![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
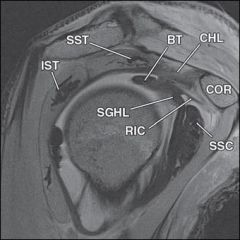
The superior glenohumeral ligament is under the greatest stress when the humeral head and arm are in which of the following positions? |
Inferiorly translated with the arm in 5 degrees of adduction
These studies have demonstrated that the superior glenohumeral ligament provides the most restraint to the shoulder joint when the arm is at zero degrees of abduction or in adduction and pulled inferiorly. |
|
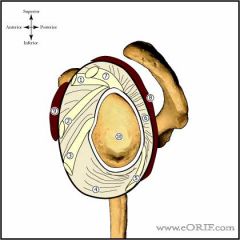
What structure provides dynamic glenohumeral stability by compressing the humeral head against the glenoid? |
Rotator cuff muscles |
|
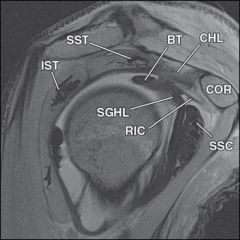
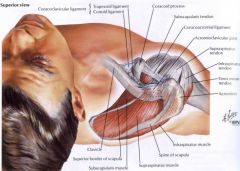
Besides the biceps tendon, which of the following structures also pass through the rotator interval?
|
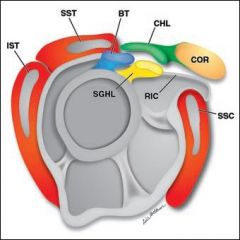
The coracohumeral and superior glenohumeral ligaments
RIC rotators internal capsule |
|
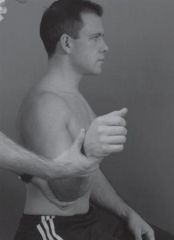
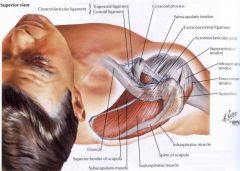
Which of the following is a primary restraint of anterior and posterior humeral translation at the position of a patient's right shoulder as shown in Figure A
|
Middle glenohumeral ligament (MGHL)
The MGHL restrains anterior and posterior translation in the midrange of abduction. The CHL limits inferior translation and external rotation when then arm is adducted and limits posterior translation when the arm is flexed, adducted, and internal rotation. The SGHL also restrains inferior translation and external rotation of the adducted shoulder. The IGHL has an anterior band that is the primary restraint to anterior translation at 90 degrees of shoulder abduction. It also has a posterior band to limit posterior translation. The CA ligament prevents superior head migration in rotator cuff deficient shoulders. |
|
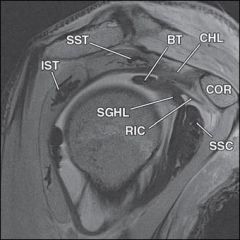
Which of the following is considered the primary static restraint to anterior gleno-humeral translation with the arm in 90 degrees of abduction?
|
Inferior gleno-humeral ligament complex
With the arm at 90 degrees abduction, the anterior band of the inferior gleno-humeral ligament complex is the primary static stabilizer to anterior translation. The middle (MGHL) resists anterior translation at 45 degrees of abduction. The superior (SGHL) resists inferior translation with the arm at one's side. |
|
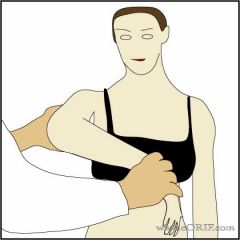
Hawkins Sign
positive with ? |
Hawkins Sign
positive with subacromial impingement |
|
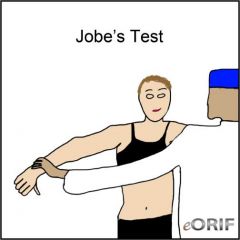
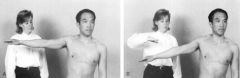
Jobe’s Test
positive with? |
Impingement Tests
Jobe’s Test positive with supraspinatus weakness and or impingement |
|
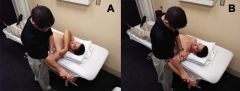
Internal Impingement?
