![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Differentiate btwn possible types of pnuemothorax
open closed tension nontension |
open- plueral hole, defect in thoracic wall
closed- lung hole tension- hole & flap created, allowing air in but not out nontension- open hole, air may pass in & out |
|
|
In the case of a tension pnuemothorax, what is the actual cause of death?
|
Cutting off oxygen supply to heart = death
As air is sucked in, thoracic cavity expands greater and greater, compressing vena cavas. Eventually vena cava blood flow is completely stopped, thus no venous return to the heart, no oxygenated blood = death |
|
|
What are the anatomical borders of the lungs and pluera?
|
Superior:
-pleura & lung project above the 1st rib Anterior: -pleura approaches midline on R & not as far on L -lung to costomediastinal Inferior & Posterior: -lungs are higher anterior than posterior -at mid-clavicular line, lung to 6th rib, pleura to 8 -at mid-axillary line, lung to 8th rib, pleura to 10 -at scapular line, lung to 10th rib, pleura to 12 -lung to costadiaphragmatic recess |
|
|
In plain film radiography, radiation is ____________ by matter, leaving an image on the film.
|
attenuated
*attenuation affected by atomic #/density & thickness, whitest = thickest/densest |
|
|
T/F
The structure that you want to see most clearly should be closest to flm |
TRUE
|
|
|
What does AP & PA refer to?
|
AP: anterior to posterior , PA: posterior to anterior
-refers to x ray beam's path through patient |
|
|
What is the standard view for thorax imaging?
|
PA & left lateral
-left lateral for full inspiration |
|
|
What structures should be seen in PA view?
|
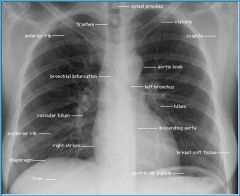
mediastinum
trachea cardiac silhouette lung hili costophrenic angles diaphram lung parenchyma bone |
|
|
What structures should be seen in Left lateral view?
|
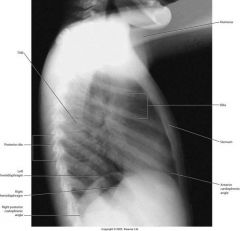
pulmonary hilum
pulmonary vessels costophrenic angles RETROSTERNAL SPACE RETROCARDIAC SPACE hemidiaphrams tracheal air shadow thoracic spine left ventricular border LEFT ATRIAL BORDER right ventricular border |
|
|
What may clubbing of nails (rounded fingertips) be associated with?
|
cardiac disease
pulmonary disease malignancy |
|
|
When evaluation a film what MUST you have?
|
a search pattern!
makes eval Complete & Consistent! |
|
|
Satisfaction of search, are you done looking at film when you find an irregularity?
|
NO, you are responsible for EVERYTHING visible on film, need to check everything before you are done
|
|
|
What is a silhouette sign?
|
when two objects of the same density are in contact, you cannot determine their borders
|
|
|
Normally the air-filled bronchi are not visible on the x-ray because they are in direct contact w/ the air-filled lung tissue. when would they become visible?
|
in the case of lung CONSOLIDATION
|
|
|
Recognize the benefits of the following techniques:
CT MRI Ventilation/Perfusion Studies |
CT-
eliminates overlap & increases contrast MRI- shows hilar vascular structures Ventilation/Perfusion Studies- shows lung function, pulmonary embolism can be seen |

