![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
235 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Thermoregulation |
Mechanism where the body balances heat production and heat loss |
|
|
|
Anatomy |
The branch of science that studies the structure of the body. For example anatomy describes what the heart looks like, how big it is, what it is made of, how it is organized, and where it is located. |
|
|
|
Physiology |
The branch of science that describes how the body functions. For example, how the heart pumps blood and why the pumping of blood is essential. |
|
|
|
What is a saggital plane? |

The Sagittal plane divides the body lengthwise into right and left portions. |
|
|
|
Is the leg distal or proximal to the thigh? |
Distal |
|
|
|
If an organ is inferior to the diaphragm what does it mean? |
That it is located (below) |
|
|
|
Is the foot proximal or distal to the leg? |
Distal |
|
|
|
Is the foot proximal or distal to the leg? |
Distal |
|
|
|
What is proximal? |
Proximal means that the structure is nearer to the point of attachment, often to the trunk of the body. |
|
|
|
What is distal? |
A part is farther away from the point of attachment than another part. |
Ex: The wrist is distal to the elbow, and the fingers are distal to the wrist. |
|
|
Is the foot proximal or distal to the leg? |
Distal |
|
|
|
Is the leg distal or proximal to the thigh? |
Distal |
|
|
|
Where is the dorsal cavity located and what lies in it? |
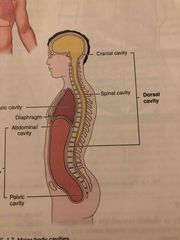
It is located toward the back of the body and has two divisions, the cranial cavity and spinal cavity. |
|
|
|
Where are these regional terms located in the body axillary, occipital, cervical, diaphragm and inguinal? |
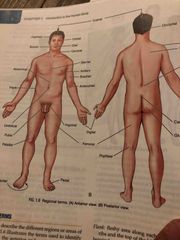
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is a frontal (coronal) plane? |

It divides the body into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) portions. This plane creates the front part of the body and the back part of the body. |
|
|
|
What is a transverse plane? |

It divides the body horizontally, creating an upper (superior) and a lower (inferior) body. |
|
|
|
What is a saggital plane? |

The Sagittal plane divides the body lengthwise into right and left portions. |
|
|
|
If an organ is inferior to the diaphragm what does it mean? |
That it is located (below) |
|
|
|
Integumentary System |
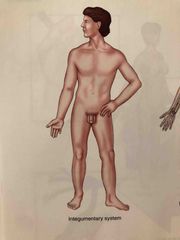
It consists of the skin and related structures such as hair and nails. The integumentary system forms a covering of the body, helps regulate body temperature and contains some of the structures necessary for sensation. |
|
|
|
Skeletal System |
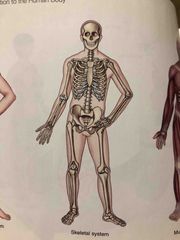
Forms the basic framework of the body. It consists primarily of bones, joints and cartilage. The skeleton protects and supports body organs and enables us to move around. |
|
|
|
Muscular System |
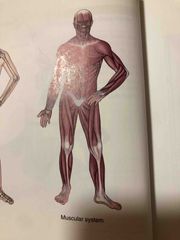
Has 3 types of muscles, skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles attach to bones and are responsible for movement of the skeleton and maintenance of body posture. Smooth and Cardiac muscles are found in various organs and tubes, contraction and relaxation of these muscles help the organ systems carry out their functions. |
