![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
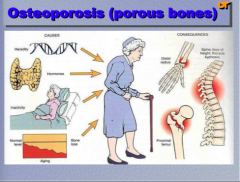
What does osteoporosis mean? What are some causes? What are some consequences? |
|
|
|
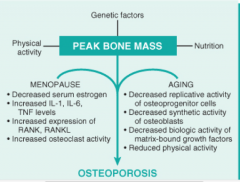
What is the pathogenies of osteoporosis? What two processes contribute? (think about estrogen, ILs, osteoblast and osteoclast activity) |
|
|
|
Which is normal and which is osteoporotic? |
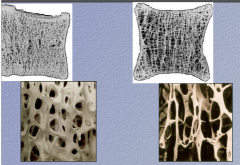
Left = normal |
|
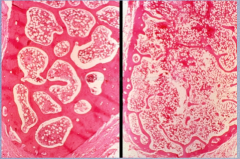
Which is normal, which is osteoporotic? |
Left = normal |
|
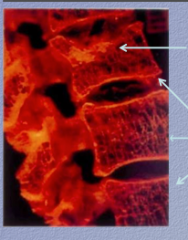
What complication of osteoporosis is shown here? |
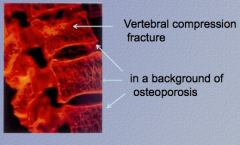
|
|
|
What do biphosphonates do? When are they released? What signaling do they modulate? What bones are the they concentrated in and where are they located? |
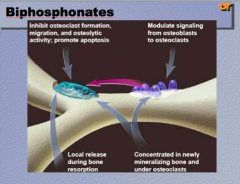
|
|
|
What two drugs can inhibit osteoclasts? |
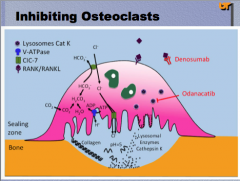
Denosumab and Odanacatib |
|
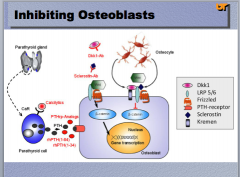
? |
? |
|
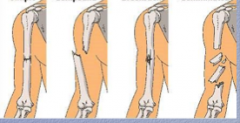
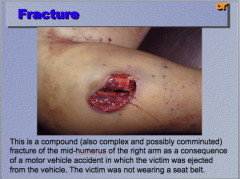
What are the three types of fractures shown? |
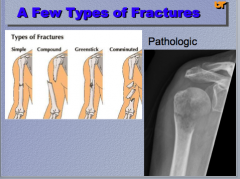
|
|
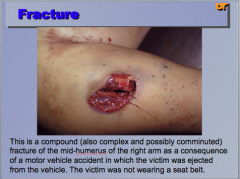
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
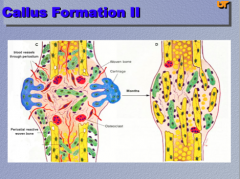
|
|
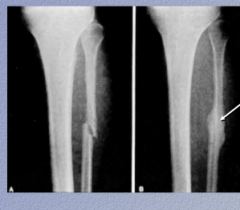
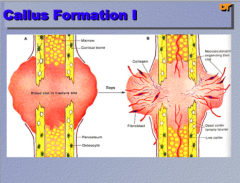
In this recent fracture of the fibula, identify the callus. |
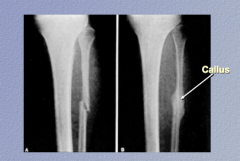
|
|
|
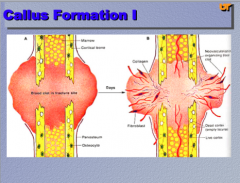
What process is taking place here? Identify the resolving hemorrhage, the fractured bony trabeculae, and the unmineralized bone. |
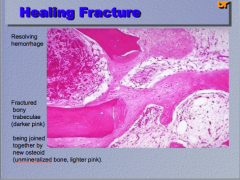
|
|
|
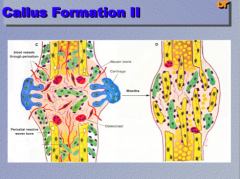
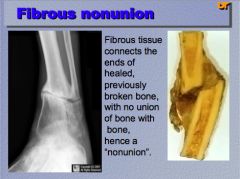
What connects the ends of healed, previously broken bone, with no union of bone with bone (hence a "nonunion") |
|
|
|
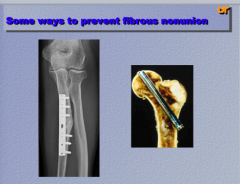
What are two ways to prevent a fibrous nonunion? |
|
|
|
