![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mesovarium
|
peritoneal fold, holding the ovary to the broad ligament
|
|
|
Suspensory ligament of the
ovary |
Attaches superior pole of ovary to the pelvic wall.
carries the ovarian vessels and nerves |
|
|
Ovarian Ligament
|
Attaches inferior pole of ovary to the uterus
|
|
|
medulla of ovary
|
located in the central
portion of the ovary and contains loose connective tissue, a mass of relatively large contorted blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves |
|
|
cortex of ovary
|
found in the peripheral
portion of the ovary surrounding the medulla. The cortex contains the ovarian follicles embedded in a richly cellular connective tissue |
|
|
Surface of the ovary
|
covered by a single layer of
cuboidal and, in some parts, almost squamous cells. This cellular layer, known as the germinal epithelium |
|
|
Tunica albuginea
|
A dense connective tissue layer that lies between the germinal epithelium and the underlying cortex.
|
|
|
Primordial follicle
|
earliest stage of follicular development. primordial follicles are found in the stroma of the cortex just beneath the tunica albuginea.
|
|
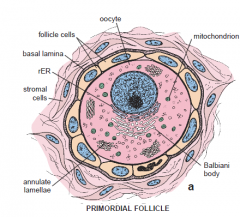
|
Primordial follicle
|
|
|
zona pellucida
|
proteins that are assembled into an
extracellular coat |
|
|
membrana
granulosa |
Through rapid mitotic proliferation, the single layer of follicle
cells gives rise to a stratified epithelium. The follicle cells are now identified as granulosa cells |
|
|
theca folliculi
|
stromal cells immediately
surrounding the follicle form a sheath of connective tissue cells, known as the theca folliculi, The fully differentiated cells of the theca interna possess ultrastructural features characteristic of steroid-producing cells. Cells of the theca interna possess a large number of luteinizing hormone (LH) receptors. In response to LH stimulation, they synthesize and secrete the androgens that are the precursors of estrogen |
|
|
oolemma
|
oocyte’s plasma membrane
|
|
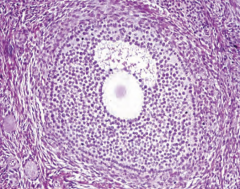
|
Graafian follicle
|
|
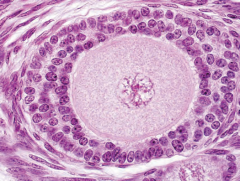
|
Secondary follicle
|
|
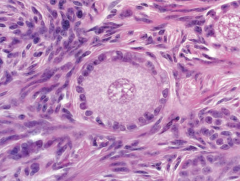
|
Primary follicle
|

