![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
189 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomic Position |
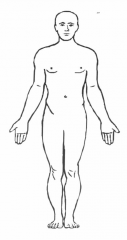
Refrence position
|
|
|
Coronal Plane |
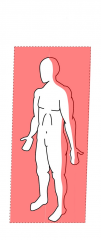
Frontal plane
|
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
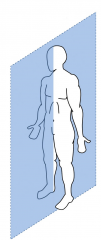
Lateral Plane Divides the body left and right. |
|
|
Transverse Plane
|
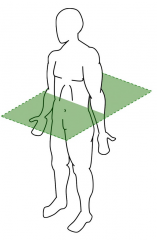
Axial Plane Divides the body top and bottom |
|
|
Midsagittal Plane |
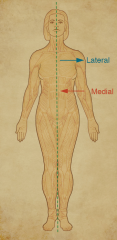
Midline The sagittal plane that runs from nose to navel. |
|
|
Midclavicular line |
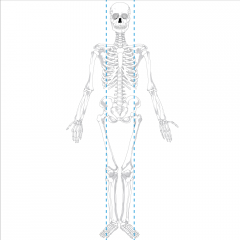
Anterior sagittal line that intersects the middle of the clavicle |
|
|
Midscapular line |
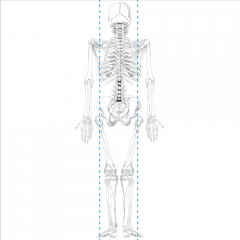
Posterioir sagittal line that intersects the middle of the scapula |
|
|
Superior |
Top The portion that is closer to the head. Opposite of inferior. |
|
|
Inferior |
Bottom The portion that is close to the feet. Opposite of superior |
|
|
Lateral
|
Outer Lie further from the midline. Opposite of medial |
|
|
Medial
|
Inner Lie closer to the midline. Opposite of lateral. |
|
|
Proximal
|
Closer to the trunk. Opposite of distal. |
|
|
Distal
|
Further from the trunk. Opposite of proximal. |
|
|
Superficial
|
Closer or on the skin. Opposite of deep. |
|
|
Deep
|
Further inside the body. Opposite of superficial. |
|
|
Ventral
|
Anterior or belly side. Opposite of dorsal. |
|
|
Dorsal
|
Posterior or spine side. Opposite of ventral. |
|
|
Anterior
|
Ventral or belly side. Opposite of posterior. |
|
|
Posterior
|
Dorsal or spine side. Opposite of anterior. |
|
|
Palmar
|
Front of the hand. Relating to the palm. |
|
|
Plantar
|
Surface of the foot; relating to the sole. |
|
|
Apex
|
The tip of a structure. Opposite of base.
|
|
|
Base |
The blunt part of a structure. Opposite apex. |
|
|
Flexion |
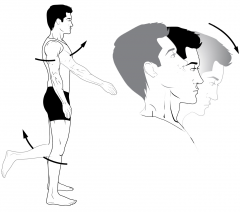
Bending of a joint. Opposite extension. |
|
|
Extension