|
|
|
Nervous System |
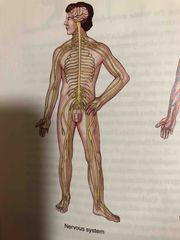
Is made up of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs. Decisions made by the brain and spinal cord are transmitted along motor nerves to various body structures. |
|
|
|
Endocrine System |
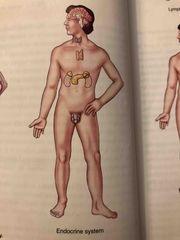
Contains numerous glands that secrete hormones and chemical substances that regulate body activities such as growth, reproduction, metabolism, and water balance. |
|
|
|
Circulatory System |
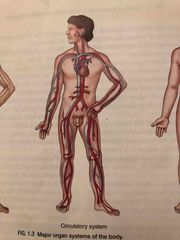
Consists of the blood, heart and blood vessels. This system pumps (heart) and transports (blood vessels) blood throughout the body. Blood carries nutrients and oxygen to all the body’s cells and also carries the waste away from the cells to the organs of excretion. |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System |
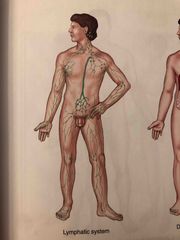
System made up of the lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, lymph and other lymphatic organs. Lymph and lymphatic structures play an important role in fluid balance and in defense of the body against pathogens and other foreign material. |
|
|
|
Immune System |
Is an elaborate defense system that protects the body not only from pathogens but also from allergens, such as pollens, bee venom and some of our own cells that have gone awry (cancer cells). |
|
|
|
Respiratory System |
Contains the lungs and other structures that conduct air to and from the lungs, the oxygen is picked up by the blood and distributed throughout the body. |
|
|
|
Digestive System |
Is comprised of organs designed to ingest food and break it down into substances that can be absorbed by the body. Food that is not absorbed is eliminated as waste. |
|
|
|
Urinary System |
Contains the kidneys and other structures that help excrete waste products from the body through the urine. Helps control water, electrolyte and acid base balance in the body. |
|
|
|
Reproductive System |
Made up of organs and structures that enable humans to reproduce. |
|
|
|
What are the levels of organization? |
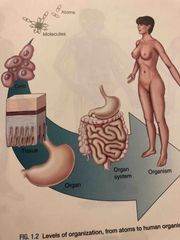
1. Atoms 2. Molecules 3. Cells 4. Tissue 5. Organ 6. Organ System 7. Organism |
|
|
|
Abdominal |
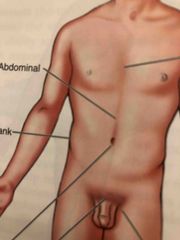
Anterior trunk just below the ribs |
|
|
|
Antecubital |
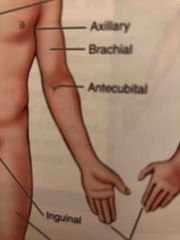
Area in front of the elbow |
|
|
|
Axillary |
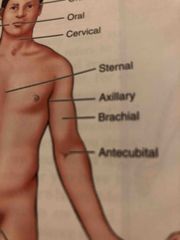
Armpit |
|
|
|
Brachial |
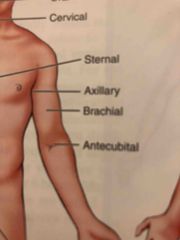
Arm |
|
|
|
Buccal |
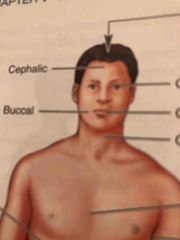
Cheek area, cavity between the gum and cheek |
|
|
|
Cephalic |
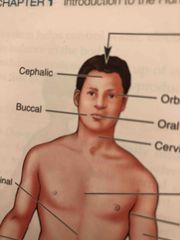
Head |
|
|
|
Cervical |
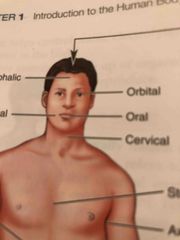
Neck region |
|
|
|
Cranial |
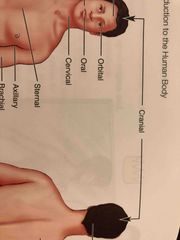
Nearer to the head |
|
|
|
Digital |
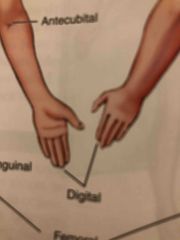
Fingers, Toes |
|
|
|
Femoral |
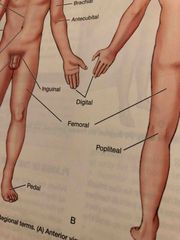
Thigh Area |
|
|
|
Flank |
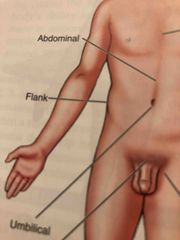
Fleshy area along each side between the lower ribs and the top of the hip bones |
