![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
251 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
When and where did agriculture begin? |
12,000 years ago In south west Asia |
|
|
|
Name 3 advantages of agriculture? |
More reliant food supply Specialization of skilled workers Developement of civilization Less time needed to feed people |
|
|
|
What and where were the first crop species domesticated? |
SW asia: wheat, pea, olive China: Rice, Millet America: Corn, beans, potato |
|
|
|
Name the 4 first domesticated livestock types? |
Dog, sheep, cattle, goat |
|
|
|
What are 4 main changes in animals during domestication? |
Changes of proportions of organs Changed reproduction cycles Imcrease in favorable traits for humans i.e.milk yield Changed behavior |
|
|
|
Name 3 production functions of agricultute. |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 service functions of agriculture. |

|
|
|
|
Define domestication. |
Reorganization of wild animals and plants into domestic and cultivated forms according to the interests of the people by isolation of the wild forms and later targeted breeding. |
|
|
|
What are 3 challenges faced by agriculture in developed regions? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 challenges faced by agriculture in less developed regions? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 global challenges facing agriculture today? |

|
|
|
|
Define soil. |

|
|
|
|
What are the five things soil is made of? What percentages? |

|
|
|
|
Name 6 functions of soil. |
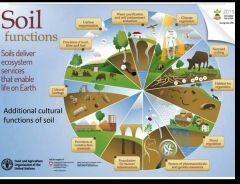
|
|
|
|
Name the 3 types of soil parent material. |

|
|
|
|
Name the 5 factors that contribute to soil formation. |

Time, parent material, climate, organisms and topography |
|
|
|
What are 3 examples of physical/mechanical weathering? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 examples of chemical weathering? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 ways organisms can form soil? |

|
|
|
|
What are the 3 soil organisms and what do they do? |

|
|
|
|
What is "O horizon"? |

|
|
|
|
What is "A horizon"? |

Top soil- dark in color |
|
|
|
What is "B horizon" |

Subsoil, under topsoil, mineral rich, clay, less air supply |
|
|
|
What is "C horizon"? |

2nd deepest level (R horizon or parent rock/bedrock is deepest) |
|
|
|
What are the 5 characteristics used to describe soil? |

|
|
|
|
What are the 6 types of soil? What characteristics do they have? |
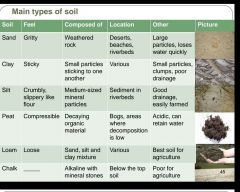
Sand, clay, silt, peat, loam, chalk |
|
|
|
What is SOM? |

|
|
|
|
From largest particle size to smallest, list clay, sand and silt. |
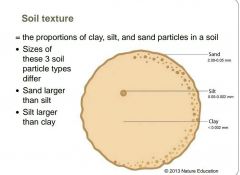
|
|
|
|
What is the optimum ph for most plants? |
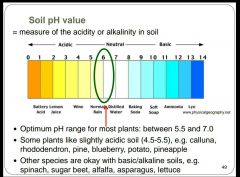
|
|
|
|
What 4 functions does SOM do? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 methods of applying fertilizer? |
Banding Foliar Fertigation Side dressing Broadcasting Injection |
|
|
|
What is a 10-10-10 mix? |

|
|
|
|
Name the 3 INORGANIC fertilizer types? |

|
|
|
|
What is a cover crop and 3 benefits? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 challenges related to using animal manure? |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 disadvantages when using Inorganic ferilizers. |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 advantages to using INORGANIC fertilizers? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 disadvantages to using organic ferilizers? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 advantages to using Organic fertilizers? |

|
|
|
|
What are inorganic fertilizers? |

|
|
|
|
What are organic fertilizers? |

|
|
|
|
Why do we use fertilizers? |

|
|
|
|
Name the 8 micronutrients provided by the soil and needed by plants? |

|
Iron man couldn't zing boring moles named Claud. |
|
|
Name the 6 macronutrients provided by the soil that plants need? |

