![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the four major tissue types
|
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nerve Tissue |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
|
-Found throughout the body
-attached to underlying connective tissue by basement membrane -usually avascular -cells reproduce rapidly (rapid healing) -Cells tightly packed together -held together by tight junctions and desmosomes -apical and basal surfaces |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue Functions
|
Absorption
Filtration Secretion Protection |
|
|
Simple Sqamous looks like?
|
Single layer, flat, very thin, with disc shaped central nuclei
|
|
|
The function of simple squamous cells is
|
-diffusion and filtration
-secretes lubricating substances in serosae |
|
|
Simple Sqamous cells are found in
|
Inner lining of:
-heart -blood vessels -avioli in lungs -Kidney glomeruli -lymphatic vessels -Ventral body cavity (serosae) |
|
|
Simple Cuboidal looks like
|
Single layer, cube-shaped, with large spherical central nuclei
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal function is
|
secretion and absorption
|
|
|
simple cuboidal cells are found in
|
lining of kidney tubules, ducts of glands, surface of ovaries
|
|
|
Simple columnar looks like
|
single layer, elongated cells with round to oval nuclei. Some cells bear cilia: layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands (goblet cells)
|
|
|
The function of simple columnar epithelium is
|
absorption: secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances
|
|
|
Simple columnar is found
|
-(nonciliated) in the lining of digestive system, starting in the stomach to the anus
-(ciliated) line broncchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus |
|
|
Goblet cells are located in
|
simple columnar
pseudostratified columnar |
|
|
The function of goblet cells is to
|
secrete mucous
|
|
|
the purpose of microvilli is to
|
increase surface area
|
|
|
Stratified squamous looks like
|
multi-layered, squamous cells. Thicker
|
|
|
The function of Stratified squamous is to
|
protect underlying areas subjected to abrasion
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous is found in
|
-In areas of high friction,
- inside of mouth -esophagus -vagina keratinized forms epidermis of the skin |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar looks like
|
appears stratified, but is only a single layer with nuclei at various levels
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar is usually
|
ciliated
|
|
|
what is the purpose of cilia
|
to sweep materials along a surface
|
|
|
what is the function of pseudostratified columnar
|
secreting and cilia-aided movement
|
|
|
pseudostratified columnar is located in
|
the lining of air passages like the trachea and tubes of the reproductive system
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium looks
|
Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells dome shaped or squamouslike, depending on degree of organ stretch.
|
|
|
What is the function of Transitional Epithelium
|
-to stretch and form barriers to block diffusion
- Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine. Can take alot of pressure |
|
|
Transitional Epithelium is found in
|
-the lining of urinary bladder
-ureters, small part of the uterus |
|
|
Connective Tissue General Characteristics
Connective Tissues have: |
-Mesenchyme as their common tissue of origin
-Varying degrees of vascularity (can be avascular also) -Presence of cells and nonliving extracellular ground substances and fibers -Wide distribution in the body |
|
|
What is connective tissue made of?
|
ground substance and fibers
|
|
|
what are the three most common cell types in connective tissue
|
Mast cells, macrophages, fibroblasts
|
|
|
what is the main function of mast cells
|
to prevent blood clots
|
|
|
macrophages are
|
phagocytic
|
|
|
Fibroblasts are ___ and _____
|
-the most abundant
-produce fibers |
|
|
what are the main types of fibers
|
1. Collagen (white fibers) fibers: Most abudant
2. Elastic fibers: Thin 3. Reticular fibers: Form network |
|
|
Functions of connective tissue
|
1. Connects different body parts or tissues together:
• Ligaments (connect bone to bone) • Tendons (connect muscle to bone) • Cartilages 2. Protects the internal body parts: Bones, Pericardium (ex. Skull protects the brain) 3. Supports: Bone 4. Flexibilty: Elastic cartilage 5. Transports: Blood (Special type of connective tissue) |
|
|
Connective Tissue Cell Types
|
1. Fibroblasts (most common)
• fat cells • mast cells • macrophages (giant cells that engulf/phagocytic) 2. Chondroblasts (young cells) and chondrocytes (mature cells) in cartilage 3. Osteoblasts (young blood cells)and osteocytes (mature blood cells) in bone 4. Hematopoietic (blood production) stem cells in bone marrow (form blood cells) |
|
|
Ligaments connect
|
bone to bone
|
|
|
connects different body parts or tissues together:
|
bones, ligaments, cartilage
|
|
|
tendons connect
|
muscle to bone
|
|
|
Elastic fibers are
|
thin
|
|
|
what is known as white fibers
|
collagenous fibers
|
|
|
Reticular fibers form
|
network
|
|
|
elastic cartilage
|
flexibility
|
|
|
3 types of loose connective
|
Areolar, Adipose and Reticular
|
|
|
4 Categories of connective tissue are
|
1. Connective Tissue Proper : Loose and Dense
2. Cartilage 3. Bone Tissue 4. Blood |
|
|
What is the function of Areolar Tissue
|
Wraps and cushions organs; its macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid.
