![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
forms entire roof of cranium in ox and pig
|
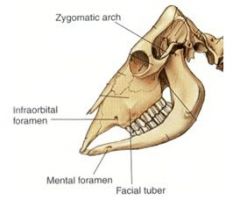
frontal bone
|
|
|
T/F - the parotid duct of the goat and sheep are variable
Where found? |
True. The parotid duct may course along the ventral border of the mandible or across the masseter m.
|
|
|
T/F Bony orbit is complete in horse but not ruminants
|
False complete in horse and ruminant, NOT in carnivores
|
|
|
What is the largest compartment in the bovine head and has a cornual diverticulum into the cornual process?
|
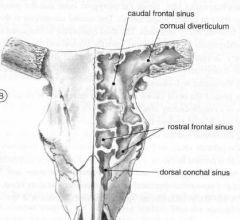
Caudal frontal sinus is largest compartment
|
|
|
How many compartments are in the rostral portion of frontal sinus?
|
2 or 3
|
|
|
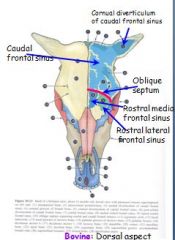
What separates the caudal and rostral frontral sinuses?
|
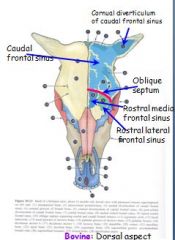
Oblique septum
|
|
|
What compartments are in the frontal sinus of the small ruminant?
Which is larger? |
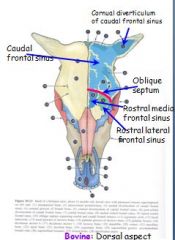
Smaller medial
Larger lateral No caudal compartment |
|
|
What sinus in the bovine is a single invagination, has a narrow, slit-like opening called the nasomaxillary aperture, and it extends into the lacrimal bulla?
|

MAXILLARY SINUS is single invagin.; with narrow opening
|
|
|
In the pig, is the maxillary or frontal sinus larger?
|
Frontal sinus is larger
|
|
|
What part of the nose in an ox is used in nose-printing?
|

Nasolabial plate
|
|
|
What is the median fissure/groove called in the upper lip of the sheep/goat?
|

Philtrum
|
|
|
What bone in the upper lip of the pig is powerful and sensitive (used for rooting)?
|

Os rostri (rostral bone)
|
|
|
What space in the upper lip allows the canine tooth to project out in the pig?
|

Ventrolateral notch
permanent notch in the upper lip of the pig, which the canine tooth projects out of |
|
|
What type of epithelium is in the oral mucosa of the ruminant and pig?
|
Thick, stratified squamous epithelium (heavy stratum corneum)
|
|
|
Which animals have well developed backwards facing papillae, particularly in the region of the commissures of the mouth?
|
Ruminants - have backward facing papillae
|
|
|
How many upper incisor or canine teeth are there in the ruminant?
|
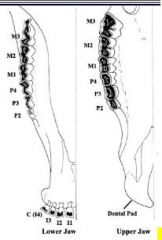
None, replaced by the dental pad
|
|
|
What is the dental formula of the ruminant?
|
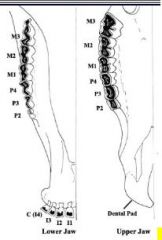
I 0/3, C 0/1, P 3/3, M 3/3 (X2) = 32
|
|
|
Which teeth are brachydont in the ruminant?
|
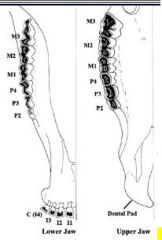
Incisor and canine
|
|
|
What type of tooth is the corner incisor in the ruminant?
|
Canine tooth
|
|
|
Which cheek tooth is considered to be lost?
|
P1
|
|
|
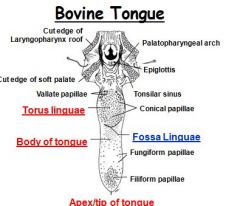
What deep groove in the tongue separates the rostral half from the torus lingue?
|
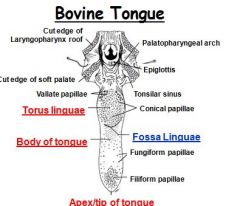
Fossa lingue
|
|
|
Do small ruminants have a facial a.? what else they got?
|
No. The job is done by transverse facial a.
|
|
|
What type of teeth are all pig teeth?
|
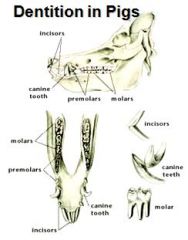
Brachydont
|
|
|
Where does the sublingual a. branch off of in the caprine and sheep?
|
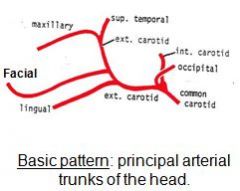
Sublingual a. is branch from the lingual a., as in the bovine.
|
|
|
What is the dental formula for a pig?
|
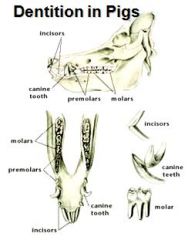
I 3/3, C 1/1, P 4/4, M 3/3 (X2) = 44
|
|
|
How can damage to the female pigs mammary gland be prevented after she gives birth?
|
Remove needle teeth of new-borns
|
|
|
What type of papillae are located in the rostral portion of the ruminant tongue and form the lingual rasp?
|
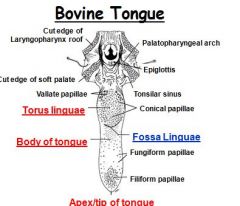
Filiform papillae
|
|
|
What type of papillae are present in the new-born piglet tongue up to 18 days of age?
|
Marginal papillae (lacelike frills)
|
|
|
How much saliva can cattle produce a day?
|
30 - 50 liters a day
|
|
|
What salivary glands supply saliva to the mouth of the ruminant?
|
Buccal glands
Parotid glands Sublingual glands |
|
|
What is unique to the basihyoid bone in ruminants?
|
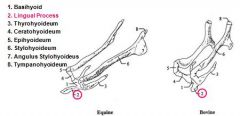
Basihyoid bone has a knob-shaped lingual process
|
|
|
What two things may cause problems during intubation in pigs?
|