|
Impingement Tests
patient supine, abduct affected side to 90° and maximally externally rotate (throwing position-late cocking phase) with extension. If this maneuver reproduces pain experienced during throwing (posteriorly located) considered it is considered positive. |
|
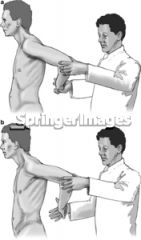
Internal Rotation Lag Sign?
|
Subscapularis Tests
|
|

Excessive ER
|
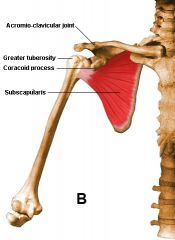
Subscapularis Tests
|
|
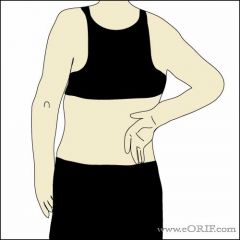
Lift Off Test
|
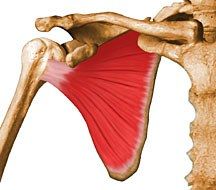
Subscapularis Tests
|
|
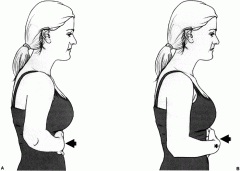
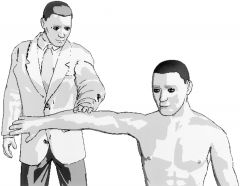
Belly Press
|
Subscapularis Tests
|
|
Jobe’s Test
|
positive with supraspinatus weakness and or impingement
|
|
Drop Sign
|
Supraspinatus Tests
|
|
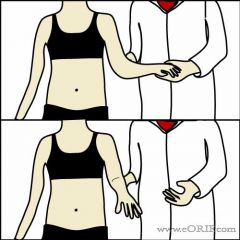
External Rotation Lag Sign
|
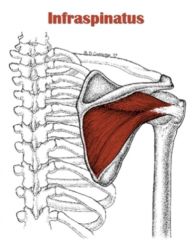
Infraspinatus
|
|
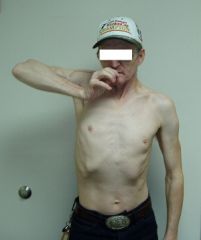
Hornblower's sign
|
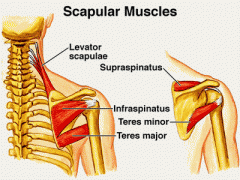
Teres Minor
|
|

Obrien's Test (Active Compression test)
|
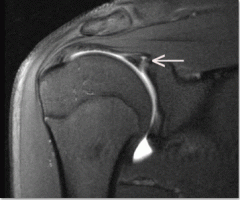
Labral Injuries (SLAP lesions) Tests
AC joint |
|
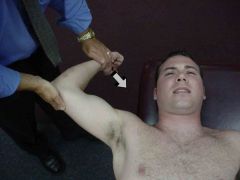
Crank Test
|
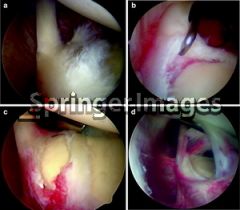
Labral Injuries (SLAP lesions) Tests
|
|

Speed's Test
|
Bicipital Groove Tenderness
|
|
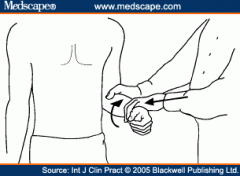
Yergason's Sign
|
Bicipital Groove Tenderness
|
|
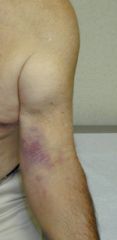
Popeye Sign
|
Biceps Injuries
|
|
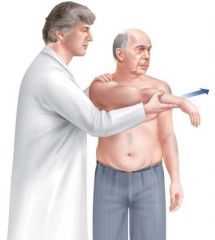
Cross-Body Adduction
|
AC Joint
|
|
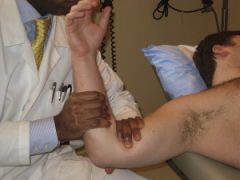
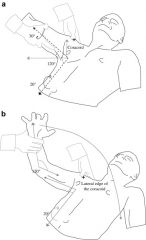
Anterior Load and Shift
|
Anterior Instability
|
|
Apprehension/Relocation/Anterior Release
|
Anterior Instability
|
|
Anterior Drawer
|
Anterior Instability
|
|
Posterior Load and Shift
|
Posterior Instability
|
|
Jerk Test
|
Posterior Instability
|
|
Posterior Drawer
|
Posterior Instability
|
|

Loss of External Rotation
|
Posterior Instability
|
|
Sulcus Sign
|
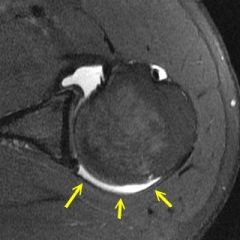
MDI or ???
