![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
289 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diabetes insipidus |
Under production of ADH |
|
|
Pituitary gland |
Master gland |
|
|
Graves disease |
Hyperthyroidism autoimmune attack on thyroid |
|
|
Hashimoto's disease |
Immune attack on thyroid |
|
|
Goiter |
Enlargement of thyroid, hypothyroidism |
|
|
Diabetes |
Abnormally high blood glucose, hyperglycemia |
|
|
Addison's disease |
Deficiency of adrenal corticosteroids, autoimmune attack on adrenal cortex |
|
|
Chronic stress |
Cortisol |
|
|
Negative feedback |
Back to set point |
|
|
Anterior pituitary |
Prolactin, responsible for lactation, milk production |
|
|
Acromegaly |
Too much growth hormone |
|
|
TSH |
Produced by anterior pituitary |
|
|
T3 |
Controls metabolism |
|
|
Pituitary Gland
|
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)-cuts down urination |
|
|
Vertebrae Facts |
(in this order) Cervical-7 / / Thoracic-12 / / Lumbar(lumbar)-5 / / Sacrum / / Coccyx |
|
|
Anabolism
|
builds molecules
|
|
|
Electrons
|
subatomic particles responsible for chemical behavior of atoms
|
|
|
hypochondriac
|
|
|
|
epigastric |
abdominal region located superior to umbilical region |
|
|
Dorsal cavity |
houses the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
ion |
charged molecule (ex. electrolytes) |
|
|
abdominopelvic cavity |
houses the digestive organs |
|
|
DNA |
nucleic acid |
|
|
polar covalent |
molecule w/ slight charge |
|
|
sodium chloride/carbon dioxide |
not a biological molecule |
|
|
biological molecules |
proteins, carbs, fats & nucleic acids. carbon is found in each. |
|
|
ATP |
provides energy to cells |
|
|
concentration
|
the amount of substance dissolved in a liquid |
|
|
solute
|
the substance being dissolved |
|
|
solvent |
the liquid something is being dissolved in
|
|
|
peptide bonds |
protein made up of amino acids |
|
|
exacerbation
|
acute flare up |
|
|
remission
|
when the disease comes back |
|
|
nucleic acids |
molecules that form the genetic material of cells |
|
|
isotopes
|
differ in the number of neutrons |
|
|
binary fission |
the process that prokaryotic cells are reproduced through |
|
|
nucleus
|
-protein synthesis (building) |
|
|
enzymes
|
proteins that speed up the process |
|
|
prokaryotic cells |
bacterial cells, no nucleus or organelles, still has DNA |
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
watery solution of organic proteins and inorganic minerals and gases that is enclosed in the cell membrane
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
packaging and processing of proteins |
|
|
ATP (energy) |
produced during cellular respiration |
|
|
Flagella |
sperm cell |
|
|
Ribosomes |
where proteins are made. organelles found on the endoplasmic reticulum or floating around the cytoplasm |
|
|
cilia |
hair like projections found on the cell surface |
|
|
enzymatic reactions |
causes catalysis (break down) reactions |
|
|
meiosis |
cell division resulting in production of gametes |
|
|
gametes |
produces eggs and sperm |
|
|
prophase |
the nucleus disappears during this phase, chromosomes become visible and centrioles move towards the sides of the cell |
|
|
metaphase |
chromosomes are in the center/middle of the cell |
|
|
PMAT (order of mitosis) |
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telephase |
|
|
anaphase
|
the chromosomes split, and the spindles pull apart |
|
|
telophase
|
the chromosomes go to the far end of the cell, the spindle disappears and the nuclei reappear |
|
|
interphase |
cell performs normal functions |
|
|
skeletal muscle
|
striated and voluntary |
|
|
compact
|
dense hard bone that forms the shafts of long bones |
|
|
sternum
|
flat bone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
