![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
The scientific study of the body’s structures |
|
|
|
Gross anatomy |
The study of the larger structures of the body, typically with the unaided eye; also referred to macroscopic anatomy |
|
|
|
Microscopic anatomy |
Study of very small structures of the body using magnification |
|
|
|
Regional anatomy |
Study of the structures that contribute to specific body regions |
|
|
|
Systemic anatomy |
Study of the structures that contribute to specific body systems |
|
|
|
Physiology |
Science that studies the chemistry, biochemistry, and physics of the body’s functions |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
Steady state of body systems that living organisms maintain |
|
|
|
Cell |
Smallest independently functioning unit of all organisms; in animals, a cell contains a cytoplasm, composed of fluid and organelles |
|
|
|
Tissue |
Group of similar or closely related cells that act together to perform a specific function |
|
|
|
Organ |
Functionally distinct structure composed of two or more types of tissue |
|
|
|
Organ system |
Group of organs that work together to carry out a particular function |
|
|
|
Organism |
Living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Assembly of more complex molecules from simpler molecules |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
Breaking down of more complex molecules into simpler molecules |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
sum of all of the body’s chemical reactions |
|
|
|
Responsiveness |
Ability of an organisms or a system to adjust to changes in conditions |
|
|
|
Development |
Changes an organism goes through during life |
|
|
|
Differentiation |
Process by which unspecialized cells become specialized in structure and function |
|
|
|
Growth |
Process of increasing in size |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
Process by which new organisms are generated |
|
|
|
Nutrient |
Chemical obtained from foods and beverages that is critical to human survival |
|
|
|
Pressure |
Force exerted by a substance in contact with another substance |
|
|
|
Set point |
Ideal value for a physiological parameter; the level or small range within which a physiological parameter such as blood pressure is stable and optimally healthful, that is, within its parameters of homeostasis |
|
|
|
Normal range |
Range of values around the set point that do not cause a reaction by the control center |
|
|
|
Negative feedback |
Homeostatic mechanism that tends to stabilize an upset I the body’s physiological condition by preventing an excessive response to a stimulus, typically as the stimulus is removed |
|
|
|
Sensor (also,receptor) |
Reports a monitored physiological value to the control center |
|
|
|
Control center |
Compares values to their normal range; deviations cause the activation of an effector |
|
|
|
Effector |
Organ that can cause a change in a value |
|
|
|
Positive feedback |
Mechanism that intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition in response to a stimulus |
|
|
|
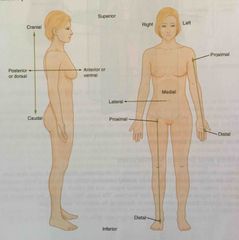
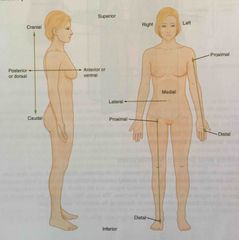
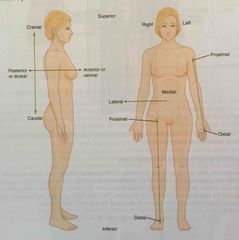
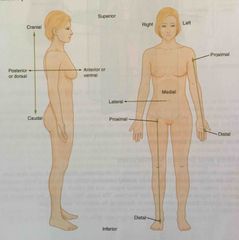
Anatomical position |
Standard reference position used for describing locations and directions on the human body |
|
|
|
Prone |
Face down |
|
|
|
Supine |
Face up |
|
|
|
Anterior |
Describes the front or direction towards the front of the body; also referred to as ventral |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Describes the back or direction toward the back of the body; also referred to as dorsal |
|
|
|
Superior |
Describes a position above or higher than other parts of the body proper; also referred to as cranial |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Describes a position below or lower than another part of the body proper; near or toward the tail (in humans, the coccyx, or the lowest part of the spinal column) also referred to as the caudal |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Describes the side or direction toward the side of the body |
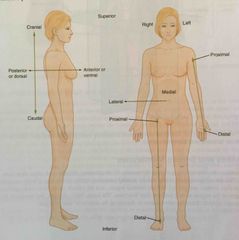
|
|
|
Medial |
Describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body |
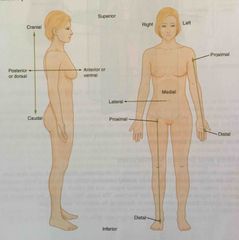
|
|
|
Proximal |
Describes a position nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body |
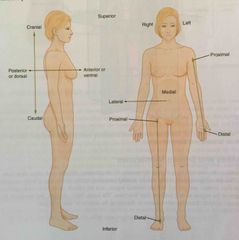
