![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What constitutes a lobular unit? |
Interlobular septa (pulm veins and lymphatics) Centrilobular (pulm artery and bronchioles) Lobular (lung acini) |
|
|
What is surfactant composed of? |
Lipid (90%) DPCC Protein (10%) -SP-A, , SP-D: innate immunity of the lung - SP-B, SP-C: reduces surface tension -ABCA3: role in transport surfactant -TTF-1: role in surfactant regulation |
|
|
What are the surfactant dysfunction disorders? |
Neonatal ARDS Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis |
|
|
What factors can increases total PVR? |
Lung compression Increased lung volume Gravity Increase interstital pressure Increase blood viscosity Positive pressure ventilation Hypoxia Sympathetic nerve stimulation |
|
|
how to calculate PAO2? |
PAO2 = FiO2 (barometric pressure - water vapor partial pressure) -PaCO2/R |
|
|
How to calculate alveolar ventilation? |
VA = Minute ventilation - dead space |
|
|
How to calculate physiologic dead space? |
VDCO2/VT = (PaCO2- Endtidal CO2)/PaCO2 |
|
|
How to calculate Arterial O2 content CaO2? |
CaO2 = (1.34 x Hb x SpO2) + (0.003 x PaO2) |
|
|
How to calculate O2 delivery DO2? |
DO2 = cardiac output x arterial O2 content |
|
|
What is the normal V/Q ratio? |
0.6-3.0 |
|
|
How to calculate shunt fraction? |
1. Need to put patient on 100% O2 for 20-30minutes 2. obtain ABG and mix venous O2 and calculate PAO2 ( a substitute for end-capillary O2 content. 3. Qs/Qt = (CcO2- CaO2)/ (CcO2- CvO2) |
|
|
How to get the most accurate pulmonary artery pressure? |
To minimize influences of the pressure differences in the 3 lung zones, need to acquire data when alveolar pressure is the lowest -catheter tip needs to be in zone 3 -acquire data at end expiration |
|
|
What factors limits gas diffuse/transfer? |
diffuse surface molecular weight/ hb binding the pressure gradient across membranes perfusion. |
|
|
Wha are the two general limitations for gas transfer?
|
Diffusion limited: example carbon monoxide |
|
|
How to do an internal validation of the blood gas?
|
every 1 change of H+ = 0.01 pH change 40nmol = 7.40 |
|
|
How does lung volume changes during pregnancy?
|
Reduced RV and FRC.
TLC is only mildly decreased in the third trimester. Tidal volume increases due to increased progesterone. |
|
|
What ABG changes are expected during pregnancy? |
Increased PO2 and decreased PCO2 |
|
|
How does PFT changes when aging? |
FEV1 decreases VC decreases RV increases |
|
|
What's considered an acceptable spirometry? |
Good start: extrapolated volume < 5% or FVC < 150cc Exhalation to RV, time > 6s Absence of artifact |
|
|
What's considered an reproducible spirometry? |
Two largest FEV1 and FVC within 150cc of each other |
|
|
What's the prerequisites before doing a bronchodilator response test? |
Avoid SABA > 4hrs Avoid LABA > 12hrs |
|
|
What's the limitation of body plephysmography? |
Expensive, and space consuming Exceeding 1 pant/sec results in overestimation of FRC |
|
|
What's the limitation of gas dilution techiques, nitrogen washout, helium rebreathing? |
It doesn't measure the trapped air, underestimate lung volume. |
|
|
What's considered a good single breath test for DLCO? |
Inhaled gas < 4 seconds Breath hold 8-12seconds Exhaled rapidly < 4 second Exhaled volume is >85% of largest VC. |
|
|
True/False: DLCO is the highest in the mornings. |
True |
|
|
True/False: DLCO is elevated in the premense period |
True |
|
|
What are the contraindications for methocholine challenge? |
ABSOLUTE: Severe airflow limitation (FEV1 < 50%) MI or CVA within in the last 3months Uncontrolled HTN (>200/100) Known aortic aneurysm RELATIVE: FEV1 <60% Pregnancy/Nursing/ On myasthenia gravis meds. |
|
|
What medications to hold prior to methocholine challenge? |
SABA: 8hrs SAMA 24hrs LABA: 48hrs LAMA: 7 days Theophyline (short acting): 24hrs Theophyline (long acting): 48hr |
|
|
What's consider + exercise challenge test? |
15% decreased FEV1 |
|
|
How does DLCO changes with pregnancy? |
Increase in the first trimester, then decreases |
|
|
What are the absolute contraindication for CPETs? |
uncontrolled cardiac issues DVTs Osat < 85% at rest |
|
|
How does cardiac output changes with exercises? |
Initially increased through increased SV and HR. As the work rate increased, CO increases almost exclusively with increased HR. |
|
|
How does BP changes with exercise? |
Systolic pressure increases diastolic pressure stay the same |
|
|
How does ventilation changes with exercises? |
At low exercise, tidal volume increases at the expenses of IRV. At peak exercise, increased ventilation is largely driven by increased RR. |
|
|
What's the considered normal anaerobic threshhold? |
>40% of Vo2Max |
|
|
How to calculate maximum heart rate? |
220-age |
|
|
What's an abnormal ventilatory reserve? |
VeMax is > 70% of MVV |
|
|
What to think about if there is cyclical flutuation in minute ventilation during exercise? |
congestive heart failure. |
|
|
What is the normal Ve/Vco2 at AT? |
32-34 |
|
|
Usually end-tidal O2 increases before end-tidal CO2 during exercise, what is the explaination when end-tidal CO2 does not increase? |
Increased dead space. |
|
|
What is acetozalmide good for in high altitude? |
prevention, usually advise to take one day prior to rapid ascend |
|
|
What can cause elevated Ve/Vco2? |
Early AT (due to elevated Vco2) Hyperventilation syndrome Increased deadspace can be seen in CHF, COPD, ILD, PH (very high level) |
|
|
What does end-expiratory lung volume do during exercise? |
It decreases, to recruit inspiratory volume. |
|
|
What's the reason why EELV may sometime increased during exercise, in diseased patients? |
At low EELV, breathing are limited by low expiratory flow. Subject increases EELV in order to avoid expiratory flow limitations. |
|
|
What's the reason why EILV (end inspiratory lung volume) are increased during exercises? |
To increase Tidal volume. In diseased lung where EILV cannot be increased, respirate rate is increased to maintain minute ventilation. |
|
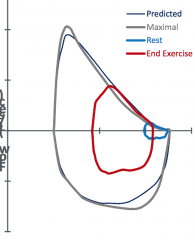
|
Obesity |
|
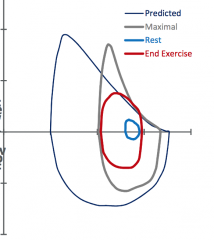
|
Restrictive lung disease |
|
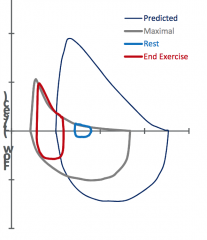
|
COPD |
|
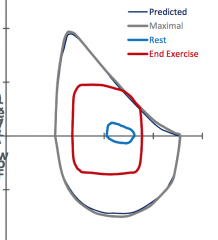
|
Normal |
|
|
True/False: A-a gradient remains normal during pregnancy |
False, there is an increase in A-a gradient during pregnancy |