main transport system of the body |
|
|
osteocyte
|
cell type that is the mature bone cell
|
|
|
osteoclast
|
breaks bone down |
|
|
osteoblast |
builds bone |
|
|
neuron |
cell that conducts information |
|
|
synovial |
membrane that is associated with connective tissue |
|
|
epithelial tissue |
|
|
|
serous membrane
|
don't open to outside |
|
|
mucous membrane
|
opens to the outside |
|
|
transitional |
epithelial tissue that is stretchy and variably shaped |
|
|
stratified |
arranged in layers |
|
|
visceral |
membrane that wraps around the outside of an organ (serous membrane) |
|
|
Serous Membrane
|
consists of the visceral and parietal membranes |
|
|
bursa |
small sac containing synovial fluid |
|
|
connective
|
most common tissue in the body; blood and lymph |
|
|
tendons |
cordlike structures that attach bone to muscle |
|
|
ligaments
|
bone to bone |
|
|
larynx (voice box) |
not an organ of the digestive system |
|
|
gliding |
joint found in wrists and ankles |
|
|
axon |
information transported away from a nerve cell body |
|
|
septicemia |
condition characterized by having a pathogen in the blood |
|
|
mucous |
membranes that line the digestive tract |
|
|
digestive tract |
starts at mouth and ends at anus |
|
|
red marrow |
site of hemopoiesis |
|
|
break down bone |
cell type that has the main role to break down bone |
|
|
medullary canal |
hollow region in long bone |
|
|
foramen |
passageway through a bone |
|
|
sarcomere |
functional unit of a muscle fiber
|
|
|
fascicle |
makes whole muscle |
|
|
warts |
caused by papilloma virus |
|
|
masseter |
muscle attached to the mandible |
|
|
origin |
end of the muscle attached to stationary bone |
|
|
myopathy
|
muscle disease |
|
|
cardiac
|
muscle type that contains intercalated discs. involuntary. striated. |
|
|
sphincter
|
doughnut shaped ring, dig
|
|
|
point of insertion
|
attached to movable bone
|
|
|
zoster
|
shingles caused by herpes |
|
|
acetylcholine
|
neurochemical transmitter responsible for muscle contraction
|
|
|
epimysium (first layer)
|
surrounds whole muscle
|
|
|
perimysiums
|
surrounds group of fascicles |
|
|
endomysium
|
surrounds each individual fascicle |
|
|
basal cell carcinoma |
least malignant and most common skin cancer |
|
|
jock itch |
known as tinea (fungus) cruris |
|
|
abbrasion |
condition characterized by the mechanical removal of skin tissue
|
|
|
eczema |
skin inflammation with redness, vesicles, scales, crusting and pustules |
|
|
dermis |
middle layer, true skin |
|
|
transdermal |
nicotine patches are an example, across the skin |
|
|
Vitamin D |
vitamin helps body utilize calcium and phosphorus |
|
|
calcium
|
released from sarcoplasmic reticulum when muscle is stimulated |
|
|
4th degree burn
|
penetrates all the way to bone |
|
|
thigh |
biceps femoris |
|
|
basale |
splinter penetrates to the deepest layer of the epidermis or stratum |
|
|
smooth muscle |
involved in moving food along the digestive tract |
|
|
eccrine glands |
help regulate body temperature
|
|
|
apocrine glands
|
puberty |
|
|
vasodilation
|
increase in the diameter of a blood vessel |
|
|
myosin and actin
|
form crossbridges. myosin thick, actin thin. |
|
|
agonist
|
primary movers |
|
|
antagonist
|
opposite of agonist |
|
|
synergist |
helps to assist agonist |
|
|
adduction |
toward midline |
|
|
1st degree burn |
sunburn |
|
|
diaphragm |
both voluntary and involuntary
|
|
|
skin does not function
|
synthesizing red blood cells (happens in bone)
|
|
|
sternoclydomastoid
|
responsible for flexing and rotating the head |
|
|
stratum corneum
|
outermost layer of skin composed largely of dead cells |
|
|
melanin |
gives skin normal color
|
|
|
melatonin
|
from pineal gland, responsible for day and night knowledge