|
|
|
Inguinal |
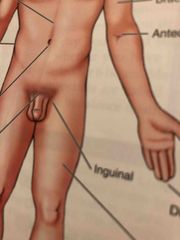
Area where the thigh meets the trunk of the body; often called groin |
|
|
|
Oral |
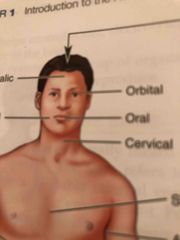
Mouth |
|
|
|
Orbital |
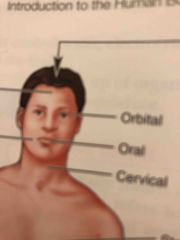
Around the eye |
|
|
|
Patellar |
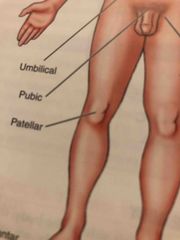
Front of the knee over the kneecap |
|
|
|
Pedal |
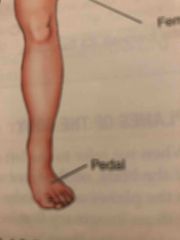
Foot |
|
|
|
Plantar |
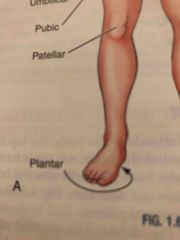
Sole of the foot |
|
|
|
Pubic |
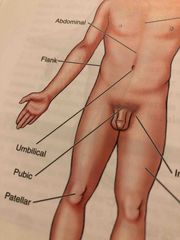
Genital Area |
|
|
|
Sternal |
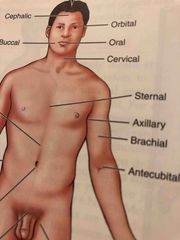
Middle of the chest (over the breastbone area) |
|
|
|
Umbilical |
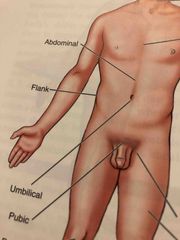
Navel |
|
|
|
Caudal |
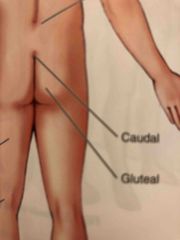
Near to the lower region of the spinal column (near the tailbone) |
|
|
|
Deltoid |
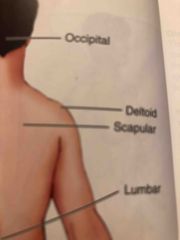
Rounded area of the shoulder closest to the arm |
|
|
|
Gluteal |
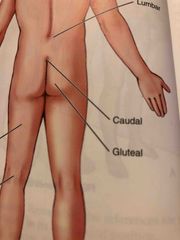
Buttocks |
|
|
|
Lumbar |
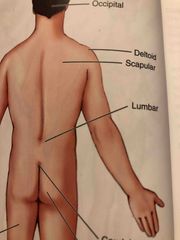
Area of the back between the ribs and the hips |
|
|
|
Occipital |
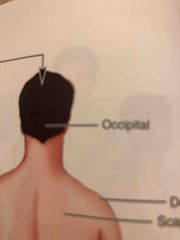
Back of the head |
|
|
|
Popliteal |
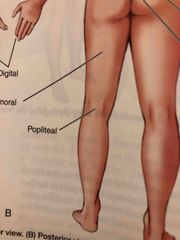
Behind, or back of, the knee area |
|
|
|
Scapular |
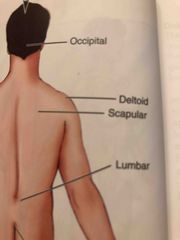
Shoulder Blade Area |
|
|
|
What are the major body cavities? |
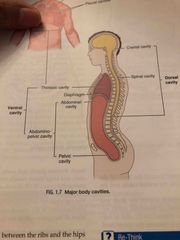
Dorsal Cavity, Ventral Cavity and Abdominopelvic Cavity |
|
|
|
What are the four quadrants? |
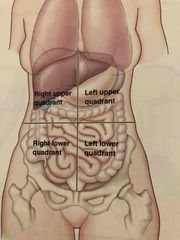
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What are the nine regions in the abdominopelvic cavity? |
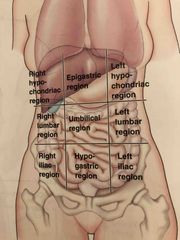
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Homoestasis |
The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment in response to various internal and external challenges |
|
|
|
Anatomical Position |
The body standing erect, arms by the side, with Palma and toes facing forward |
|
|
|
Relative positions |
Superior, Inferior, Anterior, Posterior, Medial, Lateral, Proximal, Distal, Superficial, Deep, Central and Perioheral |
|
|
|
Dorsal Cavity |
a. Cranial Cavity: Contains the brain b. Spinal (vertebral) Cavity: Contains the spinal cord |
|
|
|
Ventral Cavity |
a. Thoracic Cavity: superior to the diaphragm; contains the pleural cavities (lungs), mediastrium and pericardial Cavity b. Abdominopelvic Cavity: located inferior to the diaphragm c. Abdominal Cavity: upper part that contains the stomach, most intestines, and the liver, spleen, and the kidneys d. Pelvic Cavity: lower part that contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and lower parts of the intestines e. For reference: the Abdominopelvic Cavity is divided into four quadrants and nine regions. |
|
|
|
Medial |
Toward the midline of the body; opposite of lateral |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Structure that is nearer to the trunk than another part; opposite of distal |
|
|
|
Distal |
Part of the radius (forearm bone) that is closer to the wrist than to the elbow |
|
