![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
182 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 main shockble and non shockble rhythms? |
Shockable: ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation Non shockable: PEA and asystole |
|
|
What is the survival rate for in and out of hospital cardiac arrests? |
Out: 10% In: 23.9% |
|
|
What are the 4 components of the chain of survival? |
1. Early recognition and call for help
2. Early cpr
3. Early defib
4. Post resuscitation care |
|
|
By what percentage is survival reduced as each minute passes without defib? |
10-12% |
|
|
Draw the ALS algorithm |
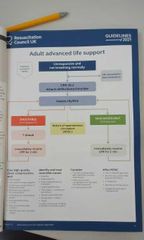
|
|
|
When do you give adrenaline and amioderone in the ALS algorithm? |
Adrenaline every 3-5 mins Amioderone every 3 shocks (6min) |
|
|
What are the 4 Hs and Ts |
H: Hypoxia Hypovolaemia Hypothermia Hyper/hypokalaemia T: Tension pneumothorax Toxins Tamponade Thrombus |
|
|
What are the 4 keynon technical skills? |
Situational awareness Decisions making Team working and leadership Task management |
|
|
Give examples of poor non technical skills |
Poor communication Poor leadership Unwillingness to help Absence of clear roles Poor decision making |
|
|
Poor communication is linked to what percentage of adverse incidents or near misses the in hospital? |
80% |
|
|
What is SBAR and RSVP? |
Sbar: situation, background, assessment, recommendation Rsvp: Reason, story, vital signs, plan |
|
|
In what percentage of patients are there clinical signs of deterioration prior to arrest? |
80% |
|
|
What are the 2 most common signs suggesting a cardiac arrest may occur? |
Hypoxia Hypotension |
|
|
What does NEWS stand for? |
National early warning score |
|
|
In order of severity, give 4 airway opening manoeuvres |
1.head tilt/chin lift 2.jaw thrust 3. Oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal adjuncts 4. Tracheostomy or intubation |
|
|
Give three neurological conditions that can cause cardiac arrest secondary to inadequate respiratory effort |
Guillain Barre Ms Myasthenia gravis |
|
|
What 2 measurements on an ABG can indicate severe respiratory problems? |
Rising C02 Low pH |
|
|
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death |
CAD |
|
|
Give 3 examples of when syncope may suggest a cardiac disorder |
During or after exercise With little or no prodrome When laying flat Repeated unexplained syncope |
|
|
What respiratory rate indicates severe illness? |
>25 |
|
|
Give 2 causes of a low diastolic BP |
Anaphylaxis or sepsis |
|
|
Give 2 causes of a narrow BP |
Suggests vasoconstriction e.g. Cardiogenic shock or hypovolaemia |
|
|
Give 4 things out would check during D when doing A-E |
Drug chart BM Examine pupils Assess alertness with AVPU |
|
|
Give 4 things out would check during D when doing A-E |
Drug chart BM Examine pupils Assess alertness with AVPU |
|
|
What are the 3 features which typically occur during rupture of a atherosclerosis plaque causing ACS |
1. Plaque ruptures causing thrombus in the vessel 2. Smooth muscle cells contract 3. Embolism of thrombus to distal part of vessel |
|
|
Give 2 features of unstable angina you might see on an ECG |
ST depression T wave inversion |
|
|
Define STEMI, STEMI and UA, explaining how they are differentiated by ECG changes and trops |
STEMI: ST elevation or New LBBB plus trop rise NSTEMI: ECG changes may/may not be present. Tropes elevated. Common ECG changes include ST depression and T wave inversion UA. ECG changes may/may not be present. No trop rise. |
|
|
How is the chest pain in an aortic dissection different from ACS? |
Radiates to back |
|
|
What is the ultimate treatment for STEMI and ow should it be treated if out of the treatment window |
Primary percutaneous coronary intervention within 120 mins Fibrinolysis |
|
|
What chest leads show an anterseptal MI and what vessel is occluded? |
v1-v4
Left anterior descending |
|
|
What leads would show ST elevation in a inferior STEMI? |
2, 3, aVF |
|
|
What 4 leads would show ST elevation in a lateral STEMI? |
V5, v6, 1, aVL |
|
|
What is the main ECG feature of a posterior STEMI |
ST depression in the anterior chest leads |