|
|
|
muscle fiber (muscle cell)
|
elongated muscle
|
|
|
sprain |
muscle injury caused by overstretching |
|
|
osteomyletis
|
not a neuromuscular disease
|
|
|
ATP
|
provides energy for muscle contraction |
|
|
diabetes mellitus |
when the body is not producing adequate amounts of insulin
|
|
|
Saliva |
this substance is not increased when non-epinephrine and epinephrine are released into the bloostream |
|
|
oxytocin
|
Insufficient substance that causes contractions of the uterus to stop when a woman is in labor |
|
|
diabetes insipidus |
caused by a deficiency in the release of vasopressin (ADH) by the posterior pituitary gland |
|
|
acromegaly
|
caused by hyper-secretion of the growth hormone |
|
|
iodine |
required in the diet for normal thyroid function |
|
|
Ducts |
where exocrine organs secrete their products into |
|
|
Pancreas glan |
important in regulating the blood glucose |
|
|
thyroid gland |
produces thyroxin & triodothyronine, hormones necessary for cell metabolism |
|
|
anterior pituitary |
a stature disorder of the endocrine gland in which the body produces either too much or too little growth hormone |
|
|
Pituitary gland
|
"master gland." divided into anterior and posterior segment. apart of the diencephalon. |
|
|
ADH (antidiuretic homone)
|
pituitary hormone that is responsible for decreased urination |
|
|
Hormones
|
-chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream -has the ability to affect cells for hours/days |
|
|
hypothalamus |
resets person's temperature when experiencing a fever |
|
|
set point
|
standard level that is necessary to maintain the body's homeostasis |
|
|
steroids |
specific type of hormone that has the ability to interact with the cell's DNA |
|
|
cerebrovascular accident |
caused by the lack of blood flow to a portion of the brain |
|
|
transient ischemic attack
|
mini stroke with temporary, minor symptoms that may occur prior to a major stroke
|
|
|
meningitis |
infection from virus or bacteria that causes inflammation of the membranes surrounding the CNS |
|
|
Parkinson's Disease |
characterized in part by a resting tremor (rhymic shaking). caused by the loss of dopamine neurons. |
|
|
multiple sclerosis |
medical disorder in which the myelin in the CNS has been destroyed |
|
|
hematoma |
pool of blood between layers of the meninges nd the skull |
|
|
epinephrine |
hormones controlled by the nervous system |
|
|
hypothalmus |
effectively controls the pituitary gland |
|
|
microglia |
gia cell that attacks microbes an removes debris
|
|
|
corpus callosum
|
allows communication between the right and left brain |
|
|
plexuses
|
branching patterns of spinal nerves extending from the cervical lumbar and sacral regions of the spinal cord |
|
|
parasympathetic |
resting and digesting division of the autonomic nervous system |
|
|
subdural hematoma
|
between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater |
|
|
medulla obongata
|
controls the heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure |
|
|
pia |
the third, innermost layer of the meninges |
|
|
depolarized
|
a neuron which is more positively charged than it is when resting |
|
|
oligodendrocytes |
produces the lipid insulation, myelin and causes impulses to be conducted more rapidly
|
|
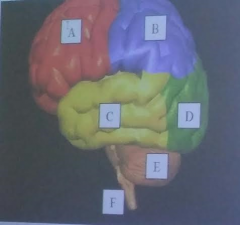
A
|
Frontal Lobe of the cerebrum
|
|
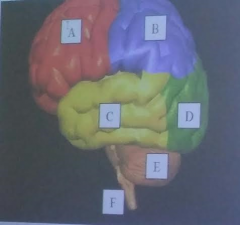
B
|
parietal lobe of the cerebrum
|
|
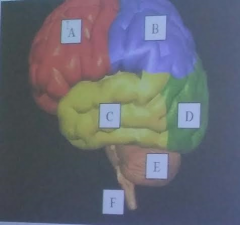
C
|
temporal lobe of the cerebrum
|
|

D
|
Occipital lobe of the cerebrum
|
|
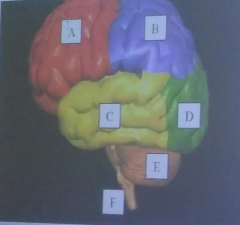
E
|
cerebellum
|
|
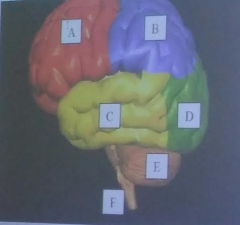
F
|
brainstem
|
|
|
limbic system |
involved in the control of emotion and mood |
|
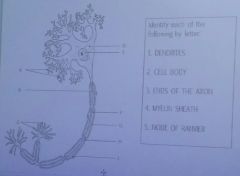
A.
