![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy (Regional) |
The scientific study of the structures of the body and the relationship of these structures to one another. |
|
|
Radiopaque |
White image on x-ray, dense tissue or bone that absorbs more rays |
|
|
Radiolucent |
Black image on x-ray, a tissue or organ of lower density, allows more rays to pass through it |
|
|
MRI |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. SNo radiation, preferable to x-ray. Better to distinguish soft tissue (i.e. ligaments and muscles) |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
Divide body into left and right parts |
|
|
Median Plane |
Divides body into EQUAL left and right parts. Only one of these planes in the body, but also could be "median plane of hand/foot" |
|
|
Coronal Plane (Frontal Plane) |
Divides the body into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) parts. No median plane. |
|
|
Transverse Plane (Axial Plane) |
Divides the body into superior (cranial) and inferior (caudal) parts, cross sections. |
|
|
Rotation |
Movement in the Transverse Plane |
|
|
Longitudinal Section |
Can be cut in the median, sagittal or coronal planes. |
|
|
Laterality: Unilateral, Bilateral, Ipsilateral, and Contralateral |
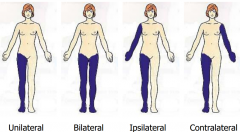
|
|
|
Flexion and Extension |
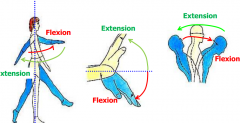
Always done in the SAGITTAL PLANE. Flexion=Anterior, Extension=Posterior (except knee) |
|
|
Abduction and Adduction |
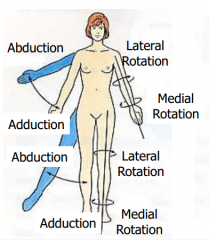
Always done in the CORONAL PLANE. |
|
|
Pronation and Supination |
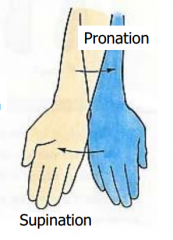
Only in the forearm |
|
|
Circumduction |

Combination of flexion, abduction, extension and adduction. |
|
|
Special movements of the Thumb |
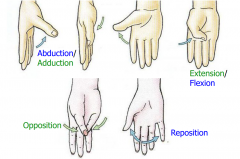
Thumb is rotated 90 degrees so movements are a bit different. |
|
|
Abduction and Adduction of the DIGITS |
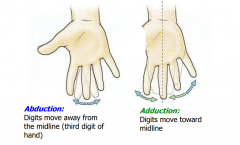
All in relation to middle finger |
|
|
Other weird movements |
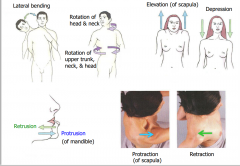
|
|
|
Axial Skeleton vs. Appendicular Skeleton. Cartilage |
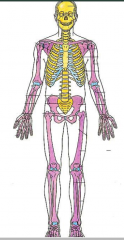
Axial=yellow (protects vital things) Appendicular- purple, includes scapula and clavicle. Costal cartilage-ribs Articular cart- joints
|
|
|
Functions of Bones |
-Protection of vital organs -Structural support of body -Acts as levers for muscles to produce movement -Reservoir for calcium and phosphorous -Contains marrow where blood cells form |
|
|
Types of Bones (3) |
1. Spongy bone (trabecular, cancellous) 2. Compact bone (cortical, dense) 3. Medullary (marrow) cavity
Red marrow- active in blood formation (kids) Yellow marrow- inert and fatty |
|
|
Long Bone |
Humerus, phalanges, clavicle etc |
|
|
Short Bone |
tarsals, carpals |
|
|
Flat Bones |
Some cranial vault bones, ribs, sternum |
|
|
Irregular Bone |
Vertebrea, sphenoid |
|
|
Sesamoid Bone |
Patella (develop within tendons) |
|
|
Pneumatic bones |
Mastoid part of temporal bone, paranasal sinus, filled with air. Mostly in the skull to lighten the weight. |
|
|
Accessory (supernumerary) Bones |
In Foot |
|
|
Elevations (bones markings) |
Crest Trochanter Line Tubercle Protuberance Tuberosity Epicondyle Malleolus Spine Process
|
|
|
Depressions (bone markings) |
Fossa Grooce Notch |
|
|
Articulations |
Condyle Facet
Where two bones meet, very smooth from rubbing by articulate cartilage. |
|
|
Holes |
Foramen (pl/ foramina) |
|
|
Ossification |
Process of bone formation |
|
|
Osteoblast |
Bone forming cells |
|
|
Osteocytes |
bones cells |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
bone resorption cells |
|
|
Chondrocytes |
cartilage cells |
|
|
Chondroblasts |
cartilage forming cells |
|
|
Intramembranous Ossification (Direct Ossification) |
Mesenchyme (embryological tissue)--->Bone
Rapid Process Flat bones of the skull only |
|
|
Endochondral Ossification (indirect ossification) |
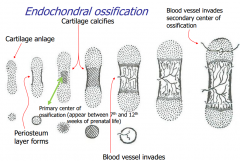
Mesenchyme (embryological tissue)---> Cartilage---->Bone
Slower Process Most bones |
|
|
Endochondral Ossification Ctn. |
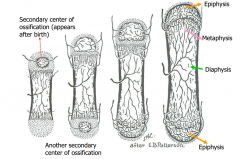
|
|
|
Bone Growth (general understanding) |
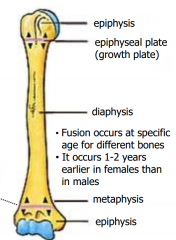
The DIAPHYSIS grows at the region of the growth plate and METAPHYSIS by proliferation of cartilage. Eventually bone replaces cartilage at growth plate; growth ceases and diaphysis fuses with epiphysis- SYNOSTOSIS. |
|
|
Timeline of endochondral ossificaiton |
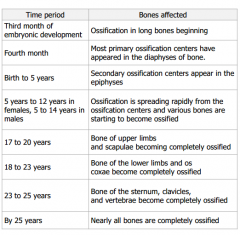
Also, generally, females fuse before males.