|
|
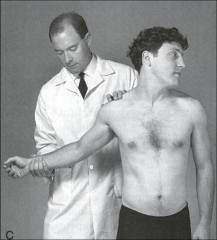
Wright's Test
|
throcacic outlet syndrome
|
|
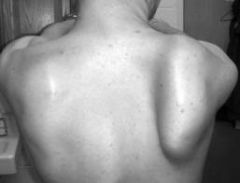
Medial Scapular Winging
|
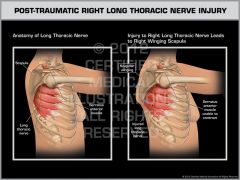
(Mexican SALTy Wings)
medial-Serratus anterior--> Long thoracic |
|
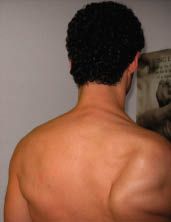
Lateral Scapular Winging
|
Lateral winging-trapezius-spinal accessory nerve
biopsy |
|
|
Shoulder trauma series includes at least (2/beer)
|
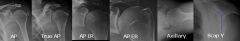
Shoulder trauma series includes at least:
“true” anteroposterior view axillary lateral view |
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
Shoulder AP |
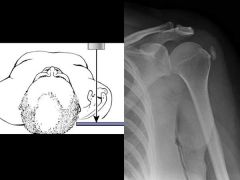
Shoulder AP
Glenohumeral joint space, DJD |
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
True shoulder AP aka |
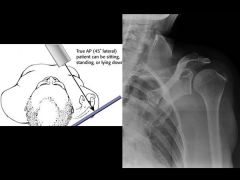
Grashey view Glenohumeral joint space, DJD, and proximal migration of humerus
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
AP in IR |
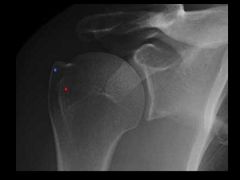
Hill Sachs lesion
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
AP in ER |
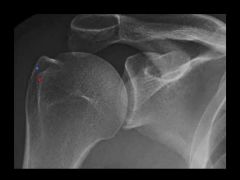
Hill Sachs lesion
|
|
|
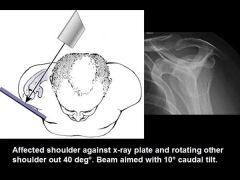
How to do & what looking for?
Axillary |
Anterior and posterior dislocation.
|
|
|
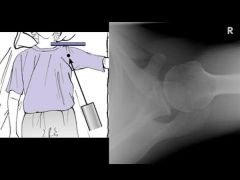
How to do & what looking for?
Velpeau view |
Anterior and posterior dislocation. if cannot abduc the arm
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
Scapular Y Lateral |
Allows classification of acromion
|
|
|
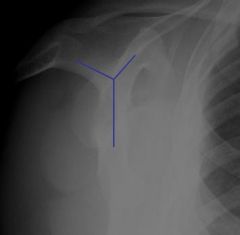
How to do & what looking for?
Supraspinatous Outlet |
Allows classification of acromion (Type I-flat, Type II-curved, Type III-hooked). Hooked acromion is associated with impingement and rotator cuff pathology.
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
Zanca |
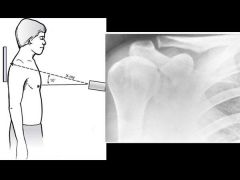
Help visualize the AC joint. Shows AC joint disease and distal clavicle osteolysis.
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
Stryker notch |
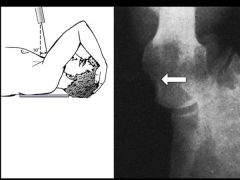
Hill-Sachs lesion
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
West Point Axillary |
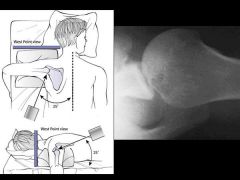
Anteroinferior glenoid, bony bankart, proximal humerus fx
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
Garth |

Anteroinferior glenoid, bony bankart
|
|
|
How to do & what looking for?
