![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Principal Extra-Temporal Connections to MTL
|
Papez's Circuit
Frontal Lobes Diencephalon |
|
|
Papez's Circuit
|
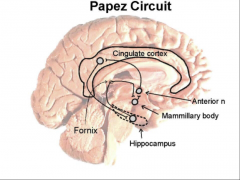
Specific brain circuit for emotional expression and recognition - Papez Circuit + Amygdala = Limbic System
PC consists of: Mamillary bodies, fornix, anterior thalamic nuclei (ATN), cingulate gyrus and hippocampus |
|
|
Papez Circuit Lesions
|
Declarative memory impairment (poor relational memory and encoding abilities). This happens most often when ATN and hippocampus are lesioned.
|
|
|
Frontal Lobes
|
Motor Programming
Executive Functions - organisation, attention, problem solving, monitoring, correction (occurs in prefrontal area) Memory role: employs strategies for encoding and retrieval Impairments - confabulation, can't remember contexts, order of things, events |
|
|
Diencephalon
|
Known as Hind Brain, comprises of:
- Thalamus and hypothalamus Thalamus damage: - Dorsal damage = can't select right info for retrieval - Intralaminar/Midline - semantic memory problems, retrieval issues. |
|
|
Action Potential
|
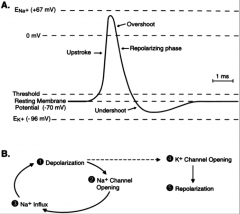
Sum up IPSP and EPSP. If more excitatory will cross threshold = Action Potential. Self propagating once it crosses threshold.
|
|
|
Long Term Potentiation
|
Strength between synapses is increased due to biochemical and structural change. LTP occurs with glutamate (excitatory NT).
LTP casuses new receptors to pick up NT in post synaptic membrane, causing increased increased receptor sensitivity. Pre Synaptic also releases more glutamate into cleft. If cell fires quickly enough, rapidly enough, it can cause permanent change. |
|
|
Hebb's Rule
|
When Cell A excites Cell B repeatedly and persistently enough by firing excitatory NT, a change occurs so that likelihood of Cell B being able to efficiently fire Cell B is much greater. Change is due to growth or metabolic change process.
|
|
|
Other of Mechanisms of Plasticity
|
Habituation - cell fires just enough so that repeated stimulation reduces the strength of the synaptic response
LTD - cells fires at low frequency which can decrease synaptic strength Sensitivity - single noxious stimulus causes an exaggerated response to repeat presentation of stimulus |
|
|
LTP and synaptic change
|
LTP causes
- increased sensitivity of receptors to glutamate - increased amount of glutamate released by pre synaptic terminal button - protein synthesis in post-synaptic dendrites. |
|
|
Sites of LTP
|
Hippocampus (CA1 to DG), entorhinal cortex
Motor cortex, prefrontal cortex, thalamus, amgydala, visual cortex |
|
|
HM & Memory
|
MTL essential for memory,MTL more essential for anterograde than retrograde memory. Distinction between how procedural and declarative memory works in brain (HM implies procedural operates elsewhere).
TL are engines of memory system, functional asymmetry. |
|
|
Hippocampus and Memory
|
Hippocampus and surrounding areas in MTL - critical to memory function, esp for declarative memory and learning new info.
H particularly important for relational learning tasks. Info integrated by sensory systems, sent to Hippo for LTS., memories can be accessed by reciprocal connections between and neocortex. |
|
|
TLE
|
Arises from sudden excitation of neurons and inadequate inhibition. .Recurrent unprovoked seizures with either loss of consciousness or not. Most common cause is hippocampal sclerosis (neuronal loss causing excess growth of glial cells) due to infection, tumours, vascular malformations often occurring early in life.
|