|
Dendrites
|
|
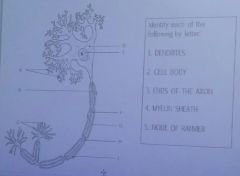
D/E
|
cell body |
|
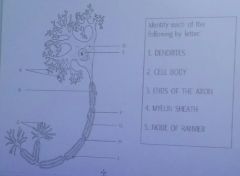
C
|
ends of the axon |
|
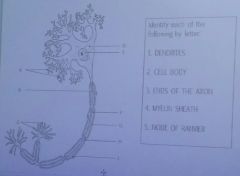
F/G
|
Myelin sheath |
|
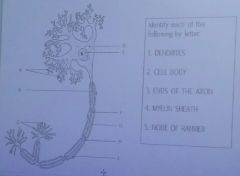
H
|
node of ranvier |
|
|
Muscle tissue
|
-can contract and relax -cardiac |
|
|
Connective tissue
|
-bone & ligament -blood -cartilage |
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
ciliated columnar |
|
|
Nervous tissue
|
brain and spinal cord |
|
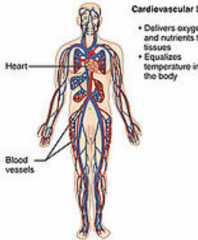
Cardiovascular system |
-houses the heart and blood vessels |
|
Reproductive system |
|
|
Endocrine system |
-secretes hormones from and to pancreas, pituitary/thyroid/adrenal glands, testes & ovaries -regulates body processes |
|
Muscular System |
provides the forces that produces body movements -helps maintain body temperature -tendons |
|
Skeletal system
|
-supports the body -enables movement |
|
Urinary System
|
removes waste products from the blood |
|
Lymphatic/Immune System |
-transports clean fluids back to blood, drains excess fluids from tissues, removes debris from cells |
|

Integumentary system |
-encloses internal body organs -site of many sensory receptors |
|
Digestive system |
breaks down food particles into a size that can be absorbed |
|

Respiratory system |
facilitates intake and output of air and exchange of gases between blood and air; releases waste gases |
|
Nervous System
|
-activates body responses |
|
Circulatory system
|
transports oxygen, nutrients, and other substances to ls and carries away wastes
|
|
|
peptide (protein) bond
|
occurs when amino acids (monomers) bond together |
|
|
facilitated diffusion |
the type of membrane transport that requires a carrier molecule |
|
|
solute |
substance dissolved in a liquid |
|
|
exocytosis |
transporting substances out of cells |
|
|
mitochondria |
provides power (ATP) for cell processes |
|
|
Meiosis
|
produces gametes, responsible for producing eggs and sperm |
|
|
gametes
|
sex cells |
|
|
mitosis
|
cellular reproduction (cell division), the process of making a new cell |
|
|
Nosocomial |
An infectious disease tou acquire while in a medical facility |
|
|
Idiopathic disease |
The name of a disease whose cause cannot be determined |
|
|
Epidemiology |
Study of transmission, frequency of occurrence, distribution and control of a disease. |
|
|
Communicable disease |
Can be spread from person to person or from insect to person |
|
|
Endemic |
A disease that is continually present within a specific population or region |
|
|
Epidemic |
A disease that suddenly occurs in large numbers over a specific region |
|
|
Pandemic |
When a disease spreads country or worldwide. |
|
|
Vital signs |
Pulse (heart rate), blood pressure, body temperature & respiratory rate |
|
|
Syndrome |
The specific grouping of signs and symptoms related to a specific disease |
|
|
Prognosis |
The prediction of the outcome pf a disease |
|
|
Vector borne transmission |
The organism is carried by an insect or other animal |
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Heart, lungs, and large blood vessels. |
|
|
Pericardial cavity |
The heart only |
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Digestive organs: stomach, liver, intestines, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen in the upper portion. |