|
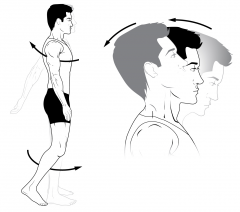
Straightening of a joint. Opposite flexion. |
|
|
Adduction
|
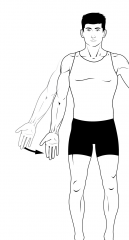
Motion toward the midline |
|
|
Abduction
|
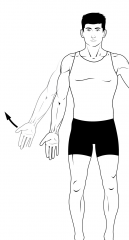
Motion away from the midline. |
|
|
Bilateral |
Appearing on both sides of the midline. (i.e. eyes, ears, etc...) |
|
|
Unilateral |
Appearing on one side of the midline. (i.e. heart, liver or stroke pain / paralysis) |
|
|
Prone position |
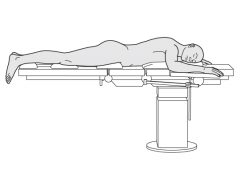
|
|
|
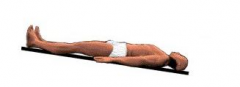
Supine position |
|
|
|
Trendelenburg position |
|
|
|
Semi-Fowler position |

Sitting up without knees bent |
|
|
Fowler's position
|
|
|
|
Modified Trendelenburg position |
Shock position Legs elevated bent at hips; torso and head level. More common. |
|
|
Left Lateral Recumbent position |
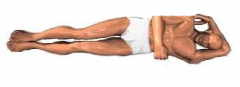
Recovery position
|
|
|
Right Lateral Recumbent position |
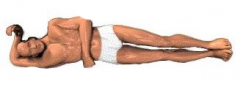
Patient lies on the right side |
|
|
Torso |
Trunk of the body |
|
|
Body Regions |
|
|
|
Body Systems |
|
|
|
Integumentary system |
Skin |
|
|
Endocrine system |
Hormones |
|
|
Ligament |
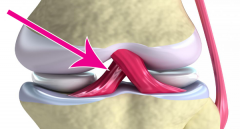
A band of tough, flexible, fibrous connective tissue that connects two bones or cartilages or holds together a joint. |
|
|
Tendon |
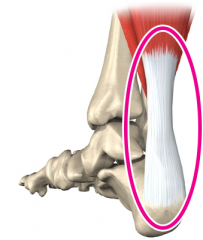
Flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen which connects muscles to bones. |
|
|
Cartilage |
|
|
|
Axial Skeleton |
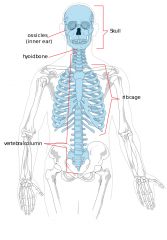
Foundation where the arms and legs are hung.
|
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
|
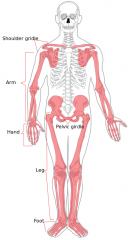
Rest of the skeleton
|
|
|
Skull |
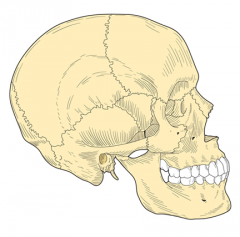
|
|
|
Cranium
|
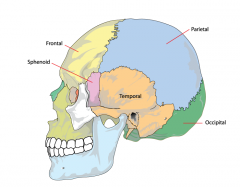
Comprised of 4 thick bones, fused bones above the eyes and ear to protect the brain.
|
|
|
Fontanelles
|
Soft spots on the top of an infant's head where the bones have not fuzed together. |
|
|
