![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Deglutition is |
chewing |
|
|
The primary site for filtering, warming and humidifying inhaled gases is the |
nose |
|
|
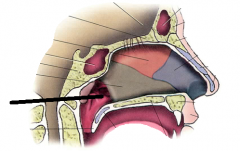
nasopharynx |
|
|
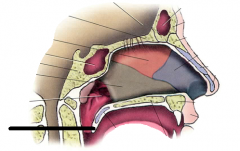
uvula |
|
|
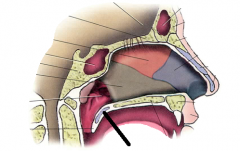
soft palate |
|
|
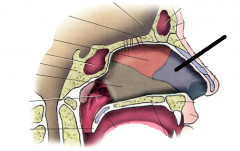
septal cartilage |
|
|
Turbinates project ________ from the _______ wall. |
medially, lateral |
|
|
Turbinates were designated to increase _______ ____ of the nasal mucus membrane and to increase __________ of inhaled gases. |
surface area, turbulence |
|
|
Particles > _microns become impated in the gel layer |
>5 microns |
|
|
________ 1/3 of the nasal cavity is covered with __________ ________ __________. |
Anterior, statified squamous epithelium |
|
|
_________ 2/3 of the nasal cavity is covered with ________________ ________ ________ _________ (_____). |
Posterior, pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (PSCCE) |
|
|
What is the official name for nose hair? |
vibrissae
|
|
|
_____ in the nasal cavity push mucus towards the nasopharynx. |
cilia |
|
|
Purpose of the oral cavity |
primary: food passage secondary: less efficient at heating, humidifying and filtering inhaled gases than the nose |
|
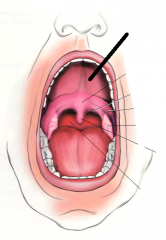
|
hard palate |
|
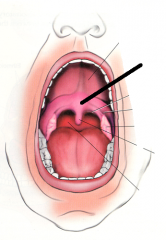
|
soft palate |
|
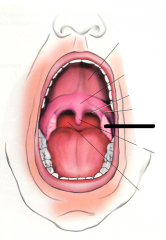
|
palatine tonsil |
|
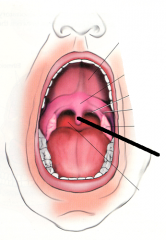
|
uvula |
|
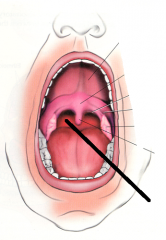
|
oropharynx |
|
|
Pharynx is a |
musculo-membrane tube used for both the passage of air and food |
|
|
Pharynx extends from the _____ ______ to the ______. |
nasal cavity to the larynx |
|
|
Pharynx is divided into three sections |
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx |
|
|
What blood supply supplies the entire conducting airways? |
bronchial |
|
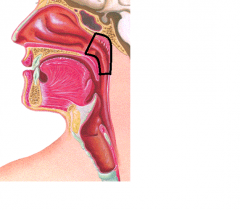
|
nasopharynx |
|
|
Nasopharynx is lined with |
PSCCE (pseudostratified ciliated solumnar epithelium) |
|
|
Nasopharynx is posterior to what and superior to what |
posterior to the nasal cavity and superior to the soft palate |
|
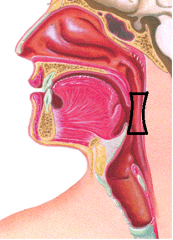
|
oropharynx |
|
|
Oropharynx is located from the |
soft palate to the base of the tongue |
|
|
Oropharynx is lined with |
stratified squamous epithelium |
|
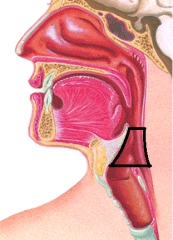
|
laryngopharynx |
|
|
Laryngopharynx is located between |
the base of the tongue to the esophageal opening |
