![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
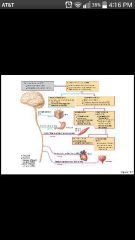
Central nervous system (CNS) |
(Brain and spinal cord) integrative and control centers |
|
|
|
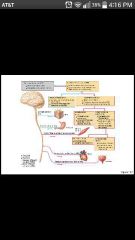
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
Communication lines between CNS and the rest of the body; cranial nerves and spinal nerves |
|
|
|
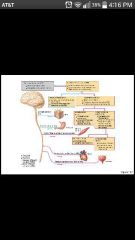
Sensory (afferent) division |
Conducts impulses from receptors to the CNS; somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers |
|
|
|
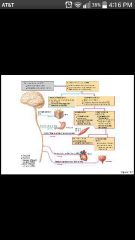
Motor (efferent) division |
Conducts impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands); motor nerve fibers |
|
|
|
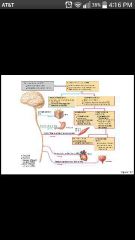
Somatic nervous system |
Somatic motor (voluntary); conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
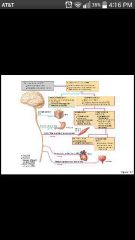
Automatic nervous system (ANS) |
Conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and glands; visceral motor (involuntary) |
|
|
|
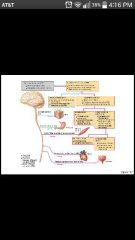
Sympathetic division |
Mobilizes body systems during activity (heart rate) |
|
|
|
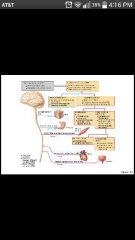
Parasympathetic division |
Promotes "housekeeping" functions during rest; conserves energy |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
1. Neurons: Excitable cells that transmit electrical signals 2. Neuroglia (glial cells): supporting cells |
|
|
|
Neuroglia |
CNS: astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes PNS: satellite cells & Schwann cells |
|
|
|
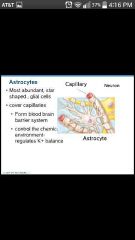
Astrocytes |
Most abundant, versatile, and highly branched glial cells; support and brace neurons; cling to neurons; form blood-brain barrier system (BBB) |
|
|
|
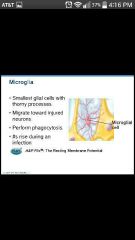
Microglia |
Smallest glial cells with thorny processes, migrate toward injured neurons; phagocytosis |
|
|
|
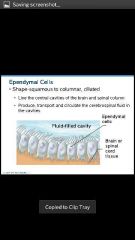
Ependymal cells |
Produce, transport, and circulate the cerebrospinal fluid in the cavities; shape: squamous to column, ciliated |
|
|
|
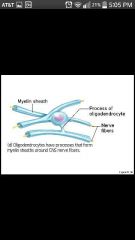
Oligodendrocytes |
Branched cells, processes wrap CNS fibers forming insulating myelin sheaths; cannot be repaired |
|
|
|
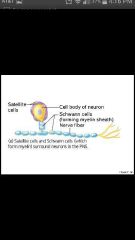
Satellite cells |
Surround neuron cell bodies in the PNS |
|
|
|
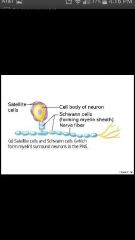
Schwann cells |
Neurolemmocytes; surround peripheral nerve fibers (wrap many times around axon) and form myelin sheaths; vital to Regeneration of damaged fibers |
|
|
|
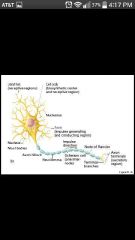
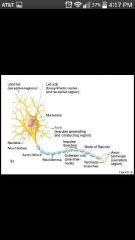
Neurons (nerve cells) |
Amiotic; high metabolism rate from oxygen and glucose; plasma membrane does electrical signaling & cell-to-cell interactions during development(only nerve&muscle cells) |
|
|
|
Cell Body |
Perikaryon/Soma; rough ER called Nissl bodies; clusters of cell bodies are called nuclei (CNS) and ganglia (PNS) |
|
|
|
Processes |
Dendrites and axons; bundles called: Tracts in CNS Nerves in PNS |
|
|
|
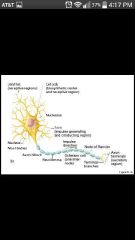
Dendrites |
Receptive/input region convey electrical signals toward the cell body |
|
|
|
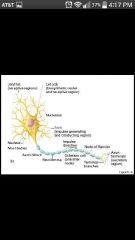
Axon |
Impulse generating (action potentials) & conducting region; -Nerve fibers: long axons -Axon collaterals: occasional branches -Telodendria : Numerous terminal branches -Synaptic knobs: Knoblike axon terminals |
|
|
|
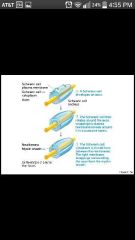
Myelin sheath |
Layers of membrane Schwann cells in PNS; formed by oligodendrocytes in CNS; protect and insulate, increase impulse speed ; white matter in brain and spinal cord (unmyelinated: gray matter) -Neurilemma: peripheral bulge of Schwann cells cytoplasm; not in CNS |
|
|
|
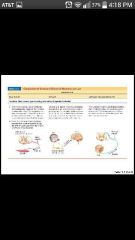
Structural Classification of Neurons |
-Multipolar: single long axons and several dendrites, most abundant, motor neurons and interneurons -Bipolar: one axon and one dendrite (sense organs: nose, ear, eyes ) -Unipolar: single short process that has two branches, within dorsal root ganglion |

|
|
|
Functional classification of neurons |
-Sensory: (afferent) transmits impulses from sensory receptors towards the CNS -Motor: (efferent) carry impulses from the CNS to effectors -Interneurons: (association neurons) shuttle signals through the CNS pathways most are entirely within the CNS; abundant |
|