Foramen Magnum
|
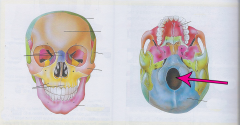
|
|
|
Frontal bone |
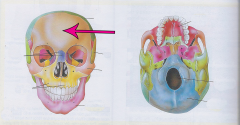
Forehead |
|
|
Sphenoid |
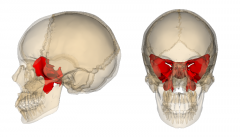
Basilar skull
|
|
|
Occiput bone |
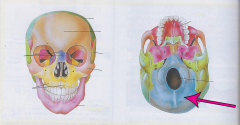
Most posterior part of the cranium |
|
|
Temporal bone |
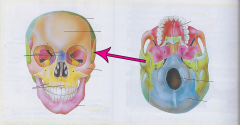
Temples Lateral portion of the cranium |
|
|
Parietal bone |
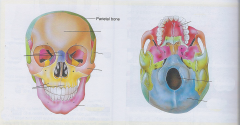
Sides and crown of the head |
|
|
Facial bones |
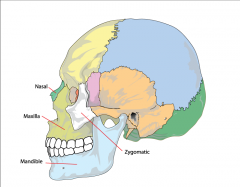
Includes:
|
|
|
Mandible |
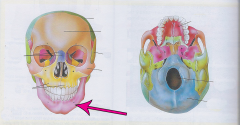
Jawbone largest, strongest and lowest bone in the face |
|
|
Maxillae
|
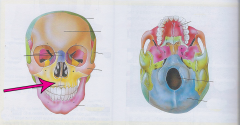
Two maxilla bones forming the upper jaw and palate of the mouth |
|
|
Zygomatic bone |
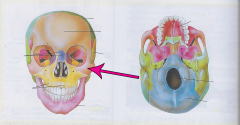
Cheekbone / malar bone largest, strongest and lowest bone in the face |
|
|
Nasal bone
|
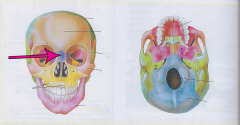
Bridge of the nose |
|
|
Orbit |
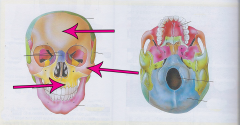
Eye Socket
|
|
|
Head & Neck Topography |
|
|
|
Mastoid process |
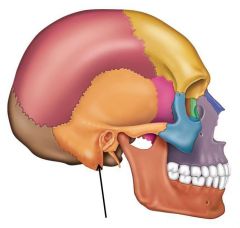
A protrusion of the temporal bone |
|
|
Temporomandibular joint |
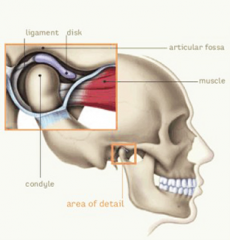
TMJ The joint between the between the mandible and temporal bone |
|
|
Spinal Column
|
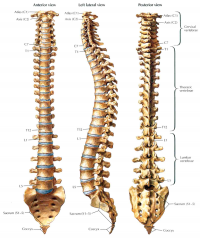
Includes:
|
|
|
Cervical spine
|
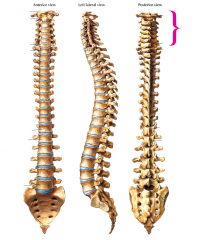
|
|
|
Thoracic spine |
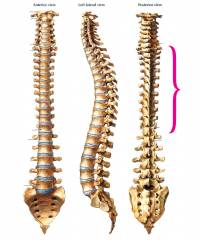
|
|
|
Lumbar spine |
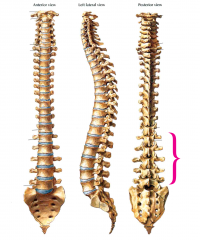
|
|
|
Sacrum
|
|
|
|
Coccyx |
Tailbone
|
|
|
Thorax
|
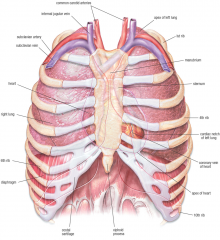
Thoratic cavity / Chest
Contains
|
|
|
Great Vessels |
Aorta and two venae cavae |
|
|
Sternum |
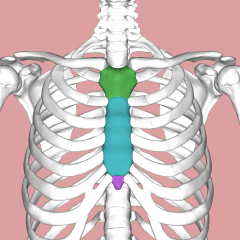
Brestplate
|
|
|
Suprasternal Notch |
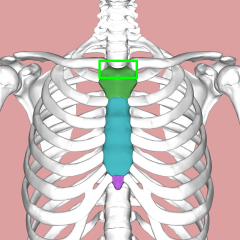
Jugular Notch
|
|
|
Mandibrim |
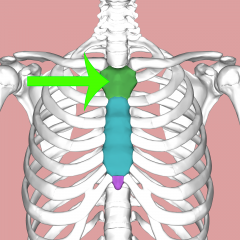
Upper section of the sternum |
|
|
Sternum Body |