|
|
Superior |
The lungs are located above the diaphragm; their position relative to the diaphragm is described as being above |
|
|
|
Anterior |
Toward the front ( belly surface) another word is ventral |
|
|
|
Armpit |
Axillary |
|
|
|
Kneecap area |
Patellar |
|
|
|
Breastbone area |
Sternal |
|
|
|
Front part of the elbow area |
Antecubital |
|
|
|
Fleshy area along the side between the ribs and hip bone |
Flank |
|
|
|
Fleshy area along the side between the ribs and hip bone |
Flank |
|
|
|
Pertaining to the mouth |
Oral |
|
|
|
Lower back area extending from the chest to the hips |
Lumbar |
|
|
|
Pertains to the space between the cheek and gum |
Buccal |
|
|
|
Groin region |
Inguinal |
|
|
|
Shoulder blade area |
Scapular |
|
|
|
This part of the humerus (arm bone is closer to the elbow than to the axillary region. |
Distal |
|
|
|
Describe the relationship of the mediastinum to the diaphragm. |
Superior |
|
|
|
The umbilical region is located |
Inferior of the diaphragm |
|
|
|
The sternal area is |
Referred to as the breastbone area |
|
|
|
Which of the following is not descriptive of the mediastinum? |
Dorsal Cavity |
|
|
|
The frontal plane |
Is also the coronal plane |
|
|
|
Which of the following terms best describes when a person sweats in order to decrease body temperature? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
|
Which of the following is true these terms: sternal, umbilical, patellar, and antecubital? |
All can be viewed on the anterior body. |
|
|
|
These structures are located within the pleural cavities, the thoracic cavity and the ventral cavitiy. |
Lungs |
|
|
|
These structures are located within the pericardial cavity, the mediastinum and the thoracic cavity. |
Heart and great vessels |
|
|
|
The common element of the words pathology, pathogen, and pathophysiology is that they all refer to |
disease |
|
|
|
Where is Epithelial Tissue found? |
Epithelial tissue helps forms the skin and covers the entire outer surface of the body. Sheets of epithelium also line most of the inner cavities such as the mouth, respiratory tract, and reproductive tract. |
|
|
|
Where is Epithelial Tissue found? |
Epithelial tissue helps forms the skin and covers the entire outer surface of the body. Sheets of epithelium also line most of the inner cavities such as the mouth, respiratory tract, and reproductive tract. |
|
|
|
What does epithelial tissue do? |
Epithelial tissue is primarily concerned with protection and transport. |
|
|
|
Where is Epithelial Tissue found? |
Epithelial tissue helps forms the skin and covers the entire outer surface of the body. Sheets of epithelium also line most of the inner cavities such as the mouth, respiratory tract, and reproductive tract. |
|
|
|
What does epithelial tissue do? |
Epithelial tissue is primarily concerned with protection and transport. |
|
|
|
Simple Squamous |
Found on walls of blood vessels Alveoli (Air sacs in lungs) Kidneys
Permits the exchange of nutrients and wastes. Allows diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Filtration of water and electolytes |
|
|
|
Where is stratified squamous tissue found? |

Mouth and Skin |
|
|
|
Where is simple cuboidal tissue found? |
