![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Excitability |
Responsiveness or irritability; able to receive and respond to stimuli |
|
|
|
Contractility |
Able to shorten when stimulated |
|
|
|
Extensibility |
Able to be stretched |
|
|
|
Elasticity |
Able to recoil to resting length |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle |
Intact muscle are wrapped in several connective tissue sheaths |

|
|
|
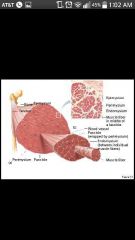
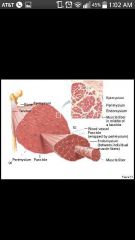
Epimysium |
Exterior collagen layer, separates muscle from surrounding tissue (skeletal muscle) |
|
|
|
Perimysium |
Surrounds muscle fiber bundles (fascicle); contain blood vessel and nerve Supply to fascicle (skeletal muscle) |
|
|
|
Endomysium |
Surrounds individual muscle cell/fiber; contains stem cells that repair damage (skeletal muscle) |

Muscle cells are muscle fibers |
|
|
Aponeurosis |
Rope-like tendon /sheet-like connective tissue wrappings that extend beyond muscle |
|
|
|
Myoglobin |
Muscle cell pigment; stores Surplus oxygen |
|
|
|
T tubules |
(Plasma membrane) sarcolemma with invaginations; conduct impulses deep into muscle fiber |
|
|
|
Myofibrils |
Rod-likes contractile units within sarcoplasm of muscle fiber (made of bundles of protein filaments: myofilaments) |
|
|
|
Myofilaments |
Responsible for muscle contraction -Thin Filament: made of protein actin, troponin, tropomyosin (I-band;light) -Thick Filament: made of protein myosin (A-band; dark) |
|
|
|
Sarcomeres |
Series of thick and thin filaments aligned in repeating, smallest contractile unit (functional) of muscle fiber |
|
|
|
Z disc |
Coin shaped sheet of proteins that hold thin filaments and myofibrils together |

|
|
|
H Zone |
Lighter mid-region where filaments do not overlap |
|
|
|
M line |
Line of protein myosin that holds adjacent thick filaments together |

|
|
|
Titin |
Elastic filament extends from the the two lines to thick filaments, helps muscle cells recoil after being stretched |

|
|
|
Dystrophin |
Structural protein that helps to link thin filaments to sarcolemma |
|
|
|
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) |
Stores and regulates calcium, network of smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
|
Synaptic cleft |
Axon terminal and muscle fiber are separated by gel filled space; Gap |
|
|
|
Acetylcholine (ACh) |
Neurotransmitter (receptors) contained by Synaptic vesicles of axon terminal, within Sarcolema |
|
|
|
Rigor mortis |
Lack of ATP after death, prevents cross Bridges from breaking and muscles remain contracted |
|
|
|
Acetylcholinesterase |
Enzyme that are quickly terminated by ACh, muscle relaxation |
|
|
|
Isotonic contraction |
Skeletal muscle changes length (tension stays same) resulting in motion |

|
|
|
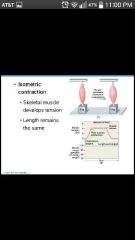
Isometric contraction |
Skeletal muscle develops tension (length is the same) |
|
|
|
Motor unit |
Motor neuron and all (four to several hundred) muscle fibers it supplies; nerve-muscle { small motor units control fine movements; fingers and eyes} { large motor units send large weight bearing muscles; thighs and hips} |
|
|
|
Muscle tone |
Constant, slightly contracted ready to respond |
|
|
|
Muscle metabolism |
ATP is only source of energy for contraction (ATP is regenerated by aerobic respiration (oxidative fibers), (anerobic pathway) glycolysis, and ADP with creatine phosphate) |
|
|
|
Lactic acid |
Diffuses into bloodstream, used as fuel by liver, kidneys, heart (muscle fatigue) -pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid and converted back into pyruvic acid by the liver |

|
|
|
Fuels |
Stored glycogen, then bloodborne glucose, pyruvic acid from glycolysis, and free fatty acids |

|
|
|
Oxygen debit (deficient) |
Oxygen needed after exercise for: replenishing oxygen reserves, glycogen stores, ATP and CP Reserves - conversion of lactic acid to: pyruvic acid, glucose, and glycogen |
|
|
|
Muscle fiber types |
Slow oxidative fast oxidative fast glycolytic fibers |
|
|
|
Hypertrophy |
Cell growth; cells increase in strength from muscle contraction |
|
|
|
Peristalsis |
Alternating contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle layers that mix and squeeze substances through Lumen of hollow organs (longitudal layer/circular layer) |

|
|
|
Hyperplasia |
Smooth muscle cells can divide and increase their numbers |
Ex. Estrogen effects on uterus at puberty and during pregnancy |