|
|
What are the 4 initial treatments for ACS? |
Morphine Nitrates e.g. GTN O2 if Sats less than 94 Aspirin 300mg |
|
|
What adjunct is sometimes given during PPCI |
Glycoprotein 2b/3a inhibitors |
|
|
Give 3 drugs used for fibrinolysis. Give 3 additional drugs given to prevent further risks of thrombosis |
Fibrinolysis : LMWH, unfractionated heparin, fondaparinox Plus: Aspirin 300mg, clopidogrel, ticagrelor |
|
|
What post acute ix should be requested for someone with an NSTEMI and in what time frame? |
Angiography within 72 hours |
|
|
What class of drugs are given post MI to preserve left ventricular function? Give one other class of drug given which is cardioprotectice and typically given? |
ACEi Beta blockers |
|
|
What is the nme of the rhythm which indicates successful reperfusion following PCI? |
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm |
|
|
What are the 3 common symptoms of aortic stenosis? |
SAD Syncope Angina Dyspnoea |
|
|
In what time frame should cpr begin to achieve the best outcomes? |
3 min |
|
|
What ix can be used to check appropriate positioning of a tracheal tube? |
Waveform capnography |
|
|
When should a precordial thump be used? How likely is it to be successful? |
While waiting for a defib when a patient is in VF or pVT Rarely successful |
|
|
What is the main difference in treatment for PEA/systole vs VF/PVT? |
Defib for VF/PVT |
|
|
Draw the ALS algorithm |
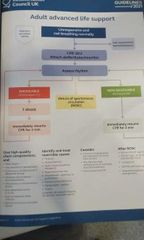
|
|
|
How common is it to have VF/PVT as the first observable rhythm? |
20% |
|
|
What is the max recommended gap between chest Compressions? |
5 sec |
|
|
What drugs may you give during CPR, when, and what amounts? |
Adrenaline, 1mg, every 3-5 mins (give in the 1st 2min cycle and then each alternate 2min cycle)
Amioderone, 300mg, every 3 shocks |
|
|
Give 4 things you should do after rosc |
Ae Temperature management Treat causes 02 Sats of 94-8% 12 lead ecg |
|
|
Give an alternative to amioderone |
Lidocaine |
|
|
When would you check for a pulse? |
2 min after giving a shock and only if the rhythm is compatible with life |
|
|
How is the ALS algorithm different in a monitored VF/PVT? |
Give up to 3 successive shocks If unsuccessfull, these 3 shocks count as one and you continue ALS as normal |
|
|
Why is there no pulse in pea? |
Electrical activity is present in myocardium but the contractions are too weak to be felt |
|
|
On the Non-shockable algorithm, what should you do if you spot VF/PVT during a brief pause? |
Finish the 2min cycle Team should prepare to give a shock at the next rhythm check |
|
|
What is the preferred airway device? How does this change the ALS algorithm? |
Igel Continuous chest compressions |
|
|
At what rate should you ventilate the lungs? |
10/min |
|
|
How can you confirm correct intubation? |
Waveform capnography |
|
|
What is the optimal rate of chest compressions? |
100-120/min |
|
|
Give 3 visible signs of rosc |
Eye opening Movement Breathing effort |
|
|
Give 3 uses of waveform capnography during cpr |
Assess quality of chest compressions Ensure tracheal tube/igel is properly positioned Indicate rosc Monitor RR Prognostic |
|
|
What does waveform capnography measure? |
End tidal co2 |
|
|
What airway is required for waveform capnography |
Intubation or igel |
|
|
Give 2 things you should do after delivering a drug through a peripheral cannula during CPR |
Flush with 20ml of saline and elevate arm Both are needed to ensure delivery to myocardium |
|
|
What are the 3 main sites for interosseous access? |
Proximal humerous Proximal tibia Distal tibia |
|
|
Give 3 contraindications to IO access |
Trauma, infection or prosthesis at proposed site
IO access in the same limb within 48hr
Failure to Id anatomical landmarks |
|
|
Give 3 cx of IO access |
Infection/osteomyelitisPain during infusionBone damageExtravasationinto into tissueCompartment syndromeNeedle dislodgementFat emboli |
|
|
Give 3 indications for calcium chloride in CPR |
Hyperkalaemia CCB overdos Hypocalcaemia |
|
|
What class of drugs are given if you suspect a PE? What after? |
Fibrinolytics Thrombectomy if available |
|
|
What are the 2 main Mx for pneumothorax? |