Pharyngeal diverticulum
Lateral ventricles |
|
|
What lymph node is always single and large in the ruminant head? (check this)
|
parotid ln.
lateral retropharygeal lymph node would be also, but not sure that considered inside head |
|
|
What lymph node is usually two, but may be single in ruminants; several in pig?
|
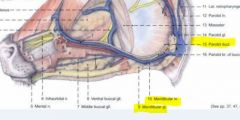
Mandibular lymph node
|
|
|
What lymph node can cause respiratory embarrassment (dypsnea), and problematic deglutition (dysphagia) when enlarged in ruminants?
|
Medial retropharyngeal lymph node
|
|
|
What lymph node is considered the master lymph node of the head in Ruminants? Pig?
|
Ruminants - Lateral retropharyngeal lymph node
Pig - Medial retropharyngeal lymph node |
|
|
The efferents of the lateral retropharyngeal lymph node form what?
|
Tracheal duct
|
|
|
Does the pig have a tapetum lucidum?
|
No
|
|
|
What are the five possible nerves that can innervate the horn of the cow?
Which nerve is deepest and not accessible - cannot be blocked? |
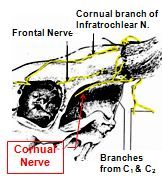
1. Cornual nerve - Terminal division of the zygomaticotemporal n. (ophthalmic V or maxillary V --- controversy); main nerve of horn
2. Cornual branch of infraTrochlear nerve 3. Frontal nerve - a branch of the ophthalmic (V) n. 4. Cutaneous branches of C1 and C2 5. Nerve of the frontal sinus - deep (about 5% of cattle) |
|
|
What is a cornual nerve block in the ox? Where is it performed?
|
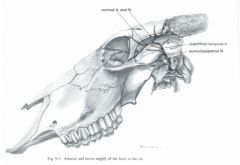
The cornual nerve block is used in dehorning to block innervation to the bovine horn.
Cornual nerve is blocked midway between the lateral canthus of the eye and the base of the horn just ventral to the temporal line |
|
|
What three nerves innervate the horn of the goat?
|
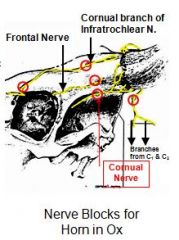
Cornual nerve
Cornual branch of infraorbital nerve Great auricular nerve – From C2 spinal nerve. |
|
|
What nerve supplies sensory innervation to the bovine horn?
What is this nerve a branch of? |
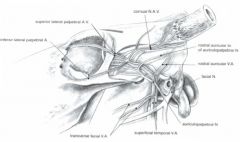
The cornual n
Branch of the zygomaticotemporal n. of ophthalmic division of trigeminal n. |
|
|
What is the innervation of the caprine horn? What is the blocking procedure necessary to dehorn goats?
|
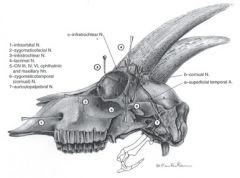
Cornual nerve
Branch of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve Blocked midway between the lateral canthus of the eye and base of the horn Infratrochlear nerve Branch of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve Blocked midway between the medial canthus of the eye and base of the horn |
|
|
In the ruminant, what is sublingual a. a branch off of?
|
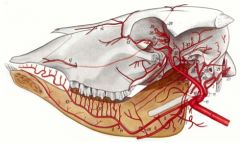
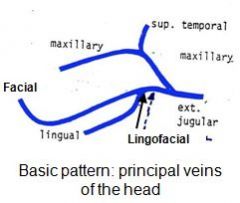
Sublingual a. (9) comes off of Lingual a. (8), not Facial a (6), as it is in the dog and horse.
|
|
|
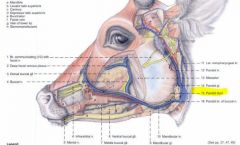
In the OX, what structures course together along the ventral border of the mandible?
|
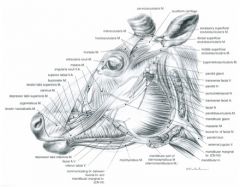
In the ox, the facial artery, facial vein, parotid duct and ventral buccal branch of facial nerve course together along the ventral border of the mandible
NO facial artery in small ruminant! |
|
|
In the small ruminant, what structures course along the ventral border of the mandible?
|
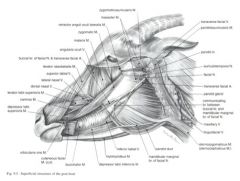
In the small ruminant, the facial vein courses along the ventral border of the mandible
The parotid duct and ventral buccal branch are variable in position |
|
|
In the horse, pig and ruminants, the upper and lower arcades do not align, otherwise known as?
|
Anisognathic
|
|
|
Which teeth of the pig are brachydont?
|
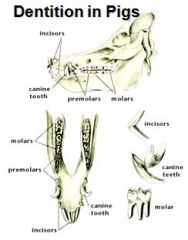
Incisor and canine.
(premolars and molars are hypsodont) |
|
|
What lymph nodes are responsible for superficial drainage of the head?
|
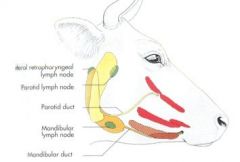
Parotid
Mandibular |
|
|
What two features might you catch during tracheal intubation of a pig?
|