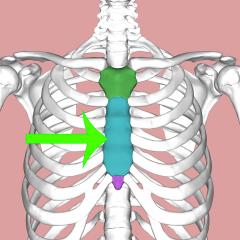
|
|
|
Xiphoid process |
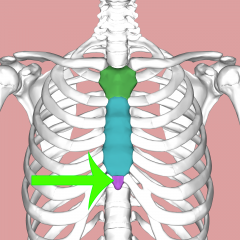
A narrow cartilaginous tip inferior to the body of Sternum |
|
|
Upper extremity
|
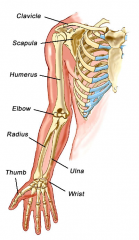
|
|
|
Shoulder Girdle |
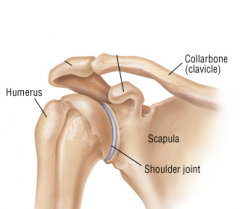
Shoulder Joint Comprised of 3 bones: Clavicle, Scapula and Humerus |
|
|
Clavicle |
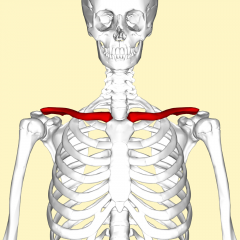
Collar Bone
|
|
|
Scapula |
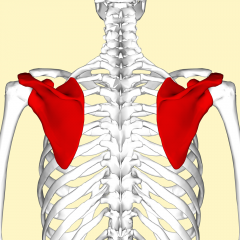
Shoulder blade
|
|
|
Humerus |
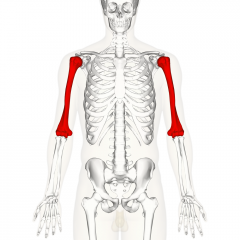
Upper Arm Long bone that runs from the shoulder to the elbow |
|
|
Radius |
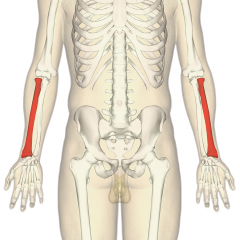
|
|
|
Ulna
|
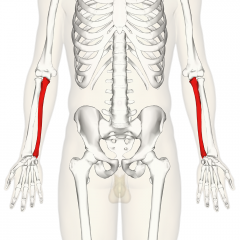
|
|
|
Hand |
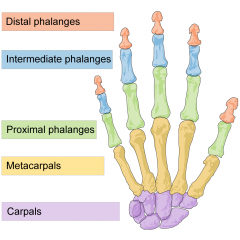
Comprised of:
|
|
|
Carpals |

Wrist
|
|
|
Metacarpals
|
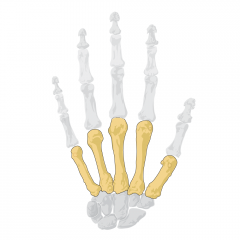
Hand bones |
|
|
Phalanges |
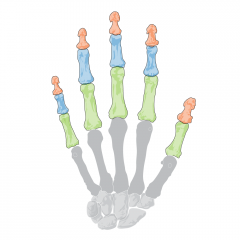
Fingers / digits
|
|
|
Bicep |
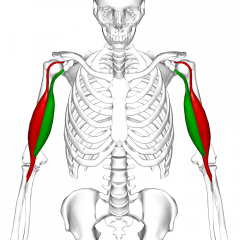
|
|
|
Tricep |
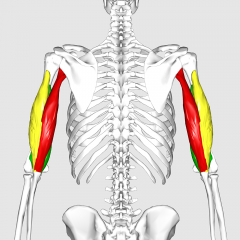
|
|
|
Brachial artery |
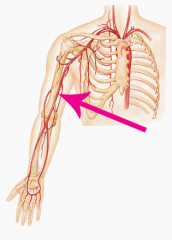
The major blood vessel of the upper arm between the elbow and wrist |
|
|
Radial artery |
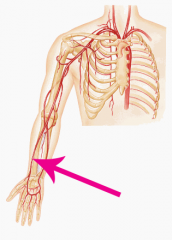
The main artery of the lateral forearm |
|
|
Ulnar artery
|
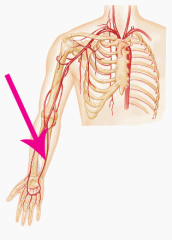
The main artery of the medial forearm |
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Space below the diaphragm and above the rim of the pelvis |
|
|
Quadrants |
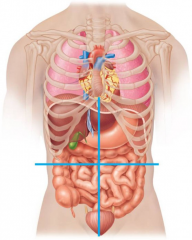
|
|
|
RUQ
|
Right Upper Quadrant
|
|
|
RLQ |
Right Lower Quadrant
|
|
|
LUQ |
Left Upper Quadrant
|
|
|
LLQ |
Left Lower Quadrant
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Double membrane that reduces friction between moving organs
|
|
|
Visceral Organs |
Solid Organs
Include:
|
|
|
Hollow Organs |
Include:
|
|
|
Pelvis |
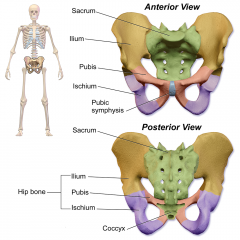
Closed bony ring that consists of three bones: the sacrum and the two pelvic bones.
