![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
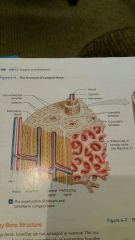
3 types of lamelle |
Concentric, circumfrential, and interstitial |
|
|
|
Which lamellae create target like pattern, with the central canal as a bulls eye |
Concentric |
|
|
|
Which lamellae fill in the spaces btw the osteons in compact bone |
Interstitial |
|
|
|
Which lamellae are found at the outer and inner surfaces of the bone (covered by periosteum and endosteum) |
Circumferential |
|
|
|
Know location of lamellae |
|
|
|
Superficial layer of compact bone that covers all bones is wrapped by a |
Periosteum |
|
|
|
Functions of periosteum (3) |
Isolates the bone fm surounding tissue, provides route foe the blood vessels and nerves, takes part in bone growth and repair |
|
|
|
Endosteum |
Incomplete cellular layer, lines the medullary cavity |
|
|
|
Thin parallel surface, form the roof of the skull, the sternum, ribs, and scapulae |
Flat bone |
|
|
|
Relatively long and slender located in arm and forearm |
Long bone |
|
|
|
Usually small, round, and flat. Develope inside tendons and are most often encountered near joints at the knee |
Sesamoid bones |
|
|
|
Small flat oddly shaped bones found btw the flat bones of the skull |
Sutural bone |
|
|
|
Complex shapes with short, flat, notched or rigid surfaces |
Irregular bones |
|
|
|
Boxlike in appearance, |
Short bones |
|
|
|
Example of sutural bones |
Skull |
|
|
|
Example of irregular bone |
Vertebrae |
|
|
|
Example short bone |
Carpal bones |
|
|
|
Example of flat bone |
Form roof of skull |
|
|
|
Example of long bone |
Humerus |
|
|
|
Example of sesamoid bones |
Patella |
|
|
|
5 primary functuons of skeletal system |
Support, storage of minerals and lipids, blood cell production, protection, leverage |
|
|
|
Bone markings |
Surface features |
|
|
|
Bone markings openings: sinus |
Chamber within a bone normally filled with air |
|
|
|
Bone markings elevations and projections PROCESS |
projection por bump |
|
|
|
Bone marking openings foramen |
Rounded passageway for blood vessels or nerves |
|
|
|
Bone marking openings fissure |
Deep furrow cleft or slit |
|
|
|
Bone marking opening meatus |
Passage or channel especially opening of canal |
|
|
|
Bone markings opening canal |
Duct or channel |
|
|
|
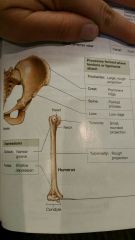
Bone marking elevation projection: process |
Projection or bump |
|
|
|
Bone marking elevation projection: ramus |
Extension of a bone that forms angle wih the rest of the structure |
|
|
|
Bone marking depressions: sulcus |
Narrow groove |
|
|
|
Bone marking depression: fossa |
Shallow depression |
|
|
|
Bone marking process ligaments and tendons attach: trochanter |
Large rough projection |
|
|
|
Bone marking process ligaments and tendons attach: crest |
Prominent ridge |
|
|
|
Bone marking process ligaments and tendons attach: spine |
Pointed process |
|
|
|
Bone marking process ligaments and tendons attach: line |
Low ridge |
|
|
|
Bone marking process ligaments and tendons attach: tubercle |
Small rounded projection |
|
|
|
Bone marking process ligaments and tendons attach: tuberosity |
Rough projection |
|
|
|
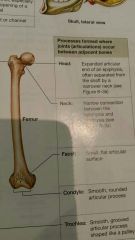
Bone marking process formed where joints occur btw adjacent bone: head |
Expanded articular end of an epiphysis, often seperated by shaft or narrow neck |
|
|
|
Bone marking process formed where joints occur btw adjacent bone: neck |
Narrow connection btw the epiphysis and diaphysis |
|
|
|
Bone marking process formed where joints occur btw adjacent bone: facet |
Small flat articular surface |
|
|
|
Bone marking process formed where joints occur btw adjacent bone: condyle |
Smooth rounded articular process |
|
|
|
Bone marking process formed where joints occur btw adjacent bone: trochlea |
Smooth grooved articular proce$ shaped like a pulley |
|
|
|
Know these |
|
|
|
Knwow these |
|
|
|
Bone markings |
|
|
|
4 types of bone cells |
Osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteogenic cells, osteoclasts |
|
|
|
Osteocytes (do and location) |
Mature bone cell that maintains the bone matrix. Located inside the matrix |
|
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Immature, produce new bone matrix in process called ossification or osteogenesis |
|
|
|
Osteogenic cells (do and location) |
Mesenchymal cells, maintain population of osteoblasts and important in fracture repair. Found in inner cellular layer of periosteum also endosteum |
|
|
|
Osteoclasts (do and location) |
Cells that absorb and remove bone matrix |
|
|