Plus carbon and oxygen... |
No man called phil sells potatoes. |
|
|
What is a decrease in soil ph that is harmful to plants called? |

|
|
|
|
What is the form of soil degradation called that is related to improper irrigation? |

|
|
|
|
What is nutrient depletion, how is it caused, and what occurs after? |

|
|
|
|
What causes soil compaction and what 2 negative impacts does it have? |

|
|
|
|
What is soil degredation? Name 5 factors that contribute to it |

|
|
|
|
What are the three levels of tillage? |
Conventional intensive tillage (most intense) Conservation tillage No-till system (least intense) |
|
|
|
Where does water transport take place and what is it driven by? |
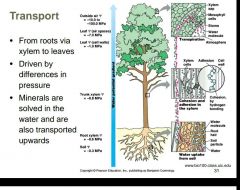
|
|
|
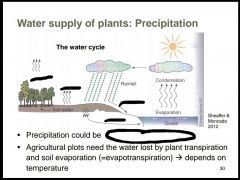
Name the missing terms^ |
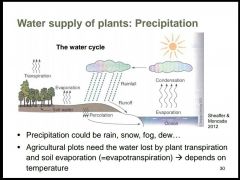
|
|
|
|
What is transpiration and why is it important? |
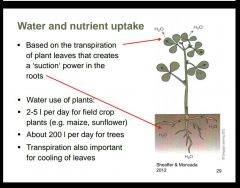
|
|
|
|
What is respiration and what is it used for? |
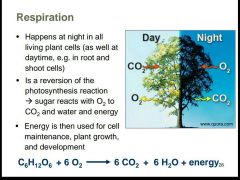
|
|
|
|
What is the chemical expression of respiration? |
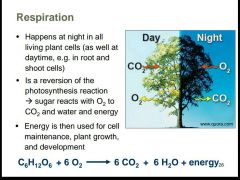
C6H12+6O2------6CO2 + 6H2O+ energy |
|
|
|
What are the main differences between C3 and C4 plants? |
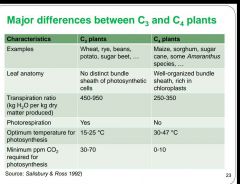
|
|
|
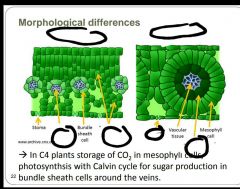
Fill in the missing words. |
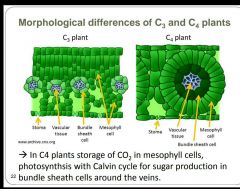
|
|
|
|
Which plants are C3 and C4 plants? What environments do they live in? What do they create? |

|
|
|
|
If you have low light levels you can help increase plant yields by having higher levels of what? |
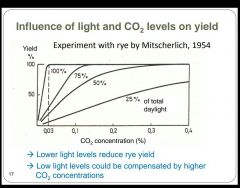
CO2 levels |
|
|
|
What is the chemical formula of photosynthesis? |
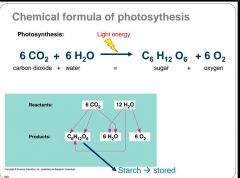
|
|
|
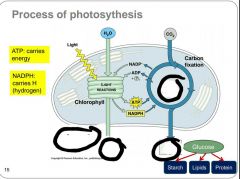
Fill in the missing terms. |
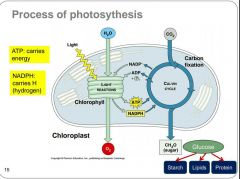
|
|
|
|
What is photosynthesis? Where does photosynthesis take place? |
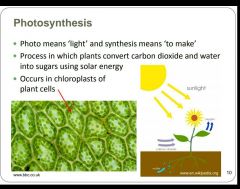
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 main processes of plant physiology? |

|
|
|
|
What are the 3 different plant life cycles. How do they differ? |
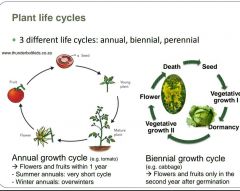
Perennial plants return year after year. |
|
|
|
Which plant life cycle resumes in spring from tubers, rhizomes or branches? |
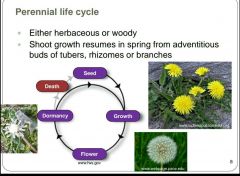
|
|
|
|
What is the meaning of growth and developement in plants? |

|
|
|
|
What is nitrification and who does it? |

|
|
|
|
What is ammonification and who does it? What cycle is this a part of? |

Part of the nitrogen cycle |
|
|
|
What are the 4 main processes involved in the nitrogen cycle? |