Needle thoracocentesis and chest drain |
|
|
How could you Dx cardiac Tamponade? |
Focused cardiac US |
|
|
Give 4 possible uses of US in CPR |
Cardiac Tamponade PE Ischaemia (via immobility) Aortic dissection Pneumothorax |
|
|
Roughly how long should you do cpr on someone with asystole? |
20 mins |
|
|
Where is the most common site of airway obstruction? |
Pharynx |
|
|
What visible sign is seen in complete airway obstruction? |
See saw breathing |
|
|
What should you with a patient who has mild airway obstruction? |
Encourage cough |
|
|
What should you do with a patient who is unconscious with severe airway obstruction? |
Cpr |
|
|
What should you do with a patient who is conscious with severe airway obstruction? |
5 back blows
5 abdo thrusts Continue to alternate and start cpr if unconscious |
|
|
What are the 3 manoeuvres for opening airway? |
Head tilt Chin lift Jaw. Thrust |
|
|
When should you try to avoid using a nasopharyngeal airway? |
Basal skull fracture |
|
|
How much 02 does a mask with a resevoir provide? |
85% |
|
|
How long is a normal qrs? |
Less than 0.12s |
|
|
Describe the appearance of VF on ECG |
Rapid, bizarre, irregular deflections. No effective coordination. No cardiac output. No pulse |
|
|
Describe the different spaces on ECG paper and how long they are in sec |
1 small square = 1mm 5 small squares = 5mm = 0.2 sec 1 big square (5×5 small squares) = 1 sec |
|
|
How do you calculate hr from an ECG? |
Count number of cardiac cycles (r wave to r wave) in 6 sec (30 large squares) and multiply by 10 In shorter rhythm strips count the number of large squares in 3 sec (15 large squares) and multiply by 20 |
|
|
On an ECG, what determines a narrow QRS? If longer than this, where in the heart does the rhythm originate? |
Less than 0.12 sec which is 3 small squares or less Ventricles or supra ventricular but with BBB |
|
|
What is the common heart rate of atrial flutter? Describe the appearance of the p waves |
300 Saw tooth |
|
|
Give three characteristic visivle features of atrial fibrillation |
Broad qrs Irregular Tachycardic |
|
|
Give one other rhythm which could be confused with atrial fibrillation |
Polymorphic vt |
|
|
What type of rhythm may result from a prolonged qt? |
Polymorphic vt |
|
|
Give 2 electrolyte abnormalities associated with torsades de pointes |
Hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia |
|
|
Give 2 emergency treatments for bradycardia |
Pacing Atropine |
|
|
What is the normal pr interval? |
0.12-2 seconds. 3-5 small squares |
|
|
Describe the appearance of 1st degree hb What causes it? |
Fixed and prolonged pr greater than 0.2 seconds (5 small squares) Delayed conduction through AV node or bundle of his |
|
|
Describe second degree hb mobitz type 1 and 2 |
Progressive increase in pr followed by dropped qrs Fixed and prolonged pr with dropped qrs |
|
|
Describe 2:1 AV block |
2 P wave for every one qrs |
|
|
Describe 3rd degree hb |
No association between p waves and qrs I. E. separate peacemakers |
|
|
Describe an agonal rhythm |
Broad and irregular looks like a gradual straitening of the line I. E. gradual approach to asystole |
|
|
What lead best shows AF? What is the typical rate? |
1 120-180 |
|
|
What leads best show atrial flutter? What is the typical rate? |
2,3, avf5 |
|
|
For every minute which passes, what does the chance of mortality? |
7-10% |
|
|
Give 2 advantages of manual defibrillators compared AEDs |
Synchronised shocks Pacing ability |
|
|
With a manual defib, what should be the starting shock energy? |
120-150joules |
|
|
What is the intrinsic rate at the sa and AV nodes |
Sa: 60-70 Av: 40-50 Intrinsic pace decreases distally |
|
|
What are the 2 types of non invasive pacing? |
Percussion (fist pacing) Transcutaneous |
|
|
What are the 2 types of invasive pacing? |
Transvenous (temp) Permanent I. E. pacemaker |
|
|
What is the main disadvantage of Transcutaneous pacing? |
Pain |
|
|
How do you know you have chosen therrect position and current when using Transcutaneous pacing? |
Pacing spike is followed by qrs and T wave and there is a pulse |
|
|
Give 3 ways transvenous pacing may fail |
