![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the first thing you must consider in any acidosis in order to get to a diagnosis? |
Is it anion gap or non-anion gap? |
|
|
What is a normal anion gap? |
8-12 |
|
|
What clinical feature should you associate with Type 2 to Renal Tubular Acidosis?
What lab value/ abnormality should you associate with Type 2 RTA?
Where in the nephron is the problem in Type 2 Renal Tubular Acidosis? |
Fanconi Syndrome: Glucosuria, Uricosuria
↑ urine HCO₃⁻
Proximal Tubule |
|
|
What lab values/ abnormalities should you associate with Type 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis?
Where is the nephron is the problem in Type 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis?
What clinical feature is associated with Type 1 RTA? |
↓ urine HCO₃⁻ pH > 5.5
Distal Tubule
Kidney Stone |
|
|
What lab values/ abnormalities should you associate with Type 4 Renal Tubular Acidosis?
Where is the nephron is the problem in Type 4 Renal Tubular Acidosis?
What clinical features are associated with Type 4 RTA? |
↓ urine HCO₃⁻ pH < 5.5
Distal Tubule (Collecting Duct)
Hypoaldosteronism & Diabetes with CKD
|
|
|
In a patient with metabolic alkalosis, what is the likely diagnosis if urine Cl⁻ < 25 mEq/L? |
Surreptitious Vomiting |
|
|
In a patient with metabolic alkalosis and a urine Cl⁻ > 40 mEq/L, which TWO diagnoses should you consider? |
Diuretic Abuse Bartter Syndrome |
|
|
If you see contraction alkalosis, what is the differential diagnosis? |
Diuretics Bartter Syndrome Gitelman Syndrome |
|
|
What is the defect in Bartter and Gitelman that leads to contraction alkalosis?
Where is the defect located in the nephron?
What is the mechanism of the contraction alkalosis? |
Constituitively active Sodium Chloride Channels
Collecting Duct
Constantly lose sodium and chloride → leads to volume contraction → leads to secondary hyperaldosteronism → leads to alkalosis |
|
|
What is the most likely diagnosis if patient presents with metabolic alkalosis + hypokalemia + hypertension?
(Labs show ↓K⁺, ↑HCO₃⁻ in serum) |
Hyperaldosteronism |
|
|
What is the most likely diagnosis if patient presents with metabolic alkalosis + hypokalemia + hypertension BUT aldosterone is low?
|
Cushings |
|
|
What test should be done if a patient with metabolic acidosis has elevated aldosterone to determine the diagnosis? |
Renin Level |
|
|
What is the most likely diagnosis if patient presents with metabolic alkalosis + hypokalemia + hypertension + hyperaldosteronism + ↑ renin?
(Labs show ↓K⁺, ↑HCO₃⁻ in serum) |
Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) |
|
|
What is the most likely diagnosis if patient presents with metabolic alkalosis + hypokalemia + hypertension + hyperaldosteronism + ↓ renin?
(Labs show ↓K⁺, ↑HCO₃⁻ in serum)
What anatomical structure causes this problem? |
Primary Hyperaldosteronism
Adrenal Glands |
|
|
What effect does licorice have on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system? |
Decreases Aldosterone |
|
|
What are the most common causes of metabolic alkalosis? |
Vomiting Diuretics |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for high anion gap metabolic acidosis? |
Methanol Uremia Diabetic Ketoacidosis Paraldehyde Iron & Isoniazid Lactic Acidosis Ethylene glycol & Ethanol Salicylates |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for non-anion gap metabolic acidosis? |
Ureteroenterostomy Small Bowel Fistula Extra Chloride (normal saline infusion) Diarrhea
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor Renal tubular acidosis Adrenal insufficiency Pancreatic Fistula |
|
|
In a hypokalemic patient, what changes would you expect to see on EKG? |
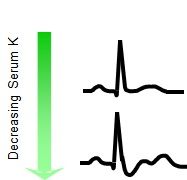
Flat T Wave
Depressed ST segment |
|
|
In a hyperkalemic patient, what changes would you expect to see on EKG? |
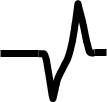
Widening of the QRS Complex |
|
|
What are the most common causes of a non-anion gap metabolic acidosis? |
Diarrhea Laxatives Renal Tubular |
|
|
If you have a high anion gap metabolic acidosis with a normal osmolar gap, what is the diagnosis? |
Salicylates |
|
|
Why does diarrhea cause metabolic acidosis? |
Loss of bicarbonate |
|
|
When is ADH released? |
↑ plasma osmolality ↓ arterial circulating volume (hypovolemia) |
|
|
What effect does ADH have on the body? |
Stimulates Thirst Decreases Water Excretion |
|
|
How is total body sodium regulated? |
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System |
|
|
Under what circumstances is the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System activated? |
↓ extracellular volume (hypovolemia) ↓ renal perfusion (hypotension) |
|
|
What are the causes of Polyuria? |
Osmotic (uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, hyperosmolar agents)
Increased Water Intake (psychogenic polydipsia, central diabetes insipidus, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus) |
|
|
What is the cause of central diabetes insipidus? |
↓ ADH production (due to hypothalamic lesion or posterior pituitary lesion) |
|
|
What causes nephrogenic diabetes insipidus? |
Inability of the kidney to respond to ADH (due to hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, tubuloinsterstitial nephropathy or genetic factor) |
|
|
In a patient with polyuria known to have a history of mental illness, what diagnosis should you be thinking of and why?
