![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Basic lab tools |
Electronic analytical balance Lab oven Desiccator Analytical glassware Pipettes |
|
|
2 two types of analytical glassware |
Accurate analytical glassware Inaccurate glassware |
|
|
Types of accurate analytical glassware |
Volumetric flaskBuretPipet Buret Pipet |
|
|
Types of inaccurate glassware |
Graduated cylinder erlenmeyer flask beaker |
|
|
Types of pipettes |
Volumetric transfer pipet Graduated measuring pipet Micropipette |
|
|
The average where is the sum of all the samples divided by the number of samples |
Mean |
|
|
The middle result when data are range in order of size which is arranged in lowest to highest |
Median |
|
|
One reading that is very different from the rest |
Outlier |
|
|
Relates to reproducibility of results |
Precision |
|
|
Deviation from the mean |
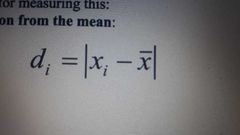
|
|
|
Measurement of agreement between experimental mean and true value |
Accuracy |
|
|
Two measures of accuracy |
Absolute error relative error |
|
|
Formula of absolute error |

|
|
|
Formula for relative error |

|
|
|
Types of error in experimental data |
Random (indeterminate) error Systematic determinate error Gross errors |
|
|
Data scattered approximate symmetrically about a mean value . Affects precision |
Random (indeterminate) error |
|
|
Errors that have several possible sources and affects accuracy |
Systematic (determinate) error |
|
|
Errors that are usually obvious and are detectable by carrying out sufficient replicate measurements |
Gross errors |
|
|
Sources of systematic error |
Instrument error method error personal error |
|
|
Errors that need frequent calibration both for apparatus and for electronic devices |
Instrument error |
|
|
Errors that are due to inadequacy and physical or chemical behavior of regions or reactions |
Method error |
|
|
Kinds of systematic errors |
Constant proportional |
|
|
Are errors that are less important for larger values of reading |
Constant systematic errors or constant |
|
|
Error that are equally significant for all values of measurement |
Proportional systematic errors or proportional |
|
|
Three approaches to minimize method errors |
Analysis of certified standards use two or more independent methods analysis of blanks |
|
|
Finite number of observations |
Sample |
|
|
Total or infinite number of observations |
Population |
|
|
Main properties of gaussian curve |
Population mean population standard deviation |
|
|
Is the measure of precision of a relation of data |
Standard deviation |
|
|
Interval around the mean that probably contains the true mean |
Confidence limits |
|
|
The magnitude of the confidence limits |
Confidence interval |
|
|
Fixes the level of probability that the main as within the confidence limits |
Confidence level |
|
|
Percentage of area under goshen curves between certain limits |

|