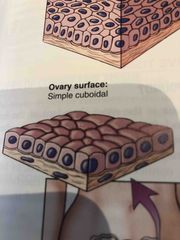
Ovary Surface |
|
|
|
Where is Pseudostratified Columnar tissue found? |
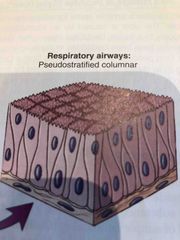
Respiratory Airways |
|
|
|
Where is Simple Squamous tissue found? |
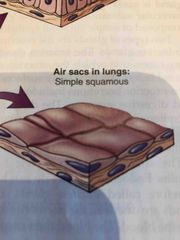
Air sacs in lungs |
|
|
|
Where is transitional tissue found? |
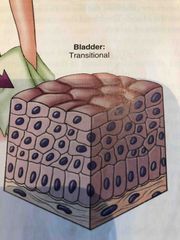
Bladder |
|
|
|
Where is simple columnar tissue found? |
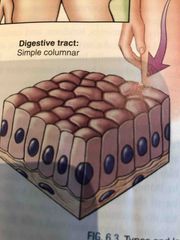
Digestive tract |
|
|
|
Exocrine Glands |
Have ducts; Includes mucus, sweat, saliva and digestive enzymes. |
|
|
|
Exocrine Glands |
Have ducts; Includes mucus, sweat, saliva and digestive enzymes. |
|
|
|
Endocrine Glands |
Ductless; secrete hormones such as insulin. |
|
|
|
What are tendons? |
Cordlike structures that attach muscles to bones. |
|
|
|
Ligaments |
Cross joints and attach bones to each other. |
|
|
|
Medical Terminology |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Important functions: secretion, absorption, excretion, and protection |
Epithelial |
|
|
|
Classified as squamous, cuboidal, or columnar |
Epithelial |
|
|
|
Classified as squamous, cuboidal, or columnar |
Epithelial |
|
|
|
Endocrine and exocrine glands arise from this type of tissue |
Epithelial |
|
|
|
Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth |
Muscle |
|
|
|
Has the greatest amount of intercellular matrix |
Connective |
|
|
|
Intercellular matrix may be liquid, gel or rigid |
Connective |
|
|
|
Intercellular matrix may be liquid, gel or rigid |
Connective |
|
|
|
Dendrites, axons and glia |
Nervous |
|
|
|
What is not a characteristic of epithelial tissue? |
Large amount of mineral-containing intercellular matrix |
|
|
|
Adipose tissue is |
A type of connective tissue that stores fat |
|
|
|
Characteristics of Osseous tissue include |
-Contains hard mineral containing intercellular matrix -Contains osteocytes -Is a type of connective tissue |
|
|
|
With regard to the pleural membranes |
There is a visceral and parietal pleural membrane |
|
|
|
The pleural and peritoneum |
Are serous membranes |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue is a vascular, meaning that it |
Contains no blood vessels |
|
|
|
The intracellular matrix of connective tissue |
Can be hard, liquid or gel like in consistency |
|
|
|
Skin Glands |
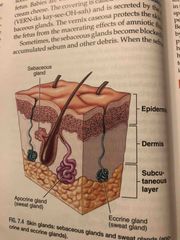
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Another name for sweat glands |
Sudoríferos Glands |
|
|
|
Apocrine glands |
Usually associated with hair follicles and are found in the axillary and genital areas. They respond to emotional stress and become active when person is frightened, upset, in pain or sexually excited. |
|
|
|
Ceruminous Glands |
Found in the external auditory canal of the ear. They secrete cerium or eat wax. |
|
|
|
Thermoregulation |
Mechanism where the body balances heat production and heat loss |
|
|
|
Hypothermia |
An excessive decrease in body temperature |
|
|
|
Hyperthermia |
An excessive increase in body temperature |
|
|
|
Radiation |
Heat is lost from a warm object (the body) to cooler air surrounding the warm object. |
|
|
|
Conduction |