|
|
|
Pelvic bone |
Hip bone Formed by fusing three separate bones
|
|
|
Pubic Symphysis
|
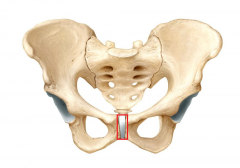
|
|
|
Iliac crest |
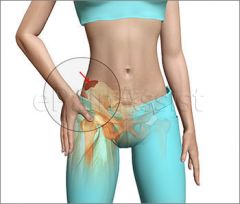
the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superolateral margin of the greater pelvis. |
|
|
Acetabulum |
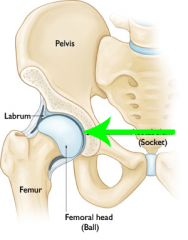
Hip joint Ball-joint where the head of the femur fits into the pelvis |
|
|
Lower Extremity
|
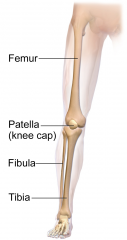
Bones: Femur, Patella, Fibula, Tibia, Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges Arteries: Femoral |
|
|
Femur |
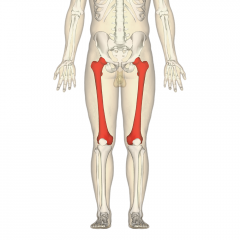
|
|
|
Patella |
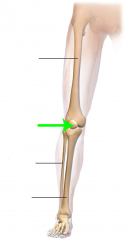
Kneecap Covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint |
|
|
Tibia |
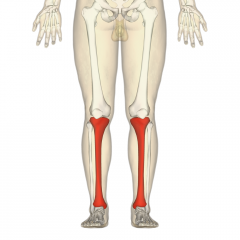
Shinbone |
|
|
Fibula |
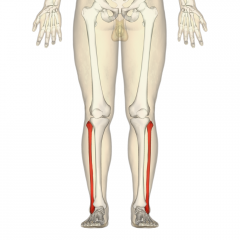
|
|
|
Foot |
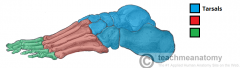
|
|
|
Tarsals |
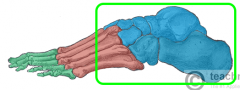
|
|
|
Metatarsals |
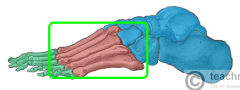
|
|
|
Phalanges |
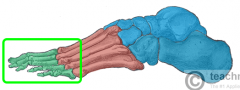
|
|
|
Femoral Artery |
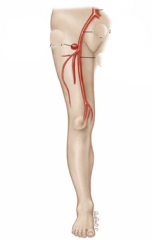
The main arterial supply to the lower limb. |
|
|
Articulation
|
Joint
|
|
|
Symphysis |
A fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones that creates a slightly movable joint. (e.g. the pubic symphysis) |
|
|
Joint capsule
|
|
|
|
Sacroiliac joint
|
|
|
|
Synovial membrane |
|
|
|
Synovial fluid
|
A thick lubricant that allow the bones to glide over each other. |
|
|
Ball-and-socket joint
|
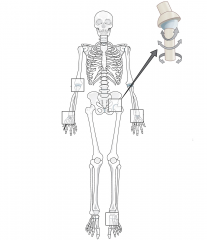
A joint that allows for rotation and bending |
|
|
Hinge joint |
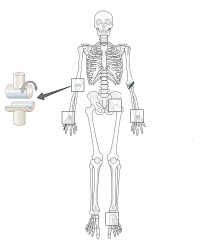
|
|
|
Pivot Joint |
|
|
|
Skeletal system |
|
|
|
Musculoskeletal system
