![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
AIRF is a Syndrome. T/F |
True |
|
|
It is an __________ ____________ in function. |
Abrupt Decline |
|
|
Recent _____________ of Azotemia |
ONSET |
|
|
T/F. It is a recognition of Azotemia |
False |
|
|
Describe AIRF |
Inability to Regulate Volume and Composition (electrolyte and acid base) of Body Fluids |
|
|
Two Subdivisions of Acute Intrinsic Failure |
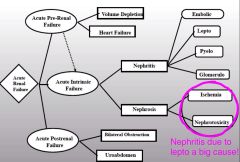
Nephritis & Nephrosis |
|
|
What is characteristic of Pre-Renal Azotemia? |
Physiologic Oliguria |
|
|
What type of lesions are seen in severe, prolonged renal hypofusion? |
Primary |
|
|
What type of lesions are these? |
Ischemic Necrosis |
|
|
Common Causes of AIRF |
Nephrotoxic nephrosis |
|
|
Potential Causes |
Dehydration |
|
|
Potential Nephrotoxins |
Ethylene Glycol |
|
|
What anti-microbials are nephrotoxic? |
|
|
|
What cancer therapies are nephrotoxic? |
Cisplatin |
|
|
How does Hypercalcemia and Causes affect the kidney? |
Calcipotriene
|
|
|
What heavy metals are toxic? |
arsenic Lead |
|
|
Nephrotoxins for Horses? |
|
|
|
Nephrotoxins for Cats? |
Easter Lily |
|
|
Nephrotoxins for Cows? |
Acorns/Oak Bud |
|
|
Nephrotoxins for Dogs? |
Raisins/Grapes Melamine-cyanuric acid contaminated food |
|
|
What does exposure to a nephrotoxin cause? |
tubular injury |
|
|
What is the spectrum of injury? |
Degeneration (nephrosis) to Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) |
|
|
Why is it important to believe clinical signs over just clinical pathology? |
Could have minimal to no light microscopic lesions but STILL develop severe renal excretory failure |
|
|
What is the Maintanence phase of AIRF? |
Sudden INCREASE in serum creatinine concentration that persists DESPITE correction of all pre-renal factors |
|
|
What pre-renal factors are corrected? |
Restoration of EC Volume and Cardiac Output |
|
|
True/False. Oliguria, Normal Urine Output, and Polyuria do NOT occur in AIRF. |
False ALL can occur depending on severity of insult Specific Cause Phase of AIRF |
|
|
How long does the maintainence phase take before restoration? |
1-3 week course |
|
|
T/F. Removal of the inciting cause at this point will NOT result in immediate return of normal renal function |
TRUE |
|
|
What does the maintainence phase signify? |
Critical amount of lethal tubular cell injury |
|
|
What is the maintainence phase characterized by>? |
Severe decrease in renal Blood flow and GFR |
|
|
If renal blood flow goes back to normal, what happens to GFR? |
Stays LOW |
|
|
True/False. Conversion from Oliguria to Polyuria may occur. |
True |
|
|
Recovery Phase of AIRF. |
Return of normal BUN & Creatinine = POSSIBLE
Complete recovery = may not be possible (greatest injury)
Partial improvement = Chronic Renal Failure
BUN & serum creatinine may return to normal but decreased GFR may persist
Urinary concentrating defect may persist |
|
|
How many tests can be definitive for? |
No Single Test is Definitive |
|
|
Important Diagnostic Steps. |
History PE U/A CBC Chem Renal Size Renal Biopsy |
|
|
What are two rule outs? |
Azotemia and Isosthenuria |
|
|
What to look for in the history? |
Absence of longstanding PU/PD Potential for renal ischemia or nephrotoxin exposure Oliguria Polyuria |
|
|
What are non-specific signs? |
Anorexia Vomit Diarrhea |
|
|
What is particularly inportant in the CBC? |
PCV! |
|
|
When should you do your CBC, Chem, U/A |
When the patient is "Healthy"--> Pre-Tx |
|
|
On physical exam, signs of UREMIA are More or Less Severe than Signs of Pre-Renal Azotemia? |
MORE |
|
|
True/False. Uremia signs may be Similar to CRF |
True |
|
|
True/False. Uremia mucus membranes (in regard to anemia) are similar to anemic signs in CRF |
False Uremia: Absence of pallor to mucous membranes |
|
|
Hypothermia= ______________ |
Nephrosis |
|
|
Hyperthermia= ____________________ |
Nephritis |
|
|
List Physical Exam Findings |
|
|
|
What is a possible consequence of Overhydration? |
Edema/Ascites |
|
|
On a hemogram of AIRF, when can you see anemia? |
NOT early on --> more common with CRF |
|
|
If there is sudden blood loss, what type of response would be seen and when? |
mild/moderate regenerative EARLY |
|
|
On a hemogram of AIRF, what do Total Protein values look like with Hydration? |
normal to elevated |
|
|
When would these values for TP possibly decrease? |
iatrogenic overhydration |
|
|
You may or may not see thrombocytopenia due to Lepto. True/False. |
True |
|
|
What type of leukogram would be seen with AIRF? |
Inflammatory / stress leukogram |
|
|
On a U/A for AIRF, is the concentration dilute or concentrated? and WHEN? |
DILUTE very early |
|
|
Often, the range for USG in AIRF is __________ to ___________. |
1.007-1.017 |
|
|
T/F. USG is only low with oliguric AIRF and not with non-oliguric AIRF. |
False. BOTH |
|
|
Will a low USG differentiate AIRF from CRF? |
NO! |
|
|
What types of -URIA's are seen with AIRF? |
Hematuria Proteinuria Glucosuria |
|
|
What is different about Glucosuria in this case? |
Can be seen with a normal blood glucose |
|
|
What does this indicate? |
Renal Tubular Injury |