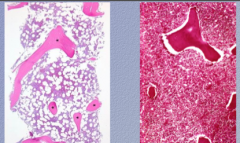
What process is shown here? |
Osteonecrosis |
|
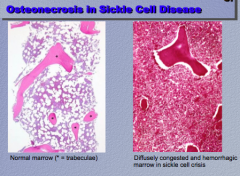
What is a disease you can see osteonecrosis in? What image is normal and which is abnormal? Describe the abnormal. |
|
|
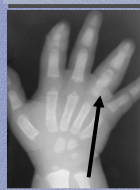
What is the process happening in this sickle cell patient? What is swelling? What is the "descriptor" for what is happening at the end of the fourth phalanx? What could be the disease? |
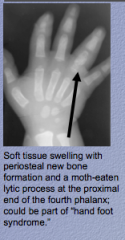
|
|
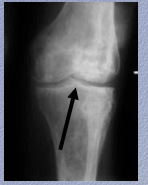
Osteonecrosis in sickle cell disease:
Chronic ______ + secondary osteoarthritis with advanced changes of irregular sclerosis + ________ on both sides of the knee joint reflecting numerous poor infarcts. What is narrowed? |
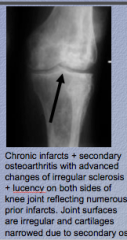
Narrowed due to secondary osteoarthritis |
|

Osteonecrosis in sickle cell disease:
What is this characteristic called? Old _____ within new ______; following multiple _______ of long bones, sclerosis may have this appearance. |

|
|
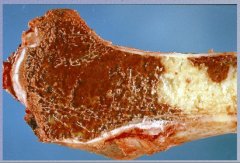
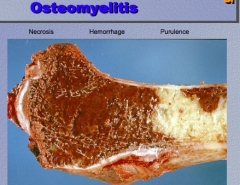
What is the process? Identify hemorrhage, necrosis, and purulence. |
|
|
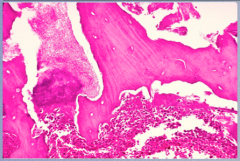
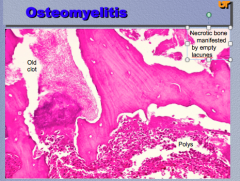
What is the process? Identify the old clot, necrotic bone manifested by empty lacunes, and polys. |
|
|
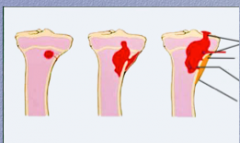
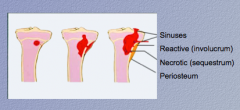
Osteomyelitis: identify reactive (involucrum, necrotic (sequestrum), periosteum, and sinuses |
|
|
|
What is involuvrum?
What is sequestrum? |
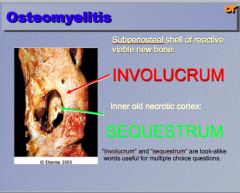
Involucrum = subperiosteal shell of reactive viable new bone
Sequestrum = inner old necrotic cortex |
|
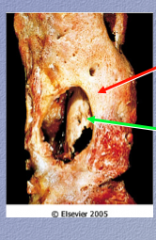
Identify "involucrum" and "sequestrum" in this osteomyelitis image. |
|
|
|
What are the three major components of osteomyelitis in diabetes? What indicated by the arrow in the calcaneus? |
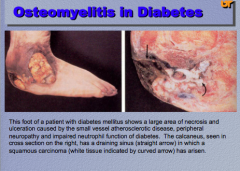
|
|
|
What are some symptoms of Paget disease of bone?