High threshold (tends to increase so needs to be regularly checked) Lead displacement Connection failure |
|
|
What are the 3 main types of treatment in a brady/tachy arrhythmia? |
Simple clinical intervention e. G. Vagal manoeuvres, percussion pacing Pharmacological Electrical e. G. Cardioversion for tachy or pacing for brady |
|
|
What is the first step for a patient who has adverse features and tachy arrhythmia? What do you do next? |
3x synchronised dc cardioversion Amioderone 300mg IV over 10-20 mins followed by further dc shock if needed |
|
|
Draw the algorithm for tachycardia |

|
|
|
What is the most common irregular Broad complex tachycardia? |
AF with BBB |
|
|
Give 3 treatment's for torsades de pointes |
Stop qt prolonging drugs Correct electrolytes /K Give Mg Consider pacing |
|
|
How would you treat a regular narrow complex tachycardia which does not have adverse features? |
Vagal manoeuvres (carotid sinus massage or. Valsalva) Adenosine 6, 12, 18 Verapamil or b blocker |
|
|
Give 2 drugs used for rhythm control |
Propafenone Flecainide |
|
|
How should you treat a patient with a brady arrhythmia and. Adverse features? |
Atropine 500mcg IV then pacing |
|
|
Draw the bradycardia algorithm |

|
|
|
Give 4 causes of high K |
Renal failure Drugs e. G. ACEi, ARBs, K sparing diuretics Tissue breakdown e. G. Rhabdomyolysis, haemolysis Metabolic acidosis e. G. renal failure, DKA Endocrine e. G. Addisons Diet |
|
|
Give 4 possible ECG changes of high K |
1st degree hb Flattened/absent P waves Tall T waves ST depression Widening of QRS |
|
|
How would treat kigh K |
Calcium resonium Insulin dextrose Calcium gluconate 10ml, 10%, 6 mins Neb salbutamol Dialysis |
|
|
Give 4 causes of low K |
Gi losses Drugs e. G. Diuretics, laxatives, steroids Endocrine e. G. Cushings Metabolic alkalosis Low Mg Low dietary intake |
|
|
Give 4 drug overdoses which can be treated with activated charcoal |
Carbemazepine Dapsone Phenobarbital Quinine Theophylline |
|
|
What are the doses for naloxone? |
400mcg if IV 800mcg if SC/IM |
|
|
What drug is used to treat benzo OD? |
Flumazenil |
|
|
What drug is used to treat TCA OD? |
Sodium bicarb |
|
|
What drug is used to treat OD on stimulants e. G. Cocaine, amphetamines? |
Benzos |
|
|
Which drug is given for organophosphate OD? |
Atropine |
|
|
What are the main mechanisms causing death in asthma? |
Bronchospasm >> asphyxia Mucous plugging >>asphyxia Arrhythmia secondary to hypoxia Tension pneumothorax |
|
|
Give 6 treatment for severe asthma |
O2 Neb salbutamol Neb ipratropium bromide Steroids 40-50mg Iv magnesium Aminophyline Intubation |
|
|
Give 3 signs of anaphylaxis |
Rapid onset of symptom Airway compromise Skin/mucosal changes |
|
|
Where should I'M adrenaline be injected in anaphylaxis? |
Angerolateralnmid thigh |
|
|
Describe treatment of anaphylaxis including dosages |

|
|
|
Give 2 drugs you might give after treatment of anaphylaxis |
Steroids Antihistamines |
|
|
What test confirms anaphylaxis has occurred? |
Mast cell tryptase within 2-4 hours |
|
|
What is commotio cordis? |
Cardiac arrest caused by blunt force trauma |
|
|
Give 1 drug that is used in traumatic hemorrhage which may stop cardiacnarrest |
Tranexamic acid |
|
|
What is the definitive treatment for cardiac Tamponade? |
Thoracotomy |
|
|
What is the treatment for tension pneumothorax? |
Needle insertion 4-5th intercostal space, mid axillary line Chest drai Thoracotomy |
|
|
What is the initial response to submersion in water? |
Breath holding leading to hypoxia and hypercapnoea and bradycardia |
|
|
What should be your immediate management when removing someone from water? |
5 rescue breaths |
|
|
How does temp affect survival in drowning? |
Hypothermia is protective |
|
|
At what temp does hypothermia begin |
Under 35 degrees |
|
|
Give 4 risk factors for hypothermia |
Old/young Drugs and alcohol Exhaustion Illness Neglect |
|
|
How long should you check for signs of life. In a hypothermic patient? |
1 min |
|
|
When should you start giving drugs in hypothermia? |
When core temp is above 30 |
|
|
What is malignant hyperthermia? |
Genetic predisposition to hyperthermia with anaesthetic drugs |
|
|
Give 4 risk factors for hyperthermia |