What other electrolyte disturbances might this patient have? |
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Due to Lithium causing Tubulointerstitial Nephropathy
Hypernatremia |
|
|
A patient who has polyuria and polydipsia undergoes a water restriction test that shows no change in urine osmolality. What is the differential diagnosis for this patient? |
Central Diabetes Insipidus Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus |
|
|
A patient who has polyuria and polydipsia undergoes a water restriction test that shows no change in urine osmolality. If the patient's urine osmolality increases with administration of exogenous ADH (vasopressin or DDAVP), what is the diagnosis? |
Central Diabetes Insipidus |
|
|
A patient who has polyuria and polydipsia undergoes a water restriction test that shows no change in urine osmolality. If the patient's urine osmolality does not change with administration of exogenous ADH (vasopressin or DDAVP), what is the diagnosis?
How is it treated? |
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Low Sodium Diet & Thiazide Diuretic |
|
|
A patient who has polyuria and polydipsia undergoes a water restriction test that shows an increase in urine osmolality. What is the diagnosis? |
Psychogenic Polydipsia |
|
|
What is the differential Diagnosis for Hypernatremia? |
Central Diabetes Insipidus Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus No access to water ↓ water intake + ↑ water loss |
|
|
What is the first thing you look at in a patient with hyponatremia in order to determine the underlying cause? |
Serum Osmolality |
|
|
If serum osmolality is normal in a patient with hyponatremia what is the diagnosis?
Why does this occur? |
Pseudohyponatremia
Lab's measurement of sodium assumes normal plasma composition, while sodium concentration in these patients is normal relative to plasma water, they have a decreased plasma water relative to normal patients which leads the lab equipment to incorrectly diagnose hyponatremia |
|
|
What type of hyponatremia has a serum osmolality of > 290 mOsm/ kg water?
What is the differential diagnosis? |
Hyperosmolar Hyponatremia
↑ glucose, mannitol, contrast |
|
|
What type of hyponatremia has a serum osmolality of < 275 mOsm/ kg water?
What could be causing this hyponatremia? |
Hypoosmolar Hyponatremia
Psychogenic polydipisa, Non-osmotic ADH secretion + ↑ water intake, impared urinary diluting ability + increased water intake, multifactorial + increased water intake |
|
|
If a patient has hypoosmolar hyponatremia and is euvolemic, what is the differential diagnosis?
How do you narrow down your differential? |
Polydipsia or SIAD, hypothyroid, adrenal failure, hypopituitary
Urine Osmolality |
|
|
If a patient has hypoosmolar hyponatremia and is euvolemic with a urine osmolality < 100 what is the diagnosis? |
Polydipsia |
|
|
How do you know if a patient has acute or chronic hyponatremia?
What is the timeline for acute vs. chronic? |
In acute patients are symptomatic while chronic patients are asymptomatic because the brain has time to adapt
Acute < 48 hours < chronic |
|
|
What complication can arise in treating chronic hyponatremia?
What causes this complication and how does one avoid this complication? |
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome due to brain shrinkage
Rapid treatment causes osmotic demyelination syndrome. It can be avoided by correcting the hyponatremia slowly
|
|
|
How does aldosterone affect serum potassium concentration?
By what mechanisms does it change serum potassium concentration? |
↓ serum [K⁺]
Stimulates movement of K⁺ into cells & Increases K⁺ excretion in the kidney |
|
|
How does an increase in luminal flow rate affect luminal [K⁺]?
How and why does an increase in luminal flow rate affect K⁺ secretion?
How might this affect serum [K⁺]? |
↑ luminal flow rate causes ↓ luminal [K⁺]
Stimulates K⁺ secretion by increasing the concentration gradient across the apical membrane of the collecting duct
↓ serum [K⁺] --- hypokalemia |
|
|
How does a decrease in luminal flow rate affect luminal [K⁺]?
How and why does an decrease in luminal flow rate affect K⁺ secretion?
How might this affect serum [K⁺]? |
↓ luminal flow rate causes ↑ luminal [K⁺]
Decreases K⁺ secretion by decreasing sodium reabsorption (affecting sodium-potassium exchanger) and altering electrochemical forces
↑ serum [K⁺] --- hyperkalemia |
|
|
How do potassium sparing diuretics work?
What is their mechanism of action?
Where in the nephron do they act? |
Reduce sodium reabsorption thus inhibiting potassium secretion
Block ENaC - prevent reabsorption of sodium, which eliminates the source of sodium used in the sodium potassium exchanger
Collecting Duct |
|
|
In what population(s) does thyrotoxic hypokalemic paralysis most commonly present? (Age, Race, Gender) |
20-40 yo Asian Male |
|
|
What mutation causes Gitelman's Syndrome?
What is the effect? |
Mutation in NaCl coatransporter
Inactivates the cotransporter |
|
|
What part of the nephron is affected in Bartter's Syndrome?
What mutations are associated with Bartter's Syndrome? |
Thick Ascending Loop of Henle
Na-K-2Cl cotransporter, K channel, Cl channel |
|
|
What is THE most common mutation associated with Bartter's Syndrome? |
Mutation of N-K-Cl2 transporter |
|
|
What syndrome is associated with a mutation in ENaC? |
Liddle's |