|
Locomotion system
|
|
|
Muscles |
|
|
|
Involuntary muscle
|
Smooth and Cardiac muscle
|
|
|
Smooth muscle |
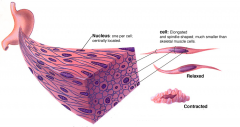
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle
|
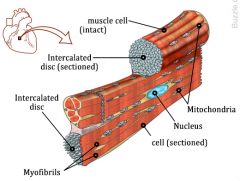
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle
|
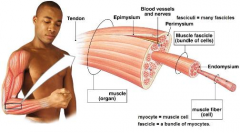
Voluntary muscle
|
|
|
Antagonistic pairs
|
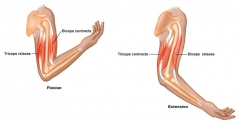
Muscle groups that work against each other to provide full range of motion (i.e. bicep & tricep) |
|
|
Pectoral |
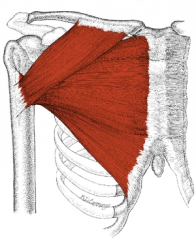
Pecs
|
|
|
Latissimus dorsi |
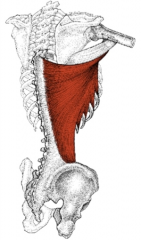
Lats
|
|
|
Rectus abdominis |
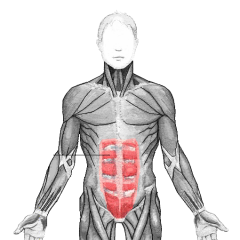
Abs
|
|
|
Tibialis anterior |
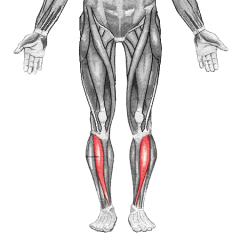
|
|
|
Gastrocnemius
|
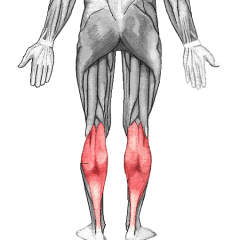
|
|
|
Quadriceps
|
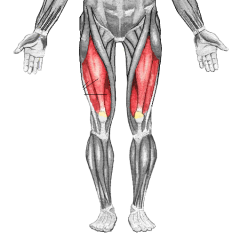
Quads
|
|
|
Biceps femoris |
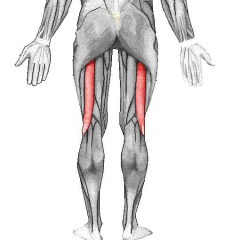
|
|
|
Gluteus
|
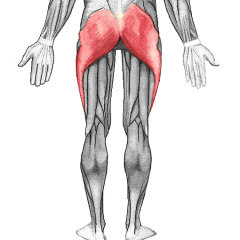
|
|
|
Pronation |
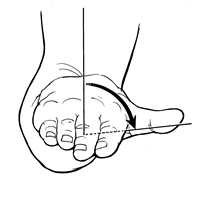
Rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces poisteriorly or down |
|
|
Supination |
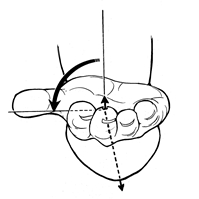
Rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces anteriorly or up |
|
|
Dorsiflexion
|
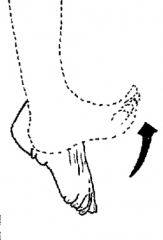
Flexion of the entire foot superiorly (point toes up) |
|
|
Plantar flexion
|
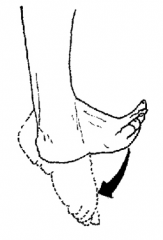
Flexion of the entire foot down (point toes down) |
|
|
Eversion
|
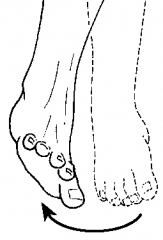
|
|
|
Inversion |
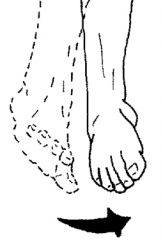
|
|
|
Respitory system
|
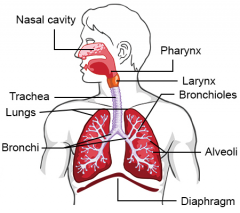