|
|
|
Distal |
Describes a position farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body |
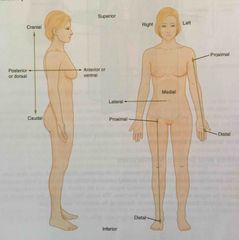
|
|
|
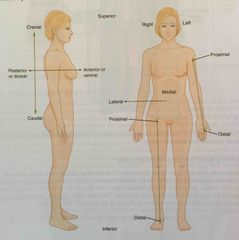
Superficial |
Describes a position nearer to the surface of the body |
|
|
|
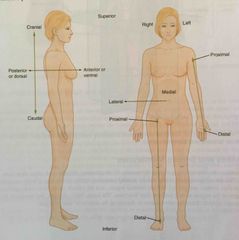
Deep |
Describes a position farther from the surface of the body |
|
|
|
Section |
In anatomy, a single flat surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut through |
|
|
|
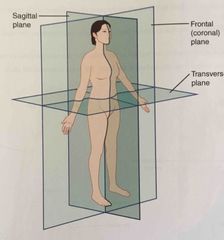
Plane |
Imaginary two-dimensional surface that passes through the body |
|
|
|
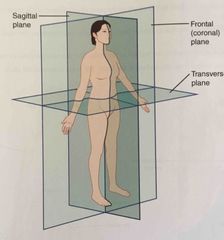
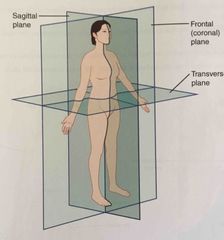
Sagittal plane |
Two-dimensional, vertical plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides |
|
|
|
Frontal plane |
Two-dimensional, vertical plane that divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions |
|
|
|
Transverse plane |
Two-dimensional, horizontal plane that divides the body or organ into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Describes the back or direction towards the back of the body; also referred to as posterior |
|
|
|
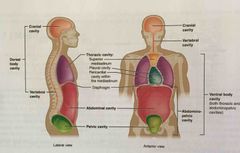
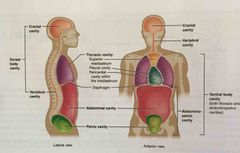
Dorsal cavity |
Posterior body cavity that houses the brain and spinal cord; also referred to the posterior body cavity |
|
|
|
Ventral |
Describes the front or direction toward the front of the body; also referred to as anterior |
|
|
|
Ventral cavity |
Larger body cavity located anterior to the posterior (dorsal) body cavity; includes the serous membrane-lined plural cavities for the lungs, pericardial cavity for the heart, and the peritoneal cavity for the abdominal and pelvic organs; also referred to as anterior body cavity |
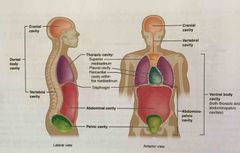
|
|
|
Caudal |
Describes a position below or lower than another part of the body proper; near or toward the tail ( in humans the coccyx or lowest part of the spinal column) also referred to as inferior |
|
|
|
Cranial |
Describes a position above or higher than another part of the body proper; also referred to as superior |
|
|
|
Anterior cavity |
Larger body cavity located anterior to the posterior (dorsal) body cavity; also referred to as ventral cavity |
|
|
|
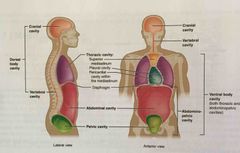
Posterior cavity |
Posterior body cavity that houses the brain and spinal cord; also referred to as dorsal cavity |
|
|
|
Cranial cavity |
Division of the posterior (dorsal) cavity that houses the brain |
|
|
|
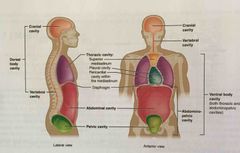
Spinal cavity |
Division of the dorsal cavity that houses the spinal cord; also referred to as vertebral cavity |
|
|
|
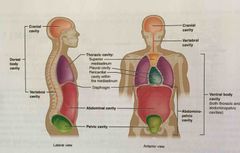
Thoracic cavity |
Division of the anterior (ventral) cavity that houses the heart, lungs, esophagus, and trachea |
|
|
|
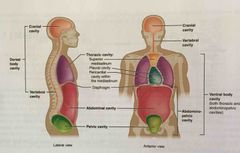
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Division of the anterior (ventral) cavity that houses the abdominal and pelvic viscera |
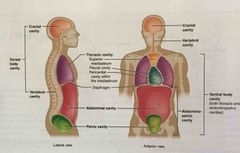
|
|
|
Serosa |
Membrane that covers organs and reduces friction; also referred to as serous membrane |
|
|
|
Serous membrane |
Membrane that covers organs and reduces friction; also referred to as serosa |
|
|
|
Pleura |
Serous membrane that lines the pleural cavity and covers the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Sac that encloses the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and covers the organs found there |
|
|
|
Renewal |
Process by which worn-out cells are replaced |
|
|
|
CT computed tomography |
Medical imaging technique in which a computer-enhanced cross-sectional x-ray image is obtained |
|
|
|
MRI magnetic resonance imaging |
Medical imaging technique in which a divorce generates a magnetic field to obtain detailed sectional images of the internal structures of the body |
|
|
|
PET positron emission tomography |
Medical imaging technique in which radiopharmaceuticals are traced to reveal metabolic and physiological functions in tissues |
|
|
|
Ultrasonography |
Application of ultrasonic waves to visualize subcutaneous body structures such as tendons and organs |
|
|
|
X-ray |
Form of high energy electromagnetic radiation with short wavelength capable of penetrating solids and ionizing gases; used in medicine as a diagnostic aid to visualize body structures such as bone |
|

