![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Components of ECM in Bone |
40% dry weight Organic materials mainly collagen type I fibres Inorganic salts calcium and phosphate |
|
|
periosteum content and location |
External layer of bone forming cells (location) Consists of collagen bundles (periosteal fibres called peforating fibres or sharpey's fibres) Fibroblasts Innermost layer contains mesnchymal osteoproginator cells |
|
|
Contents of endosteum |
Osteoprogenitor cells and osteoblasts |
|
|
Bone Composition of bulbous ends called epiphyses |
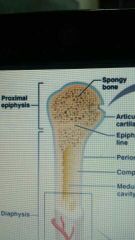
Composed of spongy bone covered by a thin layer of compact bone |
|
|
Bone composition of diaphysis |
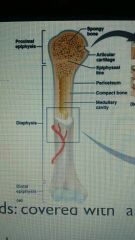
Composed of compact bone with a thin component of spongy bone on its inner surface around bone marrow |
|
|
Bone composition of short bone |
A core of spongy bone surrounded completely by c9mpact bone |
|
|
Bone composition bone that forms skull cape |
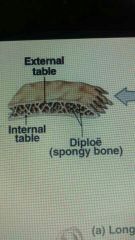
Two layers of compact bone called plates (tables) separated by a thicker layer of spongy bone |
|
|
The two types of bone gross examination shows |
Compact bone Spongy/trabecular/ cancelous bone |
|
|
Microscopic classification of Bone |
Woven bone (primary bone) Lamellar bone (secondary bone) |
|
|
Woven bone structure characterized by? |
Random disposition of fine collagen fibres and lower m8neral content |
|
|
Location or cases were woven bone can be found |
Found in embryonic development and fracture repair Near sutures of the calvaria (skull cap) in tooth sockets and some tendon insertions |
|
|
Why woven bone is found in a few places |
it is Usually Temporary and is replaced by lamellar Bone |
|
|
Organization of collagen fibres in lamellar bone |
Parrallel to each other or concentrially around a vascular canal |
|
|
Description of haversian system |
Complex of concentric lamellar surrounding a small canal CONTAINING blood vessels, nerves and loos CT |
|
|
Another name for harversian system |
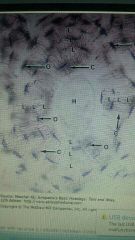
OSTEON |
|
|
Outer boundary of an osteon, more rich ollagen layer |
Cement line |
|
|
Volkmann canals function |
Enable communication central canals to communicate with the marrow çavity, periosteum and other central canals |

