![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three toxicants discussed? |
Ethanol |
|
|
What are the three antidotes discussed?
|
Disulfiram |
|
|
What are the two drugs for ethanol withdrawal?
|
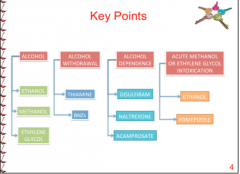
Diazepam |
|
|
What are the two drugs for chronic alcoholics?
|
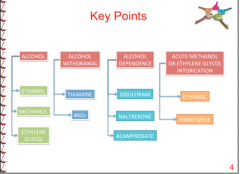
Naltrexone |
|
|
Through what two general areas do drugs treat alcohol dependency?
|
Changes in ethanol metabolism |
|
|
What enzyme does disulfram inhibit?
|
Aldehyde dehydrogenase
|
|
|
What enzyme does fomepizole inhibit?
|
Alcohol dehydrogenase |
|
|
What is the general pathway of the metabolism of alcohol?
|
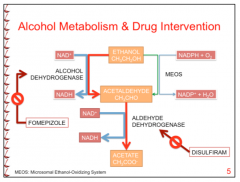
Alcohol -->acetaldehyde -->> acetate |
|
|
Which enzyme deficiency is responsible for Asian flush?
|
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (single nucleotide polymorphic changes) |
|
|
True or false, research indicates that acetaldehyde has effects in the central nervous system pleasure center in the VTA |
TRUE!
Asians experience increased pleasure from aldehyde buildup after alcohol intoxication |
|
|
Ethanol is an important inducer of which CYP? |
CYP2E1
|
|
|
If CYP2E1 is normal (or not induced by alcohol), what is acetaminophen predominantly conjugated to?
|
Sulfate conjugate (non-toxic) |
|
|
If CYP2E1 is induced (by ethanol), what does acetaminophen metabolism give rise to?
What is administered as an antidote for toxicity from acetaminophen? |
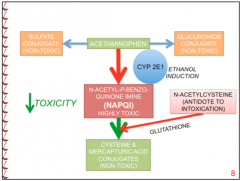
NAPQI (highly toxic) which is then converted to cysteine and mercapturic acid conjugated (non-toxic) after administration of glutathionine (N-acetylcysteine) |
|
|
At what BAL would you see PRONOUNCED incoordination?
|
50-100 |
|
|
At what BAL would you see COMA, RESPIRATORY INSUFFICIENCY AND DEATH?
|
>400 |
|
|
At what BAL would you see mood and personality changes?
|
100-150 |
|
|
At what BAL would you see nausea, vomiting, marked ataxia, amnesia, and dysarthria?
|
150-400 |
|
|
What are some key pathways in the brain that ethanol modulates?
|
Inhibitory actions of GABA |
|
|
What are some other acute effects of alcohol? Cardiovascular and uterine |
CV depressant |
|
|
Who will have a higher BAL? A person with a larger, leaner body mass or a fat person?
|
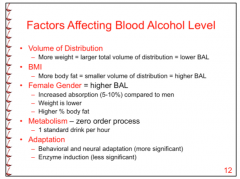
The fatty.
Alcohol excluded from fat |
|
|
What is the order of alcohol metabolism?
|
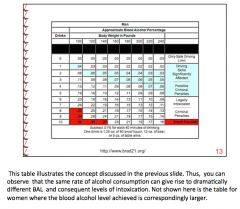
ZERO ORDER PROCESS |
|
|
What are some of the chronic effects of ethanol in the liver?
Gluconeogenesis |
--Decreased gluconeogenesis which leads to hypoglycemia. |
|
|
What are some GI problems from chronic alcoholism? |
Bleeding, scarring which leads to absorptive and nutritional deficiencies |
|
|
What are some CNS problems that result from chronic alcoholism? |
Peripheral neuropathy
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome = ataxia, confusion, ocular muscle paralysis |
|
|
What do you treat Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome with? |
Thiamine
|
|
|
What are some endocrine problems that result from chronic alcoholism? |
Gynecomastia and testicular atrophy (due to steroid insufficiency) |
|
|
What does a thiamine deficiency cause?
|
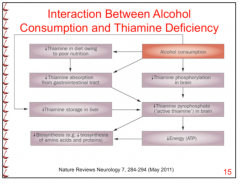
Inability to synthesize and replenish critical amino acids and proteins (especially in the CNS). |
|
|
What are some CV effects of chronic alcoholism?
|
HTN, anemia, dilated cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias with binges |
|
|
What are the positive effects of moderate alcohol consumption?
|
Increase in HDL which may protect against CHD
|
|
|
What major cancer is increased in alcoholics?
|
GI cancer
|
|
|
What are the immune system effects of chronic alcoholism?
|
Enhanced inflammation of liver and pancreas, but reduced immune response in other tissues |
|
|
What is usually administered in an "intoxicated" patient?
|
Dextrose (for hypoglycemia) |
|
|
What is administered in a "withdrawing" patient?
|
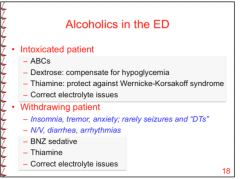
BNZ sedative (long acting diazepam or lorazepam if liver function is a concern)
Use long acting DIAZEPAM unless concern over hepatic function => use LORAZEPAM |
|
|
What drugs give a "disulfiram-like" effect? |

Sulfonylureas, cefotetan, ketoconazole, procarbazine |
|
|
What is the mechanism of disulfiram?
|
Inhibits ALDH which increases acetaldehyde. |
|
|
What is the mechanism of naltrexone?
|
Opioid antagonist
Decreases drinking through decreased feeling of reward with alcohol and/or craving |
|
|
What is the mechanism of acamprosate?
|
Weak NMDA antagonist, activates GABA receptors (predominantly GABA) |
|
|
The corticomesolimbic dopaminergic pathway (goes from ventral tegmental area (VTA) to nucleus accumbens. It is activated by alcohol through the release of what neurotransmitters?
|
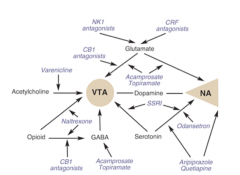
Opioids, serotonin, glutamate, GABA, and acetylcholine |
|
|
What is the product of ethylene glycol metabolism?
Negative effects? What drug acts inhibits the enzyme involved in this reaction? |
Oxalic acid (nephrotoxicity and acidosis) |
|
|
What is the product of methanol metabolism? |
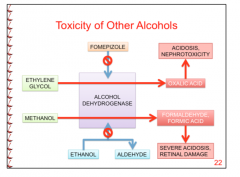
Formaldehyde (formic acid), severe acidosis and retinal damage
|
|
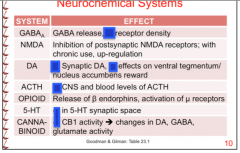
What are the effects of alcohol on each? |

|
|

What effect from alcohol?
When does this occur in pregnancy? |

|
|

|

|