Elderly Dehydration Obesity Alcohol CVD Anticholinergics |
|
|
What are the 3 features of heat stroke? |
Severe hyperthermia with temp above40 Neurological symptoms Exposure to high temps or strenuous exertion |
|
|
What can he stroke mimic? Give 4 |
Sepsis Toxicity Withdrawal Serotonin syndrome Endocrine e.g. Phaochromacytoma, thyroid storm |
|
|
Give 4 treatments for hyperthermia |
Move to cool environment Begin cooling, rapid Iv isotonic fluids Correct electrolytes |
|
|
What drug is given in malignant hypothermia? Give 2 other mx |
Dantrolene Cooling V fluids Replace electrolytes |
|
|
What are the 4 components of post cardiac arrest syndrome? |
Brain injury Myocardial dysfunction Systemic ischaemia/reperfusion response Persistent precipitating pathology |
|
|
What percentage should you maintain 02 during post resusc care? |
94-98 |
|
|
Draw post resusc care |

|
|
|
When would you consider delayed PCI (2)? |
When there is (1) a low probability of an ischaemic cause which (2) allows optimisation of post resus care |
|
|
What is the typical consequence of cardiac arrest due to hypovolaemia RE acid/base levels? |
Typically causes metabolic acidosis |
|
|
What is the consequence of hypoperfusion on pH in cardiac arrest? |
Metabolic acidosis (low bicarb and high lactate) |
|
|
Give to places you might transfer a patient post cardiac arrest |
ICU, CCU |
|
|
Give 2 drugs commonly used following cardiac arrest during post resusc care |
Dobutamine Noradrenaline Plus IV fluids |
|
|
What is the most common post resusc electrolyte abnormality? |
Hyperkalaemia first, then hypokalaemia |
|
|
What range should potassium be maintained post resus? |
4-4.5 |
|
|
Give 3 drugs used for sedation in post resus |
Propofol Alfentanil Remifentanil |
|
|
How common is seizure in cardiac arrest? What causes it? |
20-30% Hypoxic ischaemic brain injury |
|
|
Give 2 ways you could detect seizure post resus? |
Visual EEG |
|
|
Give 2 drugs used for treating sezures |
Levetiracetam Sodium valproate |
|
|
What is the optimal BM range post resus? |
4-10 |
|
|
What temperature range is appropriate in TTM and for how long? |
32-36 More than 24 hrs |
|
|
What are the 3 phaes of TTM? |
Induction Maintenance Rewarming |
|
|
What I Can be given for TTM, how much and what temp? Give 4 other methods of cooling in TTM |
IV saline or hartmanns 30ml/kg at 4 degrees Ice packs, cooling blankets, water/aircirculating blanketsintravascularheat exchanger, ECMO |
|
|
What is the biggest factor affecting survival in out of hospital arrests? |
Early recognition of cardiac arrest and CPR |
|
|
By what percentage does mortality increase for every minute which passes without defib after arrest? |
10% per minute |
|
|
Give 2 scenarios where mechanical chest compressions may be suitable |
Persistent arrhythmia needing transport for angiography or PCI Hypothermia |
|
|
Give 5 scenarios where paramedics do not need to perform CPR |
Dna cpr Decapitation Massive cranial destruction Incineration (more then 95% full thickness burns) Decompesition Rigor mortis |
|
|
Give 3 scenarios where prolonged cpr may be appropriate |
Hypothermia Drowning Under 18 Poisoning Pregnancy |
|
|
How can you treat aggressive patients post rosc? |
IV diazepam or midazolam |
|
|
When alerting a centre (e.g. Catch lab) prior to arrival, what information should you give? |

ATMIST
|
|
|
Give the 4 approaches to reading blood gas |
O2 PH Co2 Hco3 |
|
|
Describe the following: PH less than 7.35 with high paco2 PH more than 7.45 with low paco2 |
Respiratory acidosis Respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
Describe the following:PH less than 7.35 with low bicarb PH more than 7.45 with high bicarb |
Metabolic acidosis Metabolic alkalosis |
|
|
Where is bicarb produced? What is the normal range? |
Kidneys 22-26 |
|
|
What is the normal range for base access+ |
-2 to +2 (acidic-alkali) I. E. - 2 equals metabolic acidosis and vice versa |
|
|
What are the 2 scenarios where you do not need to discuss cpr with a patient or relative |
If it will cause physical or psychological harm If patient lacks capacity and you are unable to reach a relative in time 3.g. Emergency |