|
|
|
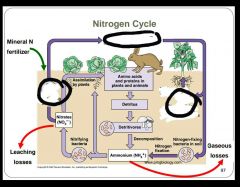
Fill in the missing terms. |
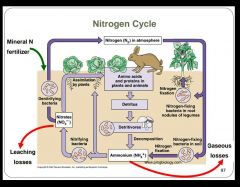
|
|
|
|
What percentage of the atmosphere is nitrogen? |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 reasons why you would till your land. |

|
|
|
|
Who is the most awesome student in the world? |

This chick right here! |
|
|
|
What is our secret nickname for Kehlenbeck? |
Plant granny |
|
|
|
Name 3 different types of leaf venation. |

|
|
|
|
Identify 4 types of blade patterns. |
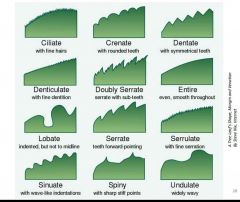
|
|
|
|
Name 5 different leaf shapes. |
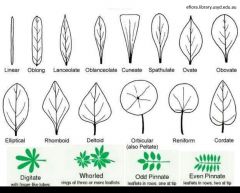
|
|
|
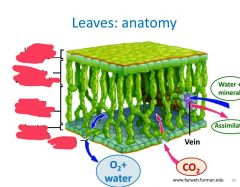
Fill in the terms. |
|
|
|
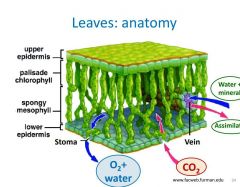
Fill in the terms |
|
|
|
|
What four functions do leaves perform? |

|
|
|
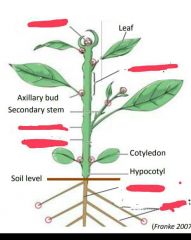
|
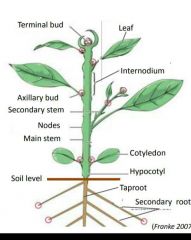
|
|
|
|
What 3 functions does the stem perform? |
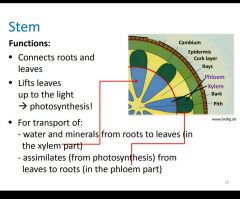
|
|
|
|
What 2 functions do root systems perform? How do they differ in monocots and dicots? |
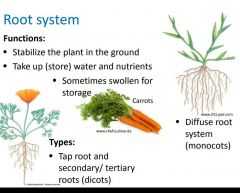
|
|
|
|
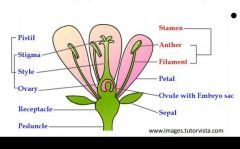
What are the 5 parts of a plant? |

|
|
|
|
What are the two types of leaf formations? |

Simple and compound |
|
|
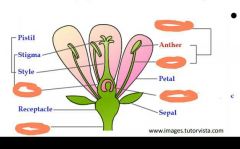
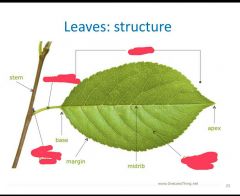
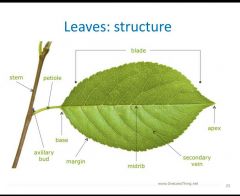
Name the missing terms |
|
|
|
|
What are a few ways to identify a plant? |

Stem, leaf arrangement, leaf venation, flower petal and stamen count, leaf: compound or simple, and fruit |
|
|
|
4 characteristics of scientific names: |

|
|
|
|
What is Binominal Nomenclature, who developed it, and when? |

|
|
|
|
Describe 5 characteristics that define a dicot plant. |
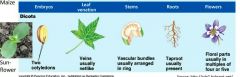
|
|
|
|
Describe 5 characteristics that define a monocot plant. |

|
|
|
|
Name the 7 taxonomic ranks in order. |
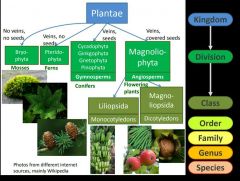
|
Kings deal cards on fresh green salad |
|
|
What function does ethylene perform in plants? |
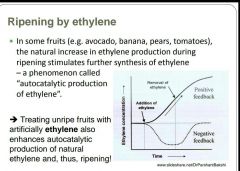
|
|
|
|
What function do auxins play in plants? |

