![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
State 5 functions of the eyelids |
Protection for the eye by reflex lid closure Reduces light and other radiations from entering the eye Provides some constituents of the tear film Moves tears across the cornea towards the Lacrimal drainage system Helps maintain and support the eyes position in the orbit |
|
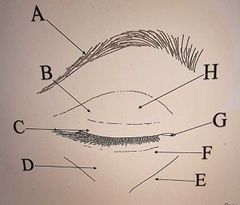
Label the Eyelids |
A: Eyebrow (Supercilia) B: Orbital Region C: Tarsal Region D: Malar Fold E: Nasojugal Fold F: Lower Lid G: Inner Canthus H: Upper Lid |
|
|
What are the 4 layers of the eyelid? |
Skin Striated Muscle Fibrous Layer Conjunctiva |
|
|
What are the 2 layers of the skin? |
Epidermis Dermis |
|
|
How many layers of cells are in the epidermis? |
6-7 |
|
|
Which glands are sebaceous in the eyelids? |
Glands of Zeis |
|
|
Which glands are sweat glands in the eyelids? |
Glands of Moll |
|
|
What is the function of the Orbicularis Oculi? The palpebral part and the orbital part |
Palpebral: Used in reflex and spontaneous blinking It assists in pumping away tears Used in voluntary winking Orbital: Used for forcible lid closure |
|
|
What is the function of the Muscle of Riolan? |
Tensions the eyelid against the globe |
|
|
Where does the orbocularis oculi originate? |
Nasal process of Frontal Bone |
|
|
What is the nerve supply of the Orbicularis oculi? |
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial |
|
|
What is the function of the Levator Palpebrae Superioris? |
Maintains position of upper lid Eye and lid move together (when you look up, eyelids move up too) |
|
|
What is the nerve supply of the levator palpebrae superioris? |
Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor |
|
|
What is the function of the tarsal muscle? |
Moves the lower lid |
|
|
What is the nerve supply of the tarsal muscle? |
Orbital sympathetic supply |
|
|
What does the fibrous layer of the eyelids consist of? |
Tarsal plates Orbital septum |
|
|
How thick are the tarsal plates? |
1mm |
|
|
What is applied directly to the plate surface at the posterior lid margin? |
Conjunctival epithelium |
|
|
How many tarsal/meibomian glands are there in the upper and lower lid? |
Upper: 25 glands Lower: 20 glands |
|
|
What do meibomian glands secrete? |
Oily substance (fatty sebum) |
|
|
What is the function of tarsal glands? |
Lubricates the eyelid Prevents the lids from sticking Limits the overflow of tears reduces loss through evaporation Keeps lids closed air tight |
|
|
Where does the orbital septum extend from and continue to? |
Periosteum at the orbital margin and continues to the edge of the tarsal plate |
|
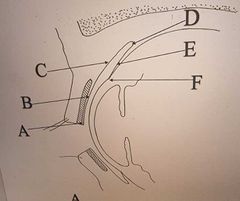
Label the regions of Conjunctiva |
A: Marginal B: Tarsal C: Palpebral D: Fornix E: Bulbar F: Limbal |
|
|
State 5 functions of the conjunctiva |
Prevent foreign bodies getting behind the eye Provides oxygen to the cornea when the lids are closed Glands produce part of the constituents of the tears film Goblet Cells produce mucin. Glands of Krause and Wolfring produce serous fluid. Meibomian glands produce meibum making up the lipid layer of the tears Provides smooth lubricated movement of lids over cornea |
|
|
Marginal Conjunctiva |
Non keratinised 5-6 layers Commences at orifices of the tarsal gland Basal cells are columnar, superficial cells are squamous Very little Stroma Squared posterior edges to move tears across the eye |
|
|
Tarsal Conjunctiva |
Non keratinised 2-3 layers Surface cells are more columnar Very few Goblet Cells Little Stroma Many blood vessels to supply cornea when lids closed |
|
|
Palpebral Conjunctiva |
Goblet Cells increase Stroma thickens Accessory glands of Krause and Wolfring found here along with rich blood supply |
|
|
How many Glands of Krause are there approx? |
20-40 in the upper fornix 6-8 in the lower fornix |
|
|
How many Glands of Wolfring are there approx? |
5 in the upper lid by the tarsal plate, none in the lower |
|
|
Fornix Region |
Max concentration of Goblet Cells Superiorly, fibrous layer continuous with the sheath of the levator muscle Inferiorly, fibrous layer continuous with the inferior rectus muscle |
|
|
Bulbar Conjunctiva |
Double layer of epithelial cells Goblet Cells decrease Stroma thins and blends with Tenons Capsule Firmly attaches to the limbus |
|
|
Limbal Conjunctiva |
Epithelial cells up to 10-15 layers Superficial cells are flatter No Goblet Cells Epithelium blends into corneal epithelium Epithelium has fold under surface Thicker regions called rete pegs Thinner regions between pegs called stromal papillae These run radially to cornea and form palisades of vogt |
|
|
State the function of each conjunctiva |
Marginal: Sweep tears across the globe Tarsal: Oxygen to the cornea Palpebral: Hosts the accessory glands Fornix: Stops foreign bodies coming round the back and also produces mucin Bulbar: Close the conjunctival sac Limbal: Anchors conjunctiva to the eye |
|
|
Plica Semilunaris |
Conjunctival fold at Inner canthus Equates to 3rd eyelid found in some animals 2mm sac during Adduction, prevents stretching as eye moves Epithelium has 10-12 layers, rich in Goblet Cells Stroma is fatty with traces of smooth muscle |
|
|
Caruncle |
Area of modified skin Covered in non-keratinised stratified epithelium with fine hairs Contains sweat glands and Goblet Cells Blood Supply is the medial branch of the dorsal nasal artery |
|
|
Blood Supply of Conjunctiva |
Derived from ophthalmic artery Upper lid: Marginal and peripheral palpebral arcades Lower lid: Marginal arcades Arteries on the posterior of the tarsal plate supply the palpebral conjunctiva The subconjunctival vessels derived from the Anterior ciliary artery are deep and run radially in the episcleral tissue to the margin Branching conjunctival vessels lie superficially and are freely movable Conjunctiva has rich system of lymphatic vessels |
|
|
Blood drainage from conjunctiva |
Superiorly, veins drain into supra orbital vein Inferiority, drain into Inferior palpebral vein then into the facial vein |
|
|
Which cranial nerve innervates the conjunctiva? |
Cranial Nerve V Trigeminal |