|
|
Laryngopharynx is lined with |
stratified squamous epithelium |
|
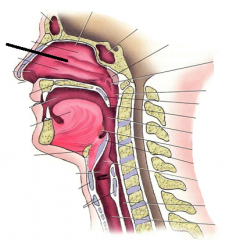
|
turbinates |
|
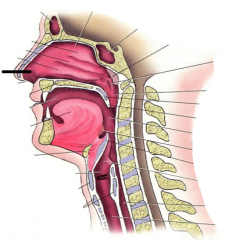
|
vestibule |
|
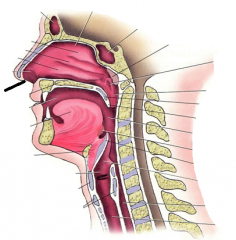
|
nares |
|
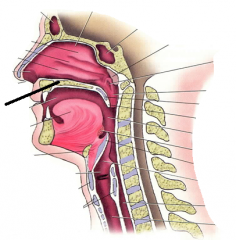
|
hard palate |
|
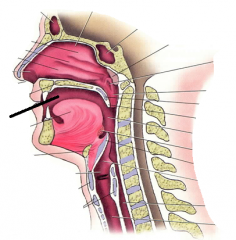
|
oral cavity |
|
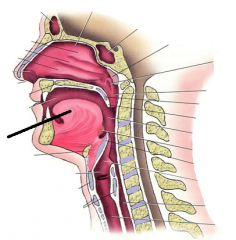
|
tongue |
|
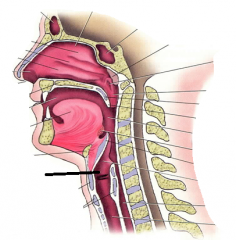
|
larynx |
|
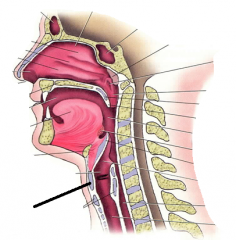
|
thyroid cartilage |
|
|
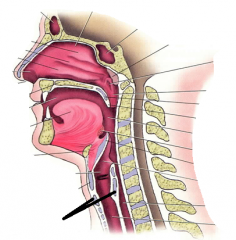
cricoid cartilage |
|
|
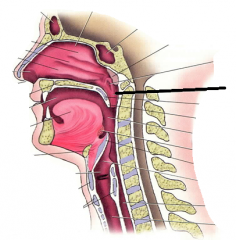
nasopharynx |
|
|
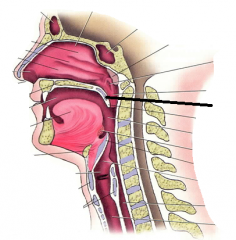
soft palate |
|
|
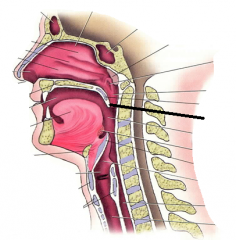
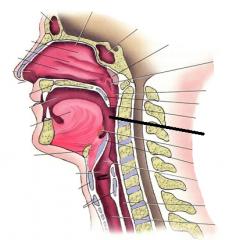
uvula |
|
|
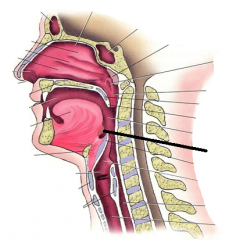
oropharynx |
|
|
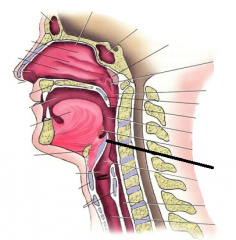
lingual tonsil |
|
|
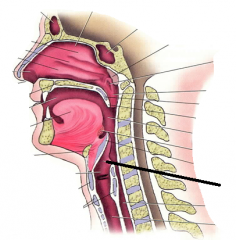
epiglottis |
|
|
laryngopharynx |
|
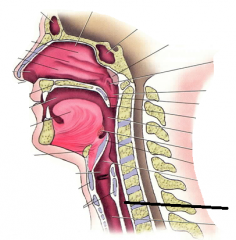
|
esophagus |
|
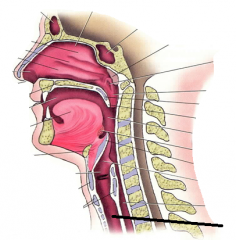
|
trachea |
|
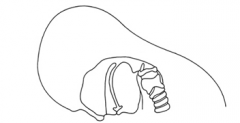
|
flexed |
|
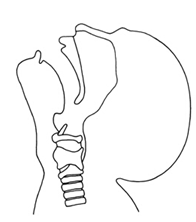
|
extended |
|
|
The larynx is located between (about) |
C3 - C6 |
|
|
The larynx is _____________. |
cartilaginous |
|
|
The larynx is a ___________ structure that hangs from the _____ bone. |
cylindrical, hyoid |
|
|
The larynx is the valve between the _______ and _______. |
pharynx and trachea |
|
|
The functions of the larynx are |
sound production and protective mechanism |
|
|
The larynx is formed by ____ cartilages |
nine |
|
|
The larynx has _____ single cartilages |
three |
|
|
The epiglottis is attached to the base of the tongue by mucus membranes that form the _________. |
vallecula |
|
|
What is the function of the epiglottis? |
to divert liquids/solids from the glottis and towards the esophagus |
|
|
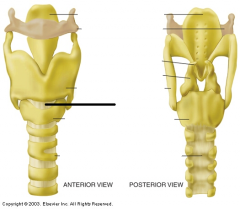
The _______ is the largest of all the laryngeal cartilages |
thyroid |
|
|
The common term for thyroid is |
"adam's apple" |
|
|
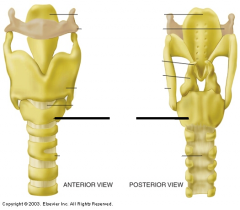
The cricoid is the only rigid that completely _________ the airway. |
encircles |
|
|
The _______ is the narrowest portion of the upper airway in infants. |
cricoid |
|
|
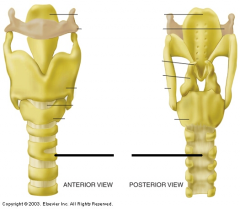
Vocal ligaments attach to the vocal processes on the base of the _________ cartilage. |
arytenoid |
|
|
Vocal cord movement is due to the _________/_________ of the arytenoids |
adduction/abduction |
