
which artery gives off the nutrients to the fibula? |
tibial nerve flexor retinaculum, and abductor hallucis muscle peroneal artery |
|
|
What are the boundries of the popliteal fossa?
What is the roof of the popliteal fossa? |
lateral boder: biceps femoris (short and long), and gastrocnemius (below) (lateral head) Medial: semimembranosus, semitendinosus (above), and the medial head of the gastrocnmeis (below)
deep fascia, (penetrated by small saphenous vein) |
|
|
What are the contents of the popliteal fossa? the floor?
__ of the foot involves adduction, inversion and plantar flexion. __ consists of abduction, eversion and dorsiflexion |
tibial and common peroneal nerv, popliteal vein and artery popliteus muscle and femur (popliteal surface) supination pronation
|
|
|
the ___ is fribrosus connective tissue extending from the calcaneal tuberosity towards all 5 toes. it provides for partial maintenance of the medial longitudinal arch in weight bearing. inflammation of the plantar fascia is called ___ The ___ is a nerve at the medial ankle and impingement here can cause heel pain |
plantar fascia/aponeurosis plantar fascitis or heal spur syndrome porta pedis |
|
|
___ is an accessory muscle to the flexor digitorum longus, it straightens out the pull of the obliquely oriented long tendon what two muscles (tendons) will cross at a point proximal to the arrows called the knot of henry? Whats a bunion? |
quadratus plantae flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus when the 1st metarsal (or any tarsal) is sticking out or subluxes |
|
|
What muscles lie in the dorsal layer of the plantar foot? 1st layer? 2nd layer? 3rd layer? 4th layer?
|
-extensor digitorum brevis, extensor hallucis br. -abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum, abductor digit minimi -quadratus plantae, lumbricals, and tendon of the flexor digitorum longus -flexor hallucis brevis, adductor hallucis, flexor digiti minimi brevis -plantar and dorasal interossei
|
|
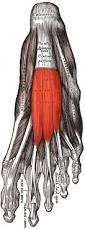
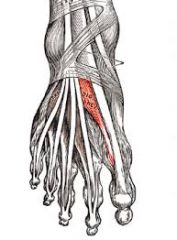
Name the muscle, innervation, and function |
extensor digitorum brevis deep peroneal nerve extends lateral toes (2-4) |
|
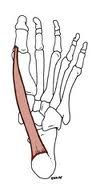
|
extensor hallucis brevis deep peroneal nerve extends great toe |
|
|
abductor hallucis medial plantar nerve abducts great toe |
|
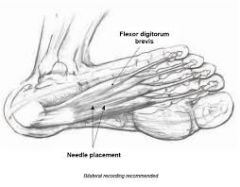
|
flexor digitorum brevis medial plantar nerve flexes middle phalanges of lateral four toes
|
|
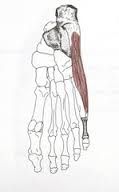
|
abductor digit minimi lateral plantar nerve abducts little toe |
|
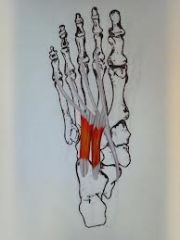
|
quadratus plantae lateral plantar nerve aids flexing lateral toes |
|
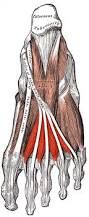
|
lumbricals first is by the medial plantar nerve, the lateral three is innervated by the lateral plantar nerve flex the metatarsophanlangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joint; lat. toes |
|
|
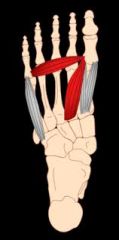
flexor hallucis brevis medial plantar nerve flexes great toe |
|
|
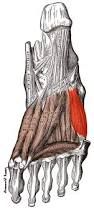
adductor hallucis lateral plantar adduct great toe |
|
|
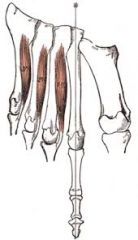
flexor digit mini brevis lateral plantar nerve flexes little toe |
|
|
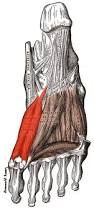
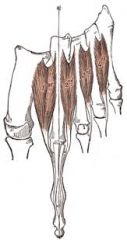
plantar interossei (3) lateral plantar nerve adducts lateral toes |
|
|
dorsal interossei (4) Lateral plantar nerve abducts lateral toes of 2 through 4
|
|
|
What type of joint is the hip? what muscles perform flexion of the hip? (5) extension of the hip? (2) adduction of the hip? (5) abduction of the hip? (1) medial rotation? (1) lateral rotation? (5)
|
ball and socket iliopsoas, tensor Fascia l, rectus fermoris, sartorius, pectineus -hamstings, gluteus maximus -adductor longus, magnus, brevis, pectnieus, gracilis -gluteus medias -gluteus minimus -obturator internus and externus, gemelli, piriformis, quadratus femoris