|
|
|
|
What is vernalisation? |

|
|
|
|
What is a Leaf Area index and why is it important? |

|
|
|
|
What is a good way to make the most of sunlight in terms of LAI? |
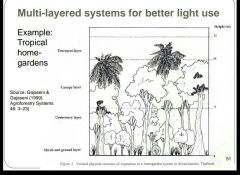
Multi-layered systems |
|
|
|
What are spores? |

|
|
|
|
What are fungi? |

|
|
|
|
In what ways can you manage a viral plant infection? |

|
|
|

What are these and what are they doing? |

Spreading viruses to plants |
|
|
|
What are 3 symptoms of plant virus infection? |

|
|
|
|
What is a virus? |
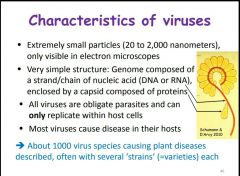
|
|
|
|
What are some steps to take to manage a bacterial plant infection? |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 symptoms of a bacterial infection? |

|
|
|
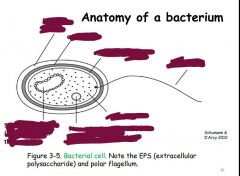
Fill in the terms |
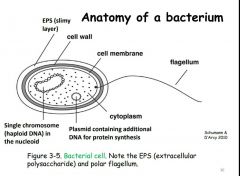
|
|
|
|
What are bacteria? |
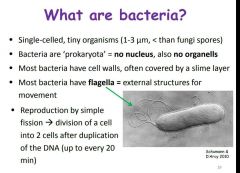
|
|
|
|
What are 4 ways to manage weeds? |

|
|
|
|
What are 4 problems caused by weeds? |

|
|
|

Identify this plant |

|
|
|

Identify this plant |

|
|
|
|
Name 5 organisms that cause biotic stress? |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 causes of abiotic stress |

|
|
|
|
What are the two categories of stress that plants experience? |
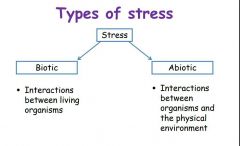
|
|
|
|
What is plant stress? |

|
|
|
|
Describe vegetables |

|
|
|
|
Describe fruits |

|
|
|
|
Describe oils and fats |

|
|
|
|
Describe roots and tubers |

|
|
|
|
Describe sugars |

|
|
|
|
Describe cereals |

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
What is fruit? What function does it serve and what are the 3 parts of the pericarp? |

|
|
|
|
What 3 functions does a flower have? |

|
|
|
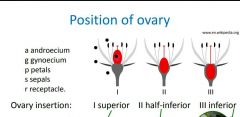
|
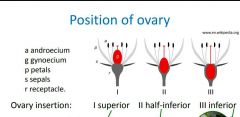
|
|
|
|
What is a "day neutral" plant? |

|
|
|
|
What is a short day plant? |

|
|
|
|
What is a long day plant? |

|
|
|
|
What 5 effects does light have on plants? |

|
|
|
|
Name 4 factors that effect plants |

|
|
|
|
In what four ways can plants conserve or save water? |

|
|
|
|
How long does it take for 1 centimeter of topsoil to form? |
500 years |
|
|

What is this? |
Your mama. |
|
|
|
Where is meat made? |

The United Steaks of America |
|
|
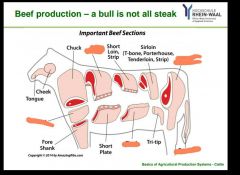
|
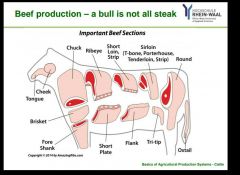
|
|
|
|
Why is wallowing important for pigs? |

|
|
|
|
Name some disadvantages to a bedded system in animal housing? |

|
|
|
|
When are pigs slaughtered? How much do they weigh? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 challenges for newly weaned pigs? |