|
|
adduction |
bringing together |
|
|
Corniculate sit on top of the _________ as a supportive structure for soft tissue. |
arytenoids |
|
|
The cuneiform is a supportive structure for the _____________ folds. |
aryepiglottic |
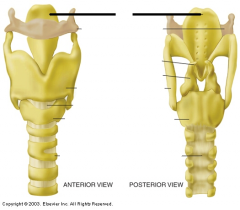
|
|
epiglottis |
|
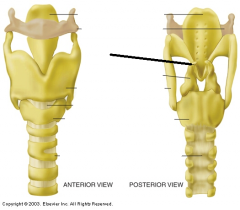
|
corniculate cartilage |
|
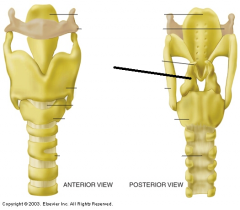
|
arytenoid cartilage |
|
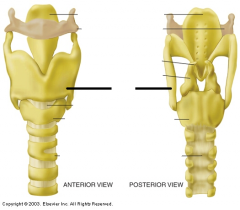
|
thyroid cartilage |
|
|
cricothyroid ligament |
|
|
cricoid cartilage |
|
|
trachea |
|
|
False vocal cords are a mucus membrane that protrudes into the ______ from the _______ walls. |
larynx, lateral |
|
|
False vocal cords ______ play a role in vocalization. |
don't |
|
|
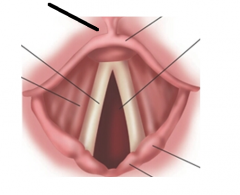
True vocal cords form a triangular opening called the |
glottis |
|
|
The true vocal cords adjust for ____________ and _________ maneuver |
vocalization and valsalva's |
|
|
What is the opposite of valsalva's maneuver |
Müller's Manoeuvre - After a forced expiration, an attempt at inspiration is made with closed mouth and nose, whereby the negative pressure in the chest and lungs is made very subatmospheric |
|
|
vallecula |
|
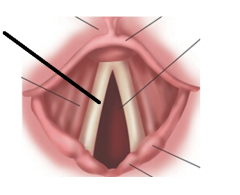
|
true vocal cords |
|
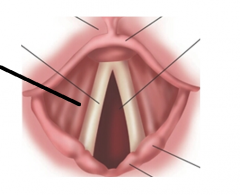
|
false vocal cords |
|
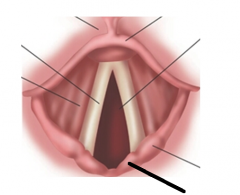
|
corniculate cartilage |
|
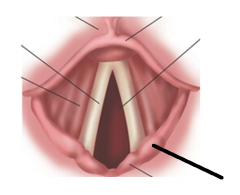
|
cuneiform cartilage |
|
|
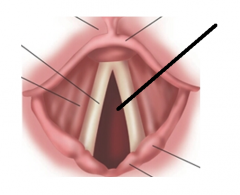
glottis |
|
|
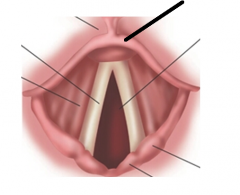
epiglottis |
|
|
Vocal cord problem areas (4) |
cysts/tumors of the vocal cords, edema, damage to the vagus nerve, laryngospasm |
|
|
Cysts/tumors of the vocal cords may be _____-______, ____ ______ or _________ ______ |
fluid filled, scar tissue or malignant tumors |
|
|
Edema of the vocal cords may be caused by ______ or _____ __________. |
trauma or viral infections |
|
|
edema may result in upper airway ___________ if severe. |
obstruction |
|
|
_______ is heard upon auscultation |
stridor |
|
|
stidor |
harsh, grating sound |
|
|
Damage to the vagus nerve could be caused by |
trauma or surgery |
|
|
Damage to the vagus nerve may result in partial or complete paralysis of the vocal cords which _________ airway resistance. |
increases |
|
|
Epithelium of the larynx above the vocal chord |
stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
Epithelium of the larynx below the vocal chords |
PSCCE (pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium) |

