![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
urachus
|
The urachus is a tube that connects bladder to umbilicus during fetal development. After birth, urachus normally closes and becomes a ligament.
|
|
|
______is a condition in which crystals in the urine combine to form stones, also called calculi or ______.
|
UROLITHIASIS is condition in which crystals in urine combine to form stones, also called calculi or UROLITHS.
(from Greek oûron, "urine" and lithos, "stone") |
|
|
calculi or uroliths can formed by many substances, but MOST COMMON in cats and dogs are ____?
|
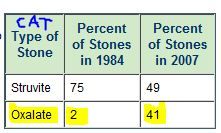
The two most common stone types in cats are #1 CALCIUM OXALATE and #2 STRUVITE
struvite = (ammonium magnesium phosphate) is a phosphate mineral Unfortunately, % of stones composed of calcium oxalate has increased. |
|
|
What causes struvite calculi to form?
|
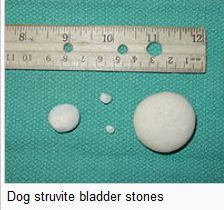
Struvite stones form readily in urine of animals infected with NH3-producing organisms; potentiated by alkaline urine, high magnesium excretion (i.e. high Mg+/plant-based diets); and potentiated by specific urinary protein, in domestic cats.
|
|
|
How to reduce occurance of struvite stones?
|
* Most commercial feline diets are now formulated to reduce likelihood of struvite formation by limiting amount of dietary magnesium and by promoting more acidic urine.
* Provide clean, fresh water at all times; keep litter boxes clean. |
|
|
What causes CALCIUM OXALATE stones to form?
|
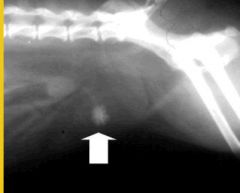
Hypercalciuria (elevated calcium in urine);
- 35% of cats with calcium oxalate bladder stones have elevated BLOOD calcium Role-if any-that diet plays in formation of calcium oxalate stones is actively being studied. One theory is that acidifying of cat food (and urine) leads to more Ca+ into urine, both factors in dev. of calcium oxalate stone. |
|
|
How are calc. oxalate obstructions treated?
|
Unlike struvite stones, calcium oxalate stones cannot be dissolved with special diets, and more aggressive treatment is needed.
Flushed back into bladder (from penile urethra); and can remove via cystotomy. Recurrence is a major problem with calcium oxalate uroliths. |
|
|
How are calc. oxalate obstructions prevented?
|
* maintain urine pH at 6.5-7.5 and urine specific gravity <1.020
* also “ideal” diet is considered to be low oxalate C2O4- , low protein, and low sodium ~ but again...role-if any-that diet plays in formation of oxalate stones is still being studied. |
|
|
True or False: Male and neutered male cats are at greater risk for obstruction than females, because their urethra is longer and narrower.
|
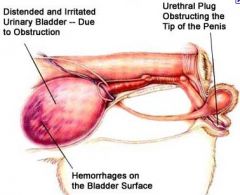
True: more serious in tomcats b/c of narrow urethra
|
|
|
Cats breeds predisposed to oxalate stones? Dog breeds?
|

Cats: Burmese and Himalayan cats appear genetically predisposed to the development of calcium oxalate bladder stones.
Most calcium oxalate stones develop in cats between ages 5 and 14 years. ------------------- Dogs: while may develop in any breed, Mini Schnauzers, Yorkshire Terriers, Bichons (pic), **** Tzus, and Mini Poodles may be predisposed; most affected are 2-10 yr old. |
|
|
Where are blockage usually in canine?
|
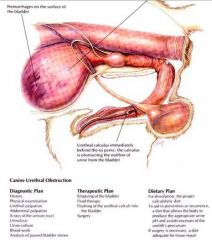
behind os penis
|