|
|
|
|
How many piglets can a mother pigs support? |

|
|
|
|
What percentage of piglet losses occur in the first 3 days? |

|
|
|
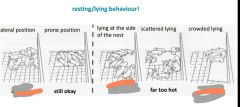
|
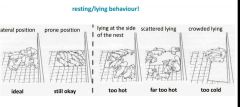
|
|
|
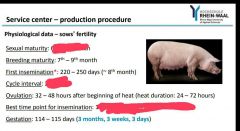
|
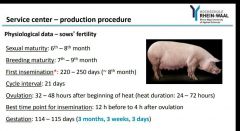
|
|
|
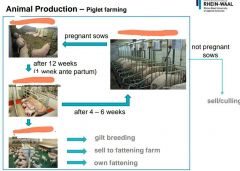
|
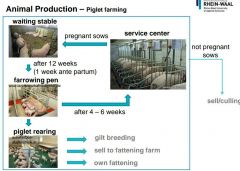
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 stages or areas for pigs to live in while they grow? |
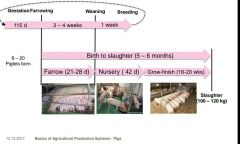
Farrow, nursery, and grow-finish |
|
|
|
What is a barrow? |
A castrated male pig |
|
|
|
What is a gilt? |
A female pig who has not yet farrowed a litter of piglets. |
|
|
|
What is gestation? |
the process or period of developing inside the womb between conception and birth. |
|
|
|
What is a litter? |
a number of young animals born to an animal at one time. |
|
|
|
What is nursing? |
Feed a newborn milk from a mammary gland. |
|
|
|
What is farrowing? |
The act of giving birth to a litter/farrow of pigs is farrowing. |
|
|
|
What is weaning? |
accustom (an infant or other young mammal) to food other than its mother's milk. |
|
|
|
What is a carcass? |
the dead body of an animal |
|
|
|
What is colostrum and why is it important? |
It is the first milk after farrowing. The calf must rely on colostrum from its mother until its own immune system is developed at 1 to 2 months of age. Colostrum contains antibodies or immunoglobulins (essential proteins) necessary to provide the calf with protection from disease. This immunity that the calf receives is known as passive immunity. |
|
|
|
Familiarize with different terms for pigs. |
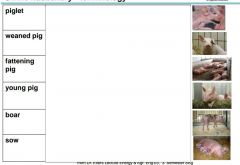
|
|
|
|
Why are pigs important? |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 things necessary when housing a pig? |

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Name the 5 freedoms as proposed by EU animal welfare legislation. |

|
|
|
|
Name 3 things the EU has banned from animal farms. |

|
|
|
|
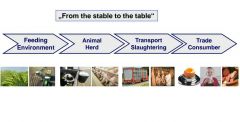
|
|
|
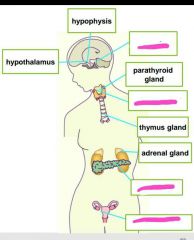
|
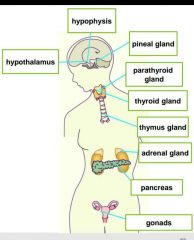
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Describe Rigor mortis. |
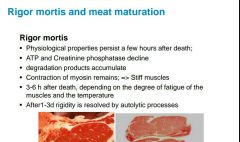
|
|
|
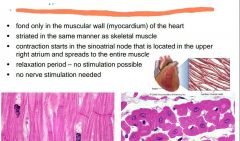
|
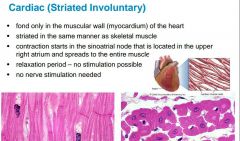
|
|
|
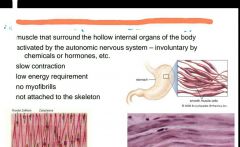
|
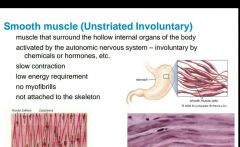
|
|
|
|
What is ATP and what does it do? |

|
|
|
|
How are skeletal muscles attached to your body? |

|
|
|
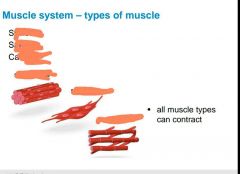
|
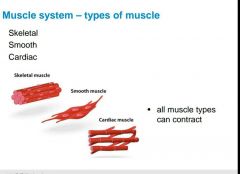
|
|
|
|
What is meat? |

|
|
|
|
What is the difference between digestion and absorption? |

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
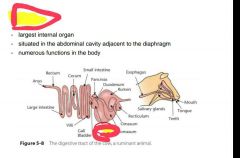
|