What will you see histologically? |
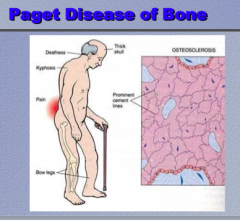
|
|
|
What do you notice in this proximal femur with Paget disease? Irregular, thick, replacement, etc. |
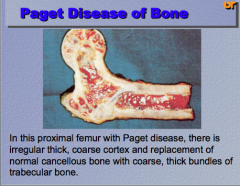
|
|
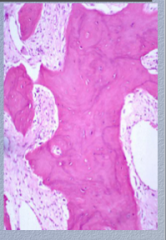
What two phases are mixed in Paget disease? What happens in the osteosclerotic phase? What histologic hallmark is prominent? |
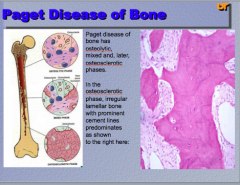
|
|
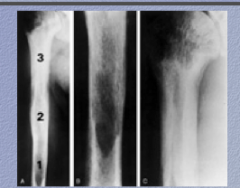
What is the disease? Identify 1, 2, and 3 (phases) |
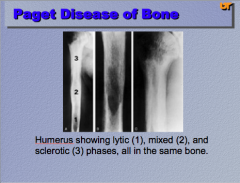
|
|
|
What is a disease caused by inadequate vitamin D and/or calcium in children? What does it produces in adults? |
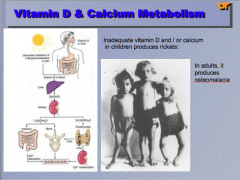
|
|
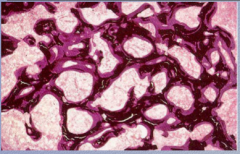
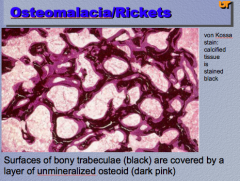
What is the disease? What stain is used? Surfaces of _________ (black) are covered by a layer of ___________ (dark pink). |
|
|
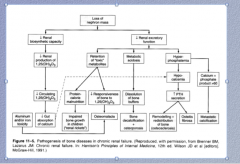
Look over... |
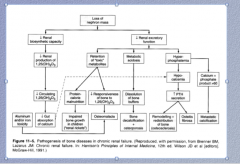
|
|
|
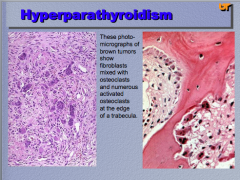
What are two causes of hyperparathyroidism? Which type on left and on right? |
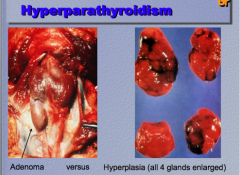
|
|
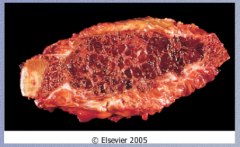
What is this? Two characteristics of this lesion. |
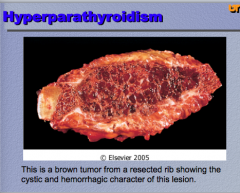
|
|
|
What is the condition? Identify the hemorrhagic cysts and the brown tumor. What does it cause? |
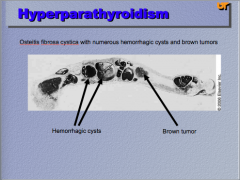
|
|
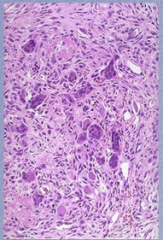
Hyperparathyroidism:
What is is this an image of? What is mixed with osteoclasts? |
|