The loss of heat from a warm body to a cooler object in contact with the warm body. |
|
|
|
Convection |
The loss of heat by air currents moving over the surface of the skin. |
|
|
|
Evaporation |
Occurs when a liquid becomes a gas. |
|
|
|
Where is the thermostat of the body located? |
In the hypothalamus |
|
|
|
What is another word for fever? |
Pyrexia |
|
|
|
What is Eschar? |
Dead, burned tissue that forms a thick, inflexible, scablike layer over the burned surface. |
|
|
|
Paronychia |
A skin infection around the nail usually at the site of a hangnail or cuticle. |
|
|
|
What is Trichotillomania? |
An impulse control disorder in which the person compulsively twists strands of hair until they break off. |
|
|
|
Acne Vulgaris |
Common acne, characterized by scaly red skin, comedones, papeles, nodules and pustules. |
|
|
|
Dermatitis |
Inflammation of the skin |
|
|
|
Paoriasis |
An autoimmune disease often confused with eczema. Affects the life cycle of skin cells, causing them to build up on the surface of the skin. |
|
|
|
Impetigo |
A bacterial infection that appears most often on the face and is caused by beta-hemolytic streptococci or staphylococci. |
|
|
|
Dermatophytosis |
Also called ringworm, refers to infection by a group of fungi called dermatophytes and occurs primarily in the skin, nails and hair. |
|
|
|
Onychocryptosis |
An ingrown nail usually in the big toe most often caused by improper cutting of the toenails or the wearing of tight shoes. |
|
|
|
Thin outer layer of skin |
Epidermis |
|
|
|
Layer that sits on the hypodermis and supports the edpidermis |
Dermis |
|
|
|
A protein that flattens, hardens, and makes the skin water resistant |
Keratin |
|
|
|
A layer of insulation |
Subcutaneous layer |
|
|
|
Contains the stratum germinativum and stratum corneum |
Epidermis |
|
|
|
Contains the stratum germinativum and stratum corneum |
Epidermis |
|
|
|
Contains blood vessels that nourish the stratum germinativum |
Dermis |
|
|
|
Oil glands |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Glands that secrete Vernon caseosa |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Glands that play a crucial role in body temperature regulation |
Eccrine |
|
|
|
Modified sweat glands that secrete ear wax |
Ceruminous |
|
|
|
Modified sweat glands that secrete milk |
Mammary |
|
|
|
Classified as sudoriferous |
Eccrine |
|
|
|
Most related to blackhead, pimple and cradle cap |
Sebaceous |
|
|
|
Secretes sweat during intense exercise |
Eccrine |
|
|
|
Tanning pigment |
Melanin |
|
|
|
Tanning pigment |
Melanin |
|
|
|
Condition in which the skin has a bluish tint because of poor oxygenation |
Cyanosis |
|
|
|
Yellowing of the skin because of bilirubin |
Jaundice |
|
|
|
Patches of white skin caused by loss of pigmentation |
Vitiligo |
|
|
|
Black and blue mark; bruising |
Ecchymosis |
|
|
|
Ashen color due to decreased amount of oxygenated blood |
Cyanosis |
|
|
|
The stratum germinativum |
Gives rise to epidermal cells |
|
|
|
The epidermis is nourished by the |
Blood vessels in the underlying dermis |
|
|
|
Secretion is the eccrine glands |
Lowers body temperature |
|
|
|
Shivering thermogenesis |
Increases body temperature |
|
|
|
Blushing, flushing, and pallor are due to |