Liver |
|
|
|
What is produced by the exocrine pancreas? |
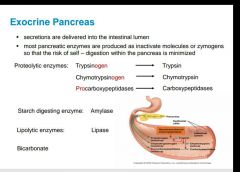
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
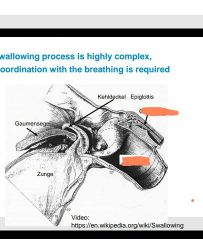
|
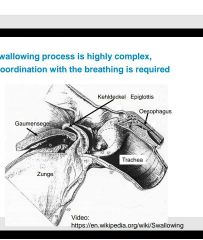
|
|
|
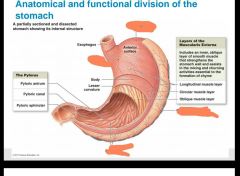
|
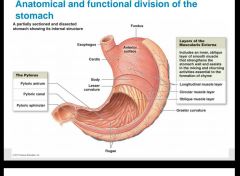
|
|
|
|
How many liters a day of saliva do cattle produce? |
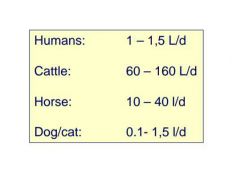
|
|
|
|
What purpose does saliva have? |
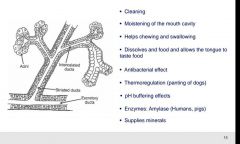
|
|
|
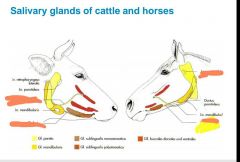
|
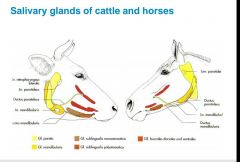
|
|
|
|
What is ergotism and what is it caused by? |
: a toxic condition produced by eating grain, grain products (such as rye bread), or grasses infected with ergot fungus or by chronic excessive use of an ergot drug |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
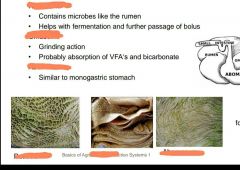
|
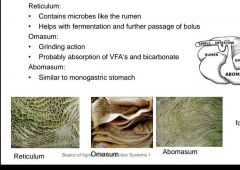
|
|
|
|
What organism/mechanisms help break down food inside the rumen? |

|
|
|
|
What is a rumen? |

|
|
|
|
What are ruminants? |
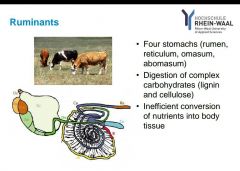
|
|
|
|
What are monogastric animals? |

|
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of digestive systems? |

|
|
|
|
What are the 5 main elements that make up a diet? |
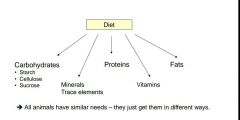
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
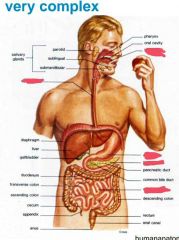
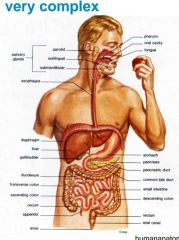
Name the 8 main parts of a digestive system? |
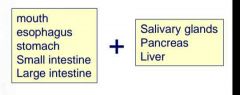
|
|
|
|
What are the 5 functions of the digestive system? |

|
|
|
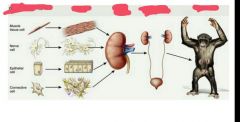
|
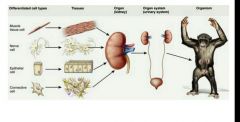
|
|
|
|
What is the difference between anatomy and physiology? |

|
|
|
|
How much has world food production increased in the last 20 years? |

18% |
|
|
|
What are the 4 main animal groups consumed for meat? |
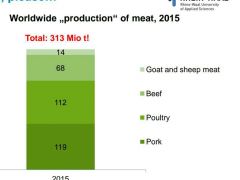
|
|
|
|
What is the daily recommemdation for fat intake? |

|
|
|
|
What are 3 types of fatty acids? |

|
|
|
|
Name the 4 most important oil crops in order. |

|
|
|
|
How many different amino acids make up protein? |

|
|
|
|
Where is most plant protein found? |
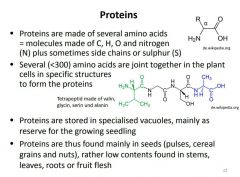
|
|
|
|
Name the four most important root crops. |