All of the structures in the body that contribute to breathing. Includes the mouth, nose, throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles. |
|
|
Upper airway |
|
|
|
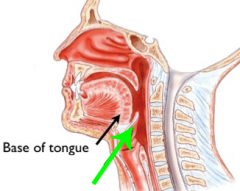
Pharynx |
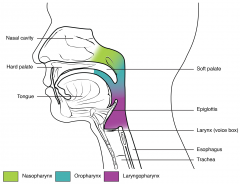
Throat
|
|
|
Nasopharynx |
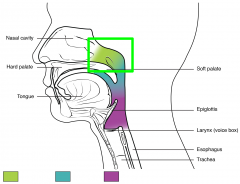
The space above the soft palate at the back of the nose and connects the nose to the mouth |
|
|
Oropharynx
|
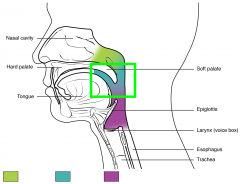
The throat at the back of the mouth |
|
|
Laryngopharynx |
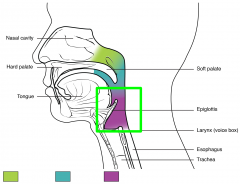
Sits behind and on either side of the larynx |
|
|
Larynx |
Voice box |
|
|
Epiglottis
|
|
|
|
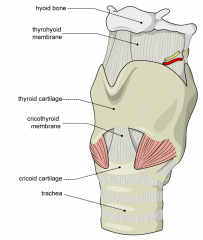
Hyoid bone |
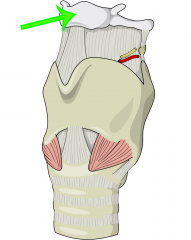
|
|
|
Thyroid cartilage |
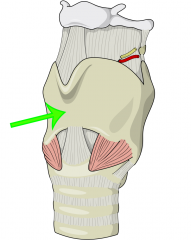
Adams Apple |
|
|
Cricoid cartilage
|
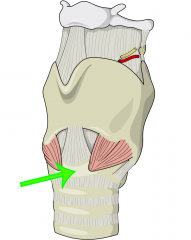
* Only full ring of cartilage in the upper airway * Location for using the Sellick maneuver |
|
|
Cricothyroid Membrane |
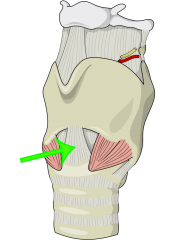
* Can be felt as a depression in the midline of the neck * Where a needle device can be inserted |
|
|
Trachea |
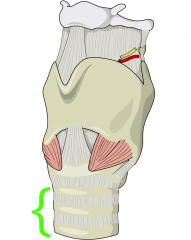
* Apart of the lower airway * About 5" long semi-rigid tube * Supported by incomplete rings of cartilage * Ends at the carina and divides into two smaller tubes |
|
|
Mainstem Bronchi
|
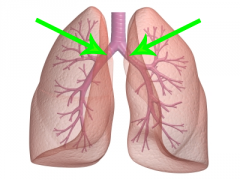
* Labeled Left and Right * Tubes that connect the trachea to the lungs |
|
|
Bronchi
|
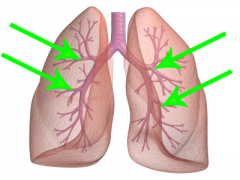
* progressively smaller branches off of the Mainstem * 3 Major on the Right, 2 on the Left |
|
|
Bronchiole
|
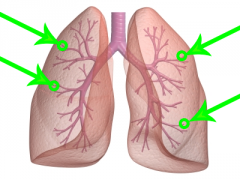
* Lowest level division of Bronchi * Have tiny sacs called alveoli |
|
|
Lung
|
|
|
|
Alveoli |
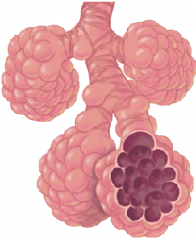