Changes in blood flow through the dermal blood vessels |
|
|
|
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton |
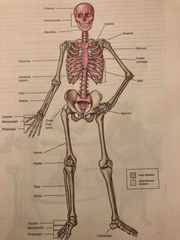
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Types of bones: |
-Long bones -Short bones -Flat bones -Irregular bones |
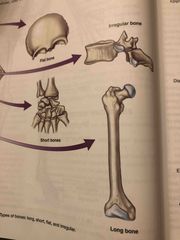
|
|
|
Compact Bone |
Refers to dense, hard bone tissue found primarily in the shafts of long bones and on the outer surfaces of other bones. |
|
|
|
Spongy Bone |
Located primarily at the ends of long bones and in the center of other bones. |
|
|
|
Diaphysis |
Long shaft is the bone. It is composed primarily of compact bone and therefore provides considerable strength. |
|
|
|
Epiphysis |
The enlarged ends is the long bone. |
|
|
|
Epiphyseal disc |
A growing long bone contains a band if hyaline cartilage located near the proximal and distal ends of long bones. |
|
|
|
Medullary Cavity |
The hollow center of the diaphysis. |
|
|
|
Periosteum |
A tough, fibrous connective tissue membrane that covers the outside is the diaphysis. |
|
|
|
Periosteum |
A tough, fibrous connective tissue membrane that covers the outside is the diaphysis. |
|
|
|
Articular Cartilage |
Found on the outer surface of the epiphysis. It forms a smooth, shiny surface that decreases friction within a joint. |
|
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Bone destroying cells |
|
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Bone Remodeling |
|
|
|
Common types of fractures: |
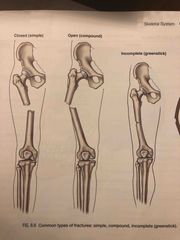
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
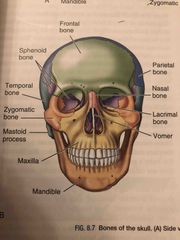
Side view of the Skull: |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Front view of the skull: |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
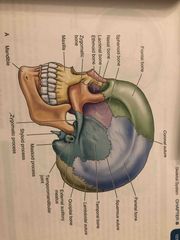
Base of the skull: |
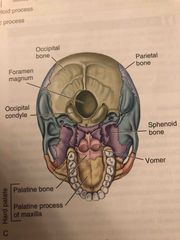
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Sinuses |
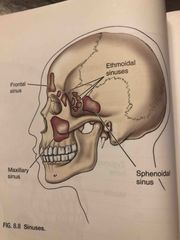
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Fontanels in the infant skull: |
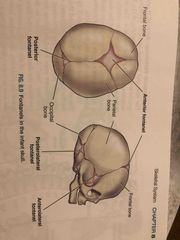
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Vertebral Column |
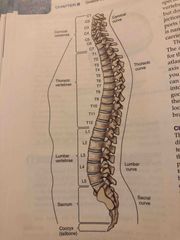
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Anatomy of a vertebra |
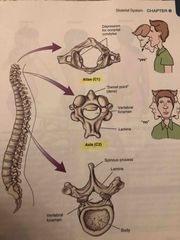
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Abnormal curvatures of the vertebral column |
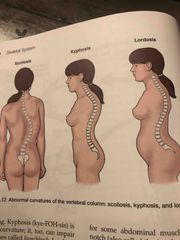
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Thoracic Cage: |
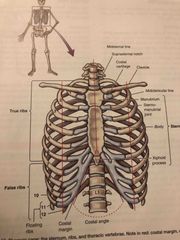
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Bones of the shoulder and upper limb: |
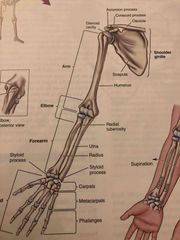
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Bones that make up the pelvis |
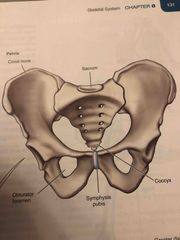
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Coxal Bone |
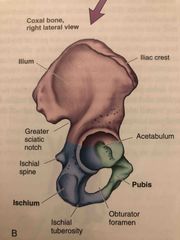
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Female vs Male Pelvis |
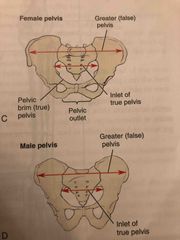
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Bones of the hip and lower limb |