|
|
|
|
What is starch? |
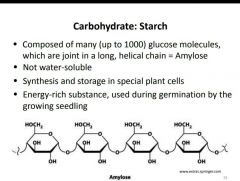
|
|
|
|
What is sucrose? |

|
|
|
|
What is a carbohydrate? |
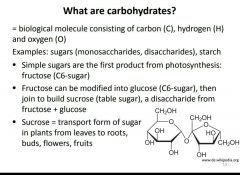
|
|
|
|
Name the 4 most important cereal crops in order. |
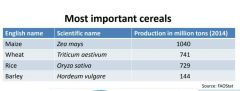
|
|
|
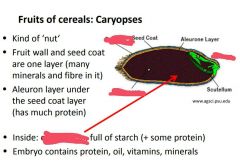
|
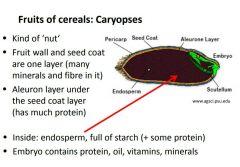
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
What are ways to reduce salt distress? |
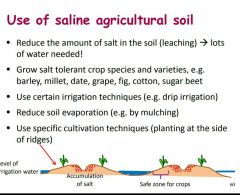
|
|
|
|
Name 3 ways to identify an abiotic plant disease. |

|
|
|
|
Name 5 things that can cause mechanical injury in plants. |

|
|
|
|
Name 4 ways salt effects plant harvests. |
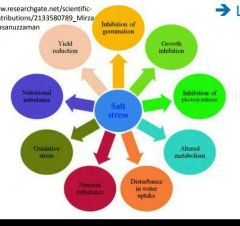
|
|
|
|
Why do herbicides damage crops? |

|
|
|
|
What happens when soil is too acid or alkaline? |
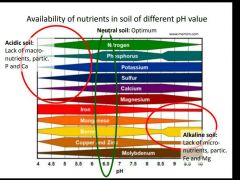
|
|
|
|
What are some dangers of too high/low temperatures? |

|
|
|
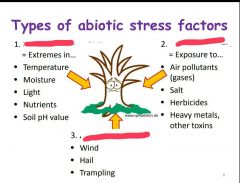
|
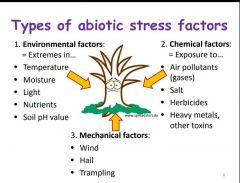
|
|
|
|
What are abiotic stress factors? |

|
|
|

Identify this insect |

|
|
|

Iddntify this little guy |

|
|
|
|
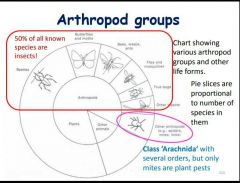
What are the differences between insects and spiders? |
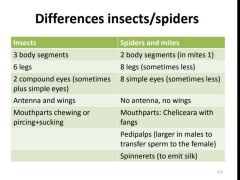
|
|
|
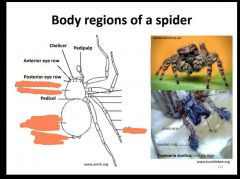
|
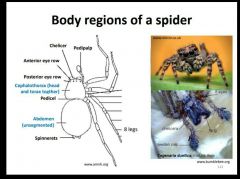
|
|
|
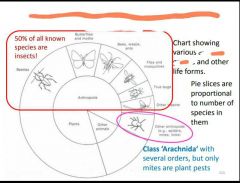
|
|
|
|

Identify |

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|

What order is this insect? |

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Which order of insects do grasshoppers belong to? |

|
|
|
|
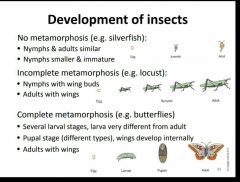
What are 3 types of metamorphosis? |
|
|
|
|
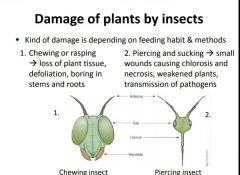
What are two types of damage done by insects? |
|
|
|
|
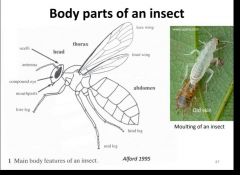
|
|
|
|
What are insects? |

|
|
|
|
What are nematodes? |

|
|
|
|
How are fungal diseases managed? |

|
|
|
|
How do fungi survive and spread? |

|
|
|
|
What are signs of fungal infection? |

|
|
|
|
How much SOM does good soil have? |
Over 3% |
|