Short bones develop the same except no secondary center (except in foot) |
|
|
Q: Why endochondral ossification? Why not have cells at the ends of the bones to produce growth? |
Moving joint would damage growing tissue, and the bone must be capable of supporting loads. |
|
|
Vascular and Innervation of Bone |
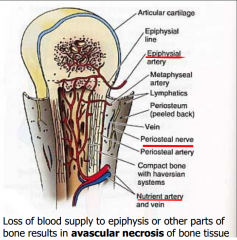
|
|
|
Upper Limb |
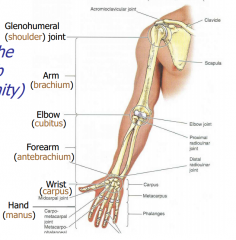
-freely mobile organ or manual activity -Not weight bearing; stability lost for mobility -Divided-shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand. |
|
|
Scapula (anterior) |
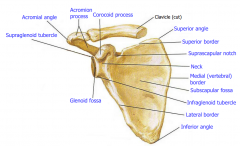
|
|
|
Scapula (posterior) |
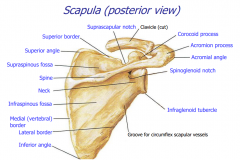
|
|
|
Scapula w/origins and insertions |
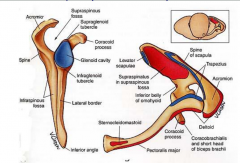
Origins- red Insertions-blue |
|
|
Clavicle (fractures) |
Commonly fractured: indirectly- force transmitted thru upper limb or directly-falling onto shoulder. When fractured, sternocleidomastoid muscle pulls medial part superiorly and lateral part (and shoulder) droops |
|
|
Clavicle Picture |
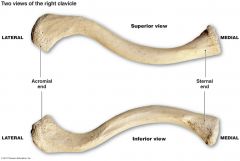
|
|
|
Humerus (anterior) |
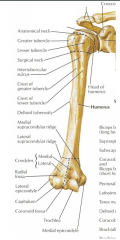
|
|
|
Humerus (posterior) |
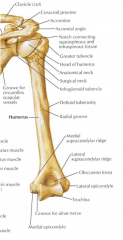
|
|
|
Ulna (medial) and Radius (lateral) Proximal End |
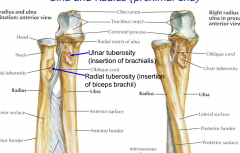
Ulna is more stationary |
|
|
Ulna and Radius Distal End |
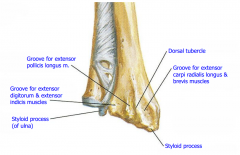
Pronated |
|
|
Wrist and Hand |
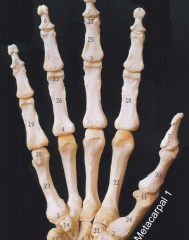
Phalanges: Proximal, Middle, Distal Metacarpals: 1=thumb, pollex, 5=pinky (digiti minimi) Carpals: 8 (next card)
|
|
|
Carpal Bones |
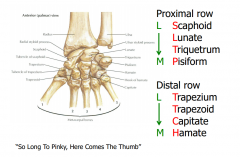
So Long To Pinky, Here Comes the Thumb, makes a C. Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Hamate, Capitate, Trapezoid, and Trapezium. |