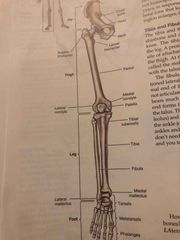
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Bones of the foot |
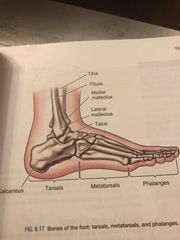
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Synovial joint (knee) structures |
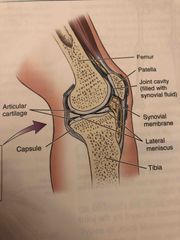
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Freely Movable Joints |
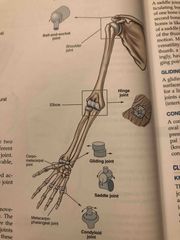
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Extension and Flexion |
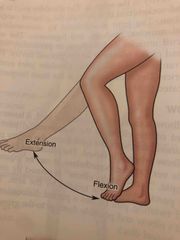
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Eversión and Inversion |
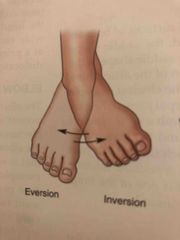
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Supination and Pronation |
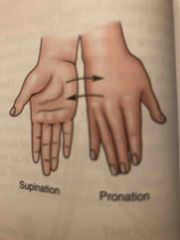
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Adduction and Abduction |
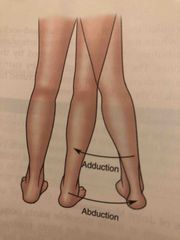
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion and Plantar flexion |
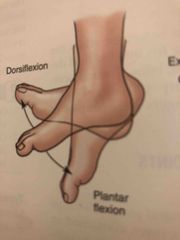
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Hypertension, Extension and Flexion |
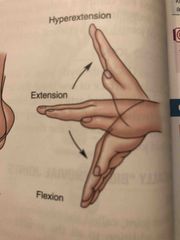
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Circumduction |
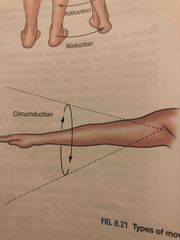
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Smooth Muscle |
Generally found in the walls of the viscera such as the stomach and is called visceral muscle. (Involuntary Muscle) |
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle |
Found only in the heart where it functions to pump blood throughout the body. |
|
|
|
Curare |
A drug classified as a skeletal muscle blocker. Curate works by blocking the receptor sites on the muscle membrane. |
|
|
|
“Chief muscle” |
Prime mover |
|
|
|
Synergists |
Work with other muscles |
|
|
|
Antagonists |
Muscles that oppose the action of another muscle |
|
|
|
Hyperteophy |
Overused muscles that increase in size. |
|
|
|
Atrophy |
If muscles are not used they will waste away or decrease in size. |
|
|
|
Contracture |
If a muscle is immobilized for a prolonged period it may develop a contracture, an abnormal formation of the fibrous tissue within the muscle. |
|
|
|
Major Muscles of the Body (Anterior View) |
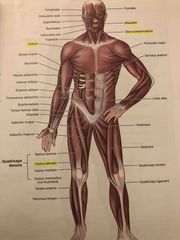
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
(Posterior View) |
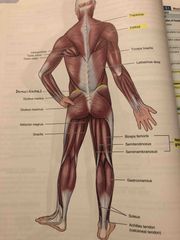
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Muscles of the Head and Neck |
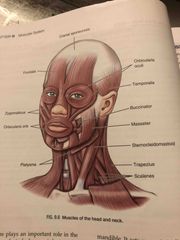
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Breathing Muscles |
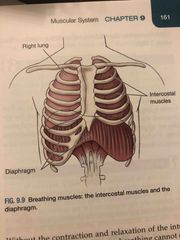
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Arthalgia |
Noninflammatory joint pain |
|
|
|
Arthritis |
Inflammation of a joint |
|
|
|
Bursitis |
Inflammation of one or more bursae |
|
|
|
Fibromyalgia |
A syndrome characterized by pain in the muscles, tendons and soft tissues. |
|
|
|
Fracture |
Broken bone |
|
|
|
Luxation |
Displacement of a bone from its joint with tearing of ligaments, tendons, and articular capsule |
|
|
|
Osteomalacia |
Softening of the bones |
|
|
|
Osteomyelitis |
A serious infection of the bone, bone marrow and surrounding tissue. |
|