|
|
|
Pleura |
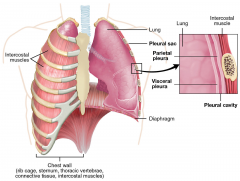
|
|
|
Parietal pleura |
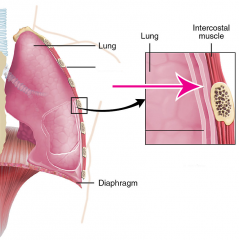
The lining in the chest wall |
|
|
Visceral pleura |
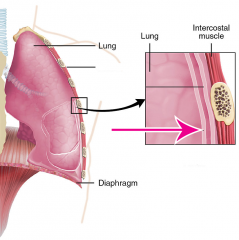
The outside covering of the lungs |
|
|
Pleural Space |
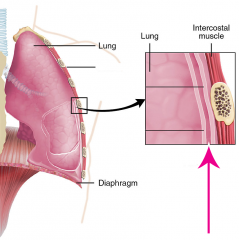
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
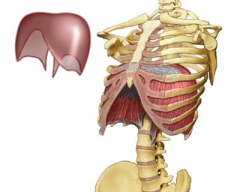
|
|
|
Negative Pressure Breathing |
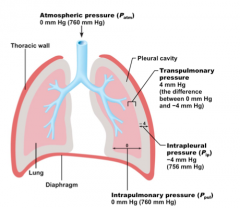
Breathing caused by the Diaphragm, intercostal muscles, abdominal muscles and pectoral muscles contracting which forms a negative space in the chest cavity which then pulls the lungs open and vaccumes air into the lungs. |
|
|
Ventilation |
Movement of air between the lungs and the environment. |
|
|
Respiration |
The process of gas exchange
|
|
|
Inhalation |
Air into the lungs
|
|
|
Exhalation |
Air flows out of the lungs
|
|
|
Inhaled Air |
|
|
|
Exhaled Air |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
A passive process where molicules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
Capillary |
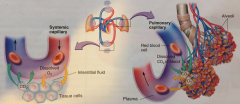
A site here gas exchange for blood occurs |
|
|
Systemic Capillary |
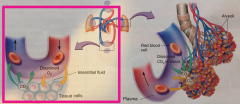
The point at which O2 is given to a cell from the blood and waste CO2 is taken |
|
|
Pulmonary Capillary |
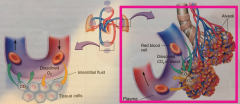
The point at which waste CO2 is given from the blood and O2 from the atmosphere is taken |
|
|
Tidal volume |
|
|
|
Inspiratory reserve volume |
IRV
|
|
|
Expiratory Reserve Volume |
ERV
|
|
|
Residual Volume |
|
|
|
Dead space |
The space in the airway that does not have alveoli and therefore does not contribute to blood gas exchange |
|
|
Lung Capacity |
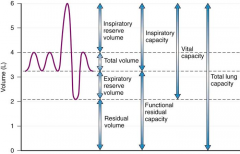
|