Hobbs |
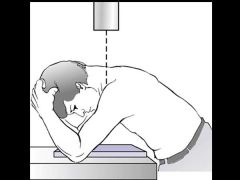
Anterior and posterior sternoclavicular dislocation
|
|
|
Serendipity
|
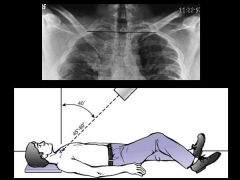
Anterior and posterior sternoclavicular dislocation
|
|
|
useful to visulaize
CT-Axial Shoulder Images |
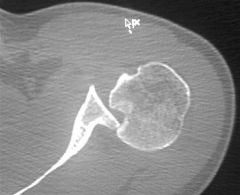
Axial Shoulder Images
Reverse Hill Sachs |
|
|
CT- 3D Reconstructions
useful to visualize |
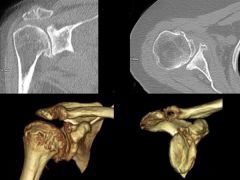
glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty
|
|
|
T2-weighted sequence
uses a long TR and long TE bright= ? (traffic light) dark=?9horse) useful to visualize? |
T2-weighted sequence
uses a long TR and long TE bright= fluid (inflammation) and bone marrow dark= bone, ligament, muscle, and fibrocartilage useful to visualize rotator cuff pathology full thickness tear |
|
|
ABER (abduction external rotation) position
sequence beyond the conventional 3 sequences (coronal, sagittal, and axial) patient position? useful to visualize? (traffic light) |
ABER (abduction external rotation) position
sequence beyond the conventional 3 sequences (coronal, sagittal, and axial) patient places affected hand behind their head instead of a true 90-90 degree abduction-external rotation position position tensions the anteroinferior glenohumeral ligament and labrum and relaxes the capsule useful to visualize Bankart lesions partial- and full-thickness tears of the rotator cuff tendons internal impingement |
|
|
MR arthrogram
optimal for? |
commonly used to augment MRI to diagnose soft-tissue problems such as SLAP tears
-dilute gadolinium-containing solution is percutaneously injected into the joint. labral and ligament pathology |
|
|
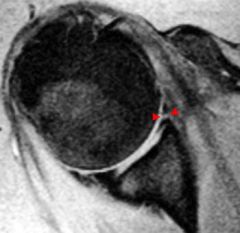
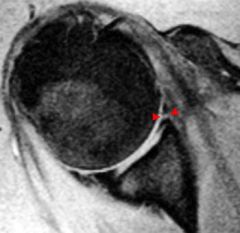
Bankart lesion
|
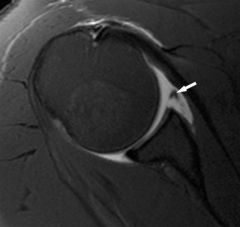
Bankart lesion
|
|
|
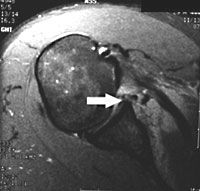
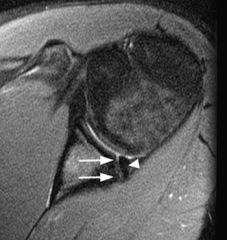
(SLAP)
|
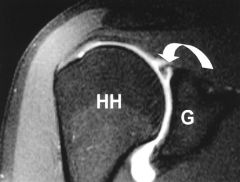
Superior labrum anterior-posterior tear (SLAP)
|
|
|
(GLAD)
|
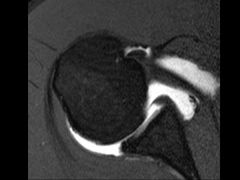
Glenoid labral articular disruption (GLAD)
|
|
|
ALPSA)
|
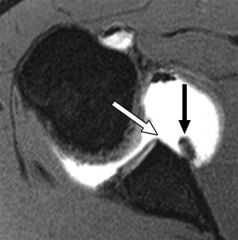
Anterior labral periosteal sleeve avulsion (ALPSA)
|
|
|
(HAGL)
|
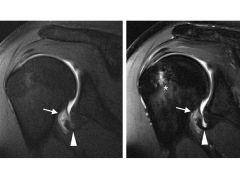
Humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament (HAGL)
|