Pharyngeal diverticulum
Lateral ventricles |
|
|
To what does the parotid lymph node drain into?
|
Retropharyngeal lymphocenter
|
|
|
What does the mandibular lymph node drain into?
|
Retropharyngeal lymphocenter
(+/- deep cervical lymph node) |
|
|
Do ruminants have lateral laryngeal ventricles?
|
No
|
|
|
An important distnguishing
feature between head of the goat and the sheep is: BE SPECIFIC WHICH ANIMALS HAVE WHAT. |
an infraorbital cutaneous sinus in SHEEP (as well as inguinal sinus and interdigital sinus)
|
|
|
Snout of the pig is supported by what bone?
|

os rostri
|
|
|
Dental formula of the pig:
|
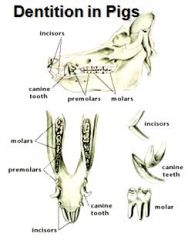
full complement 2 (I 3/3 C 1/1 P 4/4 M 3/3) = 44
|
|
|
Which porcine ear vein is used for small amounts of blood?
|
Lateral auricular vein
|
|
|
What is the largest nasal meatus in the bovine?
|
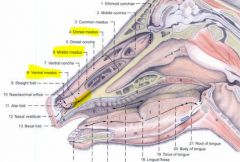
The ventral meatus
|
|
|
Which bovine nasal meatus opens into the nasomaxillary opening (maxillary sinus)?
|
The middle nasal meatus
|
|
|
What divides the middle nasal meatus in the ruminant? What does it divide into?
|
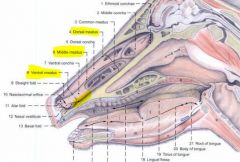
Divided into dorsal and ventral passages caudally by the middle nasal concha
|
|
|
What are the interesting feature of the ruminant cheek?
|
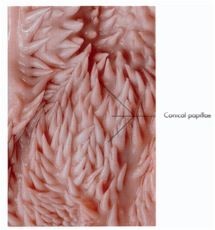
Conical buccal papillae. They are mechanical, not sensory.
|
|
|
T/F ruminant canines and incisors are movable.
|
True - this is thought to be a way to protect the dental pad from getting hit in the same spot every time.
|
|
|
What subgroups of sublingual salivary gland do the bovine have?
Where do they drain? |
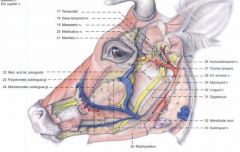
Monostomatic portion is located ventral to the rostral half of the polystomatic portion
Drains at sublingual caruncle Polystomatic portion drains directly into floor of mouth on the sublingual fold |
|
|
what salivary glands drain at the sublingual caruncle in the bovine?
|
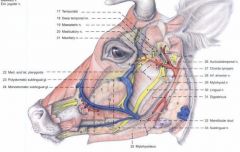
Mandibular and monostomatic sublingual salivary glands.
|