|
|
|
what is another name for Adipose
|
Fat
|
|
|
Adipose is located
|
Under skin in the hypodermis; around kidneys and eyeballs; within abdomen; in breasts
|
|
|
The function of adipose is to
|
: Provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
|
|
|
Adipose cells are called
|
Adipocytes
|
|
|
Dense (regular) connective tissue is found in
|
Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
|
|
|
Dense irregular connective tissue is found in
|
Fibrous capsules of organs and of joints; dermis of the skin submucosa of digestive tract.
|
|
|
fibrous tissue is made of
|
thick collagenous fibers and fine network of elastic fibers
|
|
|
fibrous tissue has few cells and poor blood supply resulting in
|
slow healing
|
|
|
Fibrous tissue includes
|
tendons and ligaments
|
|
|
Tendons connect
|
muscles to bones
|
|
|
Ligaments connect
|
Bones to bones
|
|
|
Hyaline cartilage is
|
More ground substances, fine collagen fiber network (almost invisible under the microscope), Chondrocytes within lacuna
|
|
|
hyaline cartilage is
|
Amorphous but firm matrix; collagen fibers form an imperceptible network; chondroblasts produce the matrix and when mature (chondrocytes) lie in lacunae.
|
|
|
hyaline cartilage is located
|
-Forms most of the embryonic skeleton;
- covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; -forms costal cartilages of the ribs; -cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx. |
|
|
What are chondrocytes
|
catrilage cells
|
|
|
Elastic cartilage is more
|
flexible and elastic
|
|
|
elastic cartilage is found
|
in the external ear and larynx
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage is
|
tough
|
|
|
Fibrocatrilage is made of
|
large numerous collagenous fibers
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage is located
|
intervertebral disks, menisci
|
|
|
Bone is known as
|
osseus tissue
|
|
|
Bone is rigid due to
|
mineral salts
|
|
|
Bone has layers
|
lamellae, haversian canals, osteocytes
|
|
|
Blood circulates
|
throughout the body
|
|
|
Reticuloendothelial is found
|
scattered throughout the body
|
|
|
The three types of muscle tissue are
|
Skeletal
Smooth Cardiac |
|
|
Skeletal muscles are
|
voluntary and striated
