![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which group of algae do kelps belong to? |
Brown algae |
|
|
Organisms that obtain nourishment from dead organisms are? |
Saprophytes |
|
|
The transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring is called ____. |
heredity |
|
|
What is the hard shell that covers the cephalothorax of some crustaceans called? |
Carapace |
|
|
What are a crustacean's claw-tipped legs called? |
Chelipeds |
|
|
What wormlike arthropod has many body segments with two pairs of legs on every segment? |
Millipede |
|
|
The four elements that compose cells are ____. |
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen |
|
|
Which group includes spiders? |
Arachnids |
|
|
Cell that contains cellulose, large vacuoles, and chloroplasts would belong to a ____. |
Plant |
|
|
The body regions of arachnids are _____. |
Cephalothorax and abdomen |
|
|
What pair of appendages does an arachnid use for seizing and crushing prey? |
Chelicerae |
|
|
What do mycologists study? |
Fungi |
|
|
Who is the "Father of Microbiology"? |
Van Leeuwenhoek |
|
|
Which of the following is a club fungus? |
Mushroom |
|
|
What disease does plasmodium cause? |
malaria |
|
|
Parasitic club fungi includes smuts and _____. |
Rusts |
|
|
Two main groups of spiders are true spiders and _____. |
Mygalomorphs |
|
|
A _____ structure is too small too be seen without magnification. |
Microscopic |
|
|
The general term for micro organisms that are found near the water's surface and provide food for larger organisms is _____. |
Plankton |
|
|
The group of micro organisms that move using hairlike projections are called ____. |
Ciliates |
|
|
An organism that makes it's own food is a _____. |
Autotroph |
|
|
The jelly like substance in cells that contain organelles |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Organelles in plant cells that enable them to carry out photosynthesis |
Chloroplasts |
|
|
Control center of the cell |
Nucleus |
|
|
Surrounds and protects the cell |
Cell membrane |
|
|
Storage spaces |
Vacuoles |
|
|
Strengthens plant cell walls |
Cellulose |
|
|
List the two parts of the cell theory. |
1. All living things are composed of cells and cell products.
2. All cells come from pre-existing cells. |
|
|
Who discovered the cells of cork? |
Robert Hooke |
|
|
What information storing substance does the nucleus contain? |
DNA |
|
|
What respiratory structure of arachnids has pages that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide? |
Book lungs |
|
|
What are the units through which characteristics are passed from parent to offspring? |
Genes |
|
|
What is the name for the entire mass of hyphae that forms the body of a fungus? |
Mycelium |
|
|
What are single celled animal like organisms called? |
Protozoa |
|
|
What does a sarcodine use to move? |
Pseudopods |
|
|
Form a significant part of marine plankton |
krill |
|
|
Crustaceans that in adulthood attached permanently to an object |
barnacles |
|
|
Have only one eye |
Copepods |
|
|
Also called water fleas |
Daphnia |
|
|
Examples include lobsters, crabs, and crayfish |
Decapods |
|
|
Ten-footed crustaceans |
Decapods |
|
|
The only terrestrial crustaceans |
Wood lice |
|
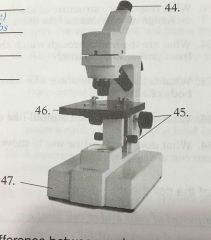
Front (Term) |
44. Eyepiece 45. Adjustment knobs 46. Stage 47. Base |
|
|
ESSAY: Explain The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes and list the major groups of organisms in each category. |
Prokaryotes are single celled organisms without organized nuclei. This group contains bacteria including, blue-green algae called Cyanobacteria. Eukaryotes are organisms with organized nuclei. This group contains plants, animals, fungi, and protozoa. |

