![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
List the common relations of the ureters from kidney to bladder.
|
- exit renal pelvis posterior to renal vessels
- medial edge of psoas separates from transverse processes - anterior to bifurcation of iliac vessels at sacroiliac joint - run along lateral wall of pelvic and curve anteromedially to enter bladder wall inferolaterally at an oblique angle - in males: superior to seminal vesicles with ductus deferens anterior - in females: ovaries, ovarian vessels in suspensory ligament anterior. Lateral to cervix |
|
|
|
What are the relations of the left ureter?
|
- lateral to IMV
- gonadal vessels (off renal vein and aorta) anterior - left colic artery anterior - sigmoid colon anterior |
|
|
|
What are the relations of the right ureter?
|
- lateral to IVC
- second part of duodenum anterior - gonadal vessels (off IVC and aorta) anterior - SMA within mesentery and right colic artery anterior - Ileocolic artery anterior - Cecum and ascending colon anterior |
|
|
|
Diagram of the relations of the ureters.
|
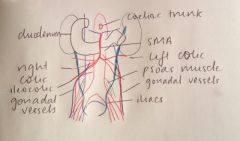
|
|
|
|
Descibe the three fascial spaces surrounding the kidneys.
|
Perirenal space: space surrounding renal capsule containing perinephric fat, adrenals and vessel in lined by renal fascia. The anterior fascia (Gerota’s) and posterior fascia (Zuckerlandl’s) are fused laterally as the lateral conal fascia.
Anterior pararenal space: lies anterior to renal fascia and posterior to posterior peritoneum. Continuous with extraperitoneal pelvic spaces inferiorly. Posterior pararenal space: posterior abdominal wall muscles to posterior renal fascia. Limited by psoas medially, but continuous laterally with extraperitoneal fatty tissue (properitoneal fat plane) |
|
|
|
What are the anterior relations of the left kidney?
|
- stomach
- pancreas and its vessels - spleen - splenic flexure - jejunal loops |
|
|
|
What are the anterior relations of the right kidney?
|
- liver
- second part of duodenum - ascending colon - small intestine loops |
|
|
|
Describe the structure of the suprarenal glands.
|
• Each gland has a body and medial and lateral limbs
• Pyramidal shaped right gland and crescent shaped left gland • Right more consistant location • Each has a hilum where veins and lymphatics exit the gland, arteries enter at multiple sites • Two parts o Outer Suprarenal cortex (90%) derived from mesoderm which secretes corticosteroids and androgens o Inner Suprarenal medulla (10%) derived from neural crest cells (ectoderm) associated with sympathetic nervous system and secretes catecholamines |
|
|
|
What are the relations of the left suprarenal gland?
|
• Posterior to splenic vein, medial to spleen and lateral to crus of diaphragm
• Extends down superomedial border of kidney towards hilum |
|
|
|
What are the relations of the right suprarenal gland?
|
• Posterior to IVC, medial to right lobe of liver and lateral to crus of diaphragm
• Apically situation over superior pole of kidney |
|
|
|
Describe the embryology of the suprarenal glands.
|
• Medulla derived from neural crest cells which migrate to medial surface of developing cortex
• Cortex derived from mesoderm adjacent to mesonephric tubule and predominates during fetal life. - 3 layers: zona reticularis, fasciculate, glomerulosa (from inside out) • Relatively much larger at birth |
|
|
|
Describe the (3) sources of arterial supply to the suprarenal glands.
|
- Superior suprarenal arteries (6-8) from inferior phrenic arteries (arise from aorta superior to coeliac trunk)
- Middle suprarenal arteries (1) from abdominal aorta near SMA origin - Inferior suprarenal arteries (1) from the renal arteries |
|
|
|
What is the lymphatic drainage of the suprarenal glands?