|
|
|
Smooth muscles are
|
in hollow organs, stomach
involuntary |
|
|
Cardiac muscles are in
|
the walls of the heart
|
|
|
Nerve tissue is found where
|
in the brain, spinal cord, nerves
|
|
|
Neurons do what
|
transmit signals
|
|
|
neuroglia does what
|
protection and support
|
|
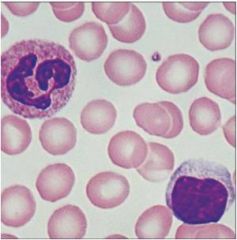
|
Blood
|
|
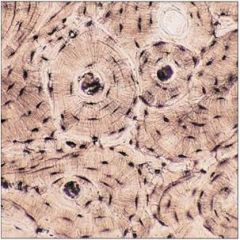
|
bone: osseous tissue
|
|
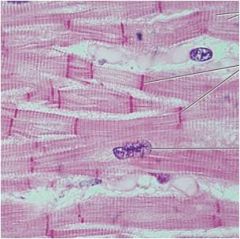
|
cardiac muscle
|
|
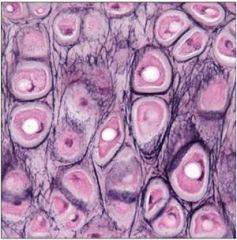
|
Cartilage: elastic
|
|
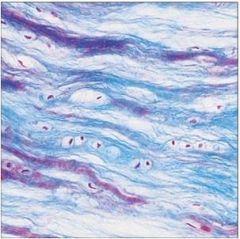
|
Cartilage: fibrocartilage
|
|
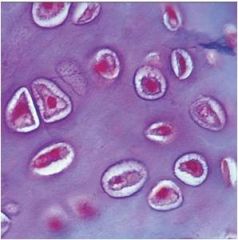
|
Cartilage: hyaline
|
|
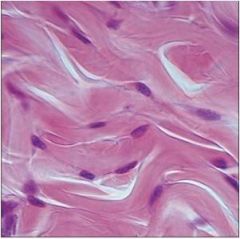
|
Connective Tissue proper: dense Connective Tissue, dense irregular
|
|
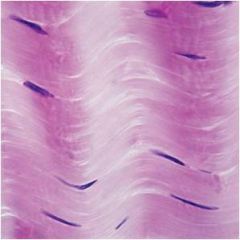
|
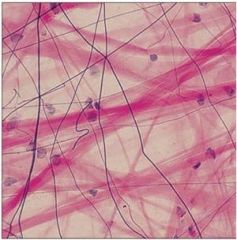
Connective Tissue proper: Dense Connective Tissue, dense regular
|
|
|
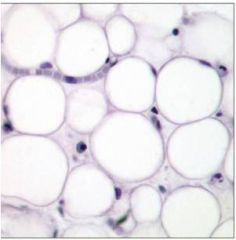
Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connevtive Tissue, adipose
|
|
|
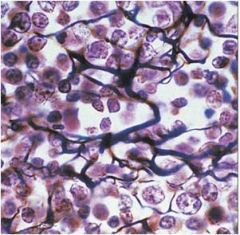
Connective Tissue Proper: loose connective tissue, areolar
|
|
|
Connective Tissue proper: loose connective tissue, reticular
|
|
|
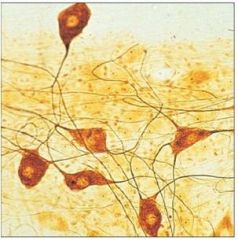
nervous tissue
|
|
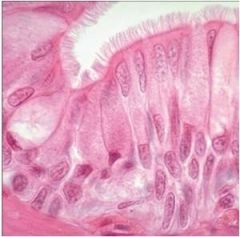
|
pseudostratified columnar epitheliem
|
|
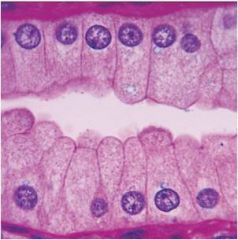
|
simple columnar epithelium
|
|
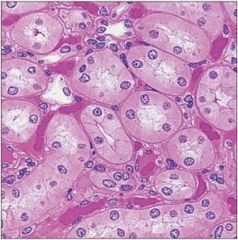
|
simple cuboidal epithelium
|
|
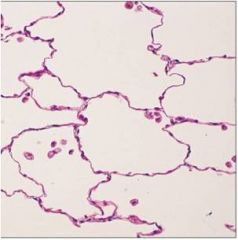
|
simple squamous epithelium
|
|
|
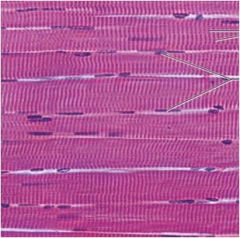
skeletal muscle
|
|
|
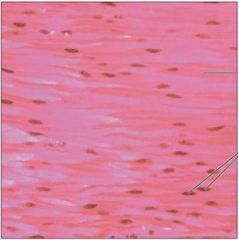
smooth muscle
|
|
|
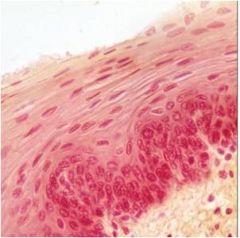
stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
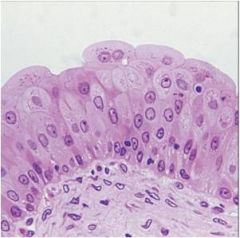
transitional epithelium
|
|
|
Keratinized is found in
|
dry areas
|
|
|
Nonkeratinized is found in
|
moist areas
|
|
|
Stratified Cuboidal
|
-Limited distribution in body
-In mammary gland |
|
|
Stratified Columnar
|
-Limited distribution in body
-Small amounts in pharynx, male urethra, and lining some glandular duct |