|
|
|
What type of joint is the knee? flexion of the knee? (5) extension of the knee? (1) Lateral rotation? (1)
|
hinge joint -hamstrings, gracilis, sartorius, gastrocnemius, popletius -quadriceps femoris -popliteus |
|
|
What type of joint is the ankle? dorsiflexion of the ankle? (4) planatar flexion of the knee? (8)
What muscles will invert the intertarsal joints? What muscles will evert the intertarsal joints? |
hinge joint -anterior tibialis, EDL, EHL, peroneus tertius -gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, posterior tibialis, peroneus longus and brevis, FDL, FHL -tibialis posterior and anterior -peroneus longus, brevis, and tertius |
|
|
The sacroiliac articulations are found spanning the S_-S_ A massive and very strong ligament runs between the sacral tuberosity and the ilial tuberosity it is called the ___, which is considered a syndesmotic ligament especially in males __ is a drug that relaxes the pelvis during pregnancy |
1-3 interosseous sacroiliac joint relaxin |
|
|
___ artery is branch of the internal iliac artery and passes through the obturator foramen (t or f) the head of the femur die if the vessels that surround are destroyed fracture of the femur at the ___, is intertrochanter, extrascapular fracture repair with plate and screw. Fracture at the ___ =subcapital intrascapular fracture blood supply to femoral head comprised, must do a hip replacement |
obturator artery true surgical neck anatomical neck |
|
|
__ is the strongest ligament and "y" shaped. It resists hypertension and lateral rotation. it allows leaning back while standing __ artery passes through notch behind transverse acetabular ligament and continues with ligament teres to the femoral head. ___ ligament will limit abduction and lateral rotation of the hip. from the pubic bone |
iliofemoral ligament acetabular artery pubofemoral ligament
|
|
|
_____ ligament will encircle the neck of the femur helping hold the head of the femur in place. Some of its fibers wrap tightly around the head of the femur forming the Zona Orbicularis. it limits medial rotation of the hip ____ attaches the head of the femur to the acetabulum. it has a slightly limiting action on adduction of the hip joint. the synovial membrane will envelop this ligament (lies with the joint capsule) and covers the floor of the acetabular fossa |
ischiofemoral ligament
ligamentum teres (ligament of the head of the hemur) |
|
|
what is the landmark of the division of the obutrator nerve (anterior and posterior)?
Between the femur and the tibia is a ____ joint of the hinge variety. Between the patella and the femur is a ____ joint the knee joint is classified as a ___ joint
|
adductor brevis
synovial hinge (ginglymus) |
|
|
the __ is a strong fibrous structure that enlcose the knee completely except anteriorly. here the synovial joint membrane forms the suprapatellar bursa. the capsule is called the what? which consist of what ligaments? |
capsule medial and lateral retinacula of the knee anterior and posterior meniscofemoral, transverse genicular and the coronary ligament |
|
|
what are your extrascapular ligaments of the knee? |
ligamentum patela, fibular collateral ligament (hyperextension), tibial collateral ligament (hyperextension) , oblique popliteal (semimembransus ms), and arcuate (popliteus) |
|
|
___ is an intrascapular ligament, which is weaker and longer than the PCL. this ligament prevents posterior displacement of the femur on the tibia and hyperextension. relaxed when the knee is flexed and tight when the knee is extended |
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
|
|
|
____ is also a intrascapular ligament that is stronger and shorter than the ACL. tight when the knee is flexed but loose when the knee is extended. it prevents displacement of the femur on the tibia and hyperflexion |
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) |