|
• Right suprarenal vein -> IVC
• Left suprarenal vein -> left renal vein |
|
|
|
Describe the anterior and posterior relations of the stomach
|
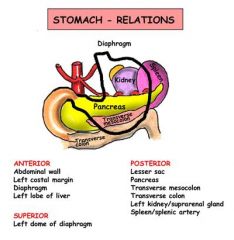
|
Anterior relations
- right side of superior stomach – left lobe of liver - left side of superior stomach – left diaphragm - remainder – anterior abdominal wall Posterior relations - lesser sac - stomach bed - pancreas and transverse mesocolon - splenic artery - spleen - aorta and coeliac trunk and surrounding plexus and nodes - diaphragm - left kidney and adrenal gland |
|
|
List the branches of the abdominal aorta.
|
3 anterior unpaired branches:
• coeliac trunk (T12/L1) supplying foregut • superior mesenteric artery (L1) supplying midgut • inferior mesenteric artery (L3) supplying hindgut 3 paired visceral branches: • adrenal (L1) • renal (L1/L2) • gonadal (L3) 6 paired parietal branches: • subcostal • inferior phrenic (T12) • 4 pairs of lumbar arteries 3 terminating branches: • the median sacral • 2 x common iliac arteries (L4) |
|
|
|
What are the relations of the abdominal aorta?
|
Left lateral: sympathetic chain
Right lateral: IVC, cisterna chyli Both lateral: azygous veins (azygous right, hemi left - commence L2), coeliac ganglia, para-aortic nodes Anterior: pancreas, splenic vein, left renal vien, 3rd part of duodenum, mesentery, nodes, autonomic plexus, lesser sac, stomach, small bowel Posterior: vertebral bodies T12-L4, left lumbar veins |
|
|
|
Draw the branches of the SMA and IMA.
|
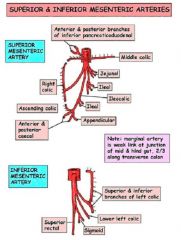
|
|
|
|
Inferior mesenteric artery.
|
Origin
• arises from front of the aorta at the inferior border of 3rd part of the duodenum • opposite L3 • much smaller than SMA Course • descends to the left across the posterior abdominal wall to reach the pelvic brim • crosses the brim at the bifurcation of the left common iliac artery over the SI jt Termination • continues below the pelvic brim as the superior rectal artery Branches • left colic artery - divides into ascending and descending branch • sigmoid arteries • superior rectal artery |
|
|
|
Write notes on the portal vein
|
Origin
- confluence of splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein at L1/L2 behind the neck of the pancreas Course - ascends anterior and to the right of IVC in free edge of lesser omentum. Enters porta hepatis posterior to bile/ artery (BAV) Branches - branches into LPV and RPV (further into RAPV and RPPV) Variants - trifurcation into LPV, RAPV, RPPV - IMV joins at confluence (rather than at SMV) - double PV (non-union splenic and SMV) |
|
|
|
Describe the surface anatomy of the liver
|
- triangular shaped
- largest internal organ within RUQ of abdominal cavity - functional unit is the hepatic lobule - covered by visceral peritoneal except 'bare area' - anterior surface marked by falciform ligament attaching diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall - free inferior margin of falciform ligament is ligamentum teres (obliterated umbilical vein) - posteroinferior surface marked by H-shaped arrangement of structures + cross porta hepatis (BAV) + IVC and GB + ligamentum teres and ligamentum venosum (remnant of ductus venosum attaching to IVC) |
|
|
|
Describe the Couinaud liver segmentation.
|
- divides liver into 8 functionally independant segmnets with own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage
- in the centre is a branch of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct - hepatic veins run between segments • middle hepatic vein divides into left and right (Cantlie's line - IVC to GB fossa) • right divides right lobe into anterior/ posterior • left divides left lobe into medial/ lateral - portal vein further divides into upper and lower segments - named I-VIII (with IV divided into a/b) • I in caudate lobe posteriorly • II - VIII in clockwise direction (II-IV left, V-VIII right) |
|