|
Bone cells |
|
|
|
Diaphysis |
Shaft |
|
|
|
Epiphysis |
Head part of long bone |
|
|
|
Metaphysis |
Part btw head and shaft of long bone |
|
|
|
Compact bone |
"Dense bone" relatively solid |
|
|
|
Medullary cavity |
Innermost part "marrow cavity" |
|
|
|
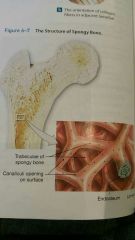
Spongy bone |
"Cancellous or trabecular bone" consists of open network of struts and plates that resembles latticework |
|
|
|
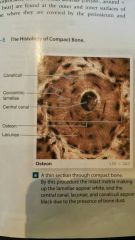
Compact bone structure |
Osteon "halversian system" Central canal "haversian canal" Perforating canals "volkmanns canal" |
|
|
|
Compact bone structure: central canal |
Contains 1 or more blood vessels that carry blood to and from the osteon |
|
|
|
Compact bone structure: perforating canals |
Extend perpendicular to the surface. Blood vessels supply blood to osteons deeper in the bone and to tissues of medullary cavity |
|
|
|
Compact bone structure |
|
|
|
Spongy bone structure: trabeculae |
Matrix forms meshwork of supporting bundles of fibers called trabeculae |
|
|
|
Spongy bone structure |
|
|
|
Canaliculi |
Microscopic passageway btw cells, permit the diffusion of nutrients and wastes to and from osteocytes |
|
|
|
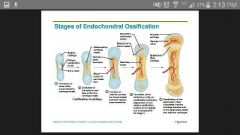
Endochondral ossification |
Cartilage models are gradually replaced by bone. Long bone |
|
|

|
Steps to endochondral ossification |
Boys cant pee with erection |
|
|
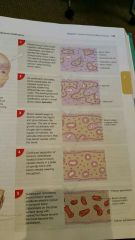
Intramembranous ossification "dermal" which bones |
Flat bones of the skull, mandible and clavicle |
|
|
|
Know the steps |
|
|
|
Intramembranous ossification |
|
|
|
|
Bone growth appositional |
Width |
|
|
|
Bone growth interstitial |
Length |
|
|
|
2 Key hormones produce calcium ion homeostasis |
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitriol (increase rate of calcium ion) Calcitonin (decrease blood calcium ions) Lg #s released bone bc weaker, lg #s deposited bones bc stronger |
|
|
|
Fracture repair |
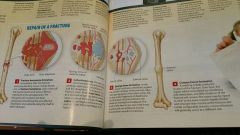
|

|
|
|
Axial skeleton (which 80 bones) |
Skull (8 cranium 14 facial) 6 auditory ossicles and hyoid bone 24 vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, sternum and 24 ribs |
|
|
|
Appendicular bones |
Support the limbs... clavicle, legs, arms |
|
|
|
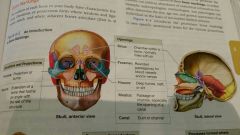
Name bones of the eye orbit |
(Top) frontal bone (rt side) lacrimal and ethmoid bone (bottom) maxilla and palatine bone (left side) sphenoid and zygomatic bone |
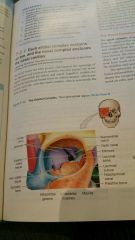
|
|
|
Synarthrosis |
(No movement)
Suture-skull Gomphosis-binds teeth to maxillae Synchondrosis- btw ribs and sternum Synostosis- 2bones fuse (frontal skull) |

|
|
|
Amphiarthrosis |
Little movement
Syndesmosis-bones connected by ligament Symphysis-bones connected by wedge or pad of fibrocartilage (btw 2 pelvic bones) |

|
|
|
Diarthrosis |
Free movement
Synovial-wider range of motion, typically at ends of long bones |

|
|
|
Diarthrosis (planes of movement) |

|
|
|
|
Extension |
Return to anatomical position |
|
|
|
Extension |
Return to anatomical position |
|
|
|
Flexion |
Flexing (bend elbow) |
|
|
|
Abduction |
Away from body |
|
|
|
Adductuion |
Toward body |
|
|
|
Spination |
Palm up |
|
|
|
Pronation |
Palm down |
|
|
|
Eversion |
Turns the sole outward |
|
|
|
Inversion |
Turns the sole of the foot inward |
|
|
|
Head rotation |
Right and left |
|
|
|
Arm rotation |
Lateral (out palm up) Medial (in palm down) |
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion |
Ankle joint (dig heel into ground) |
|
|
|
Plantar flexion |
Ankle joint (stand on tip toes) |
|
|
|
Opposition |
Bring thumb to pinky |
|
|
|
Retraction |
Bring chin to throat |
|
|
|
Protraction |
Extend chin outward |
|
|
|
Depression |
Open mouth (depress mandable) |
|
|
|
Elevation |
Close mouth |
|
|
|
Lateral flexion |
Vertebral column bends to side |
|
|
|
Spine (specific joints) (ligaments) |
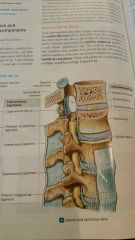
The bodies of vertebrae form symphyseal joints. Slight rotation and flexion/extension |
Also ligamentum nuchae extends frm c7 to base of skull where supraspinous ligament is fm c7 to sacrum |
|
|
Shoulder joint (joint and ligaments) |
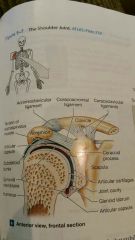
Glenohumeral joint, ball and socket diarthrosis formed by articulation of head of humerus with the glenoid cavity of scapula. **acromioclavicular ligament, coracoclavicular ligament, and coracoacromial ligament |
|
|
|
Muscles of rotator cuff |
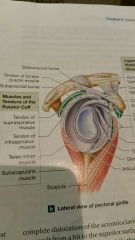
Teres minor and subscapularis |
|
|
|
Hip joint |
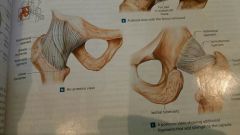
Ball and socket, **pubofemoral ligament, iliofermoral and ischiofemoral ligament |
|
|
|
Knee joint (joint and ligament) |
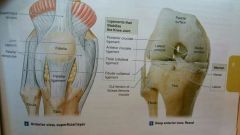
Complex hinge *patellar ligament, posterior cruciate, tibial collateral, fibular collateral |
|

