![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 types of tissue
|
Neural, muscular, epithelial, connective
|
|
|
Functions of epithelial tissue
|
protection, secretion, transportation of substances into cell or across cell, detection of senesations
|
|
|
Endothelium
|
Very thin single layer - simple squamous
Lines circulatory system |
|
|
Mesothelium
|
Thin layer lines the walls and covers the contents of closed body cavities (ex: pericardium)
|
|
|
Epithelium
|
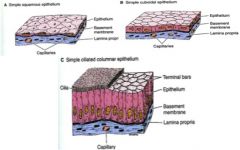
Thick often multiple layers attached to basement membrane
Identified by: cell layers - simple or stratified - shape - squamous, cuboidal, columnar - surface - micorvilli or cilia |
|
|
Pseudostratisfied columnar
|

|
|
|
Stratified
|

|
|
|
Simple
|

|
|
|
Transitional epithelium
|

Transition between stratified columnar and stratified squamous
Surface of the cells are dome shaped |
|
|
Fibroblast
|
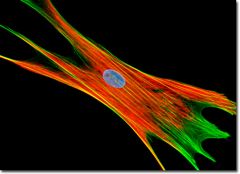
cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, (the structural framework) for animal tissue, and plays a critical role in wound healing
|
|
|
Fibrocyte
|
The less active state of a fibroblast, concerned with maintenance
|
|
|
Connective tissue
|
Classified based on the density of the matrix:
liquid (blood, lymph) solid (cartilage, bone) gel (connective tissue - tendon, ligament, meninges) |
|
|
Loose connective tissue
|

|
|
|
Mast Cell
|
Resident cell of tissues, rich in histamine and heparin. Play a role in allergy, anaphylaxis, and protective role, being involved in wound healing and defense against pathogens.
|
|
|
Collagen
|
A fibrous protein, used to connect and support other body tissues
|
|
|
Resident cells of connective tissue
|
fibroblasts, mast cells, wandering cells (eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and macrophages)
|
|
|
Dense regular connective tissue
|

Collagenous - big straight lines (stains lighter - ligaments and tendons – no stretch, very firm)
Elastic - thin thread like fibers (Stains pink, a little more wavy) |
|
|
Dense irregular connective tissue
|
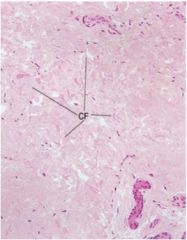
Densely packed collagen fibers interwoven into a meshwork - helps to resist stress from all directions (superficial, deep and subserous fascia)
|
|
|
Reticular fibers
|
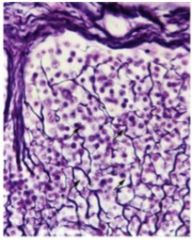
seen well under light microscope, makes a mesh work w/ a lot of cells within
|
|
|
Adventitia
|
layer of connective tissue that connects and binds some internal organs (esophagus, blood)
|
|
|
Serous membrane (serosa)
|
Membrane of connective tissue covered by a thin layer of epithelial cells which secrete serous fluid (pericardial sac surrounding heart)
|
|
|
Mucous membrane (mucosa)
|
Lines cavities connected to exterior, covered by epithelium cells that secrete mucus (respiratory and digestive tract)
|
|
|
Cutaneous membrane (skin)
|
multiple layers of epithelium and different layers of connective tissue
|
|
|
Synovial membranes
|
produce synovial fluid that protects the joints allowing for smooth movement
|