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains the urinary & reproductive organs & the last part of the large intestine. |
|
|
Dorsal cavity |
Cranial cavity (Brain) & spinal cavity (spinal cord) |
|
|
Body regions ( 1st row from L to R) |
Right hypochondriac | epigastric | left hypochondriac |
|
|
Body regions ( 2nd row from L to R) |
Right lumbar | umbilical | left lumbar |
|
|
Body regions ( 3rd row from L to R) |
Right iliac | hypogastric | left iliac |
|
|
Location of appendix |
RLQ- right lower quadrant |
|
|
Covalent bond |
When electrons are shared by atoms |
|
|
Polar covalent bond |
When one atom takes more than its share of the shared electrons |
|
|
Hydrophyllic |
Water loving |
|
|
Solution |
When one substance is dissolved in another |
|
|
Solute |
The substance being dissolved |
|
|
Solvent |
The substance doing the dissolving (usually water) |
|
|
Concentration |
The amount of solute dissolved in a solvent |
|
|
Cellular respiration |
When glucose is combined w/ oxygen & is transformed into ur mitochondria into ATP. |
|
|
Passive transport |
Diffusion, osmosis, filtration, facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Active/passive transport |
The movement of materials across the membrane |
|
|
Passive teansport |
Requires no extra energy to complete |
|
|
Diffusion |
Most common means of passive trasport. A substance of higher concentration that travels to a substance of lesser concentration. |
|
|
Osmosis |
Form of passive transport. Water travels thru selectively permeable membrane until concentrations of a substance are equalized. |
|
|
Filtration |
Pressure is applied to force water & its dissolved materials across a membrane. |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
A variation of diffusion in which a substance is helpedbin moving across the membrane. Protein helps glucose across the cell. |
|
|
Active transport |
Active transport pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
When a solid particle is engulfed by a cell. |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Occurs when the cell needs to transport substances out of itself. |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
When the intake involves liquid |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Watery solution of biological material (proteins, carbs, lipids) & (minerals & gases) chemicals that are enclosed in the cell membrane. |
|
|
Centrosomes |
Builds new cell structures |
|
|
Centrioles |
Involved in the division of the cell |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
A series of channels setup in the cytoplasm that are formed from folded membranes. |
|
|
Lysosome |
Enzymes that break things down |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Power plant for cellular repair |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells |
The cellsvthat make up the human body |
|
|
Prokaryotic cells |
Bacterial cells that do not have a nucleus or organelles |
|
|
Mitosis |
Tje division and sorting of the genetic material |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
The division of the cytoplasm |
|
|
Microorganisms
|
bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa |
|
|
bacteria
|
make up the largest group of pathogen. ex: diplocci, streptococci, staphylococci, bacillus. |
|
|
normal flora
|
normal, good bacteria that lives within or on us |
|
|
virus
|
infectious particles that have a core containing genetic material surrounded by a protective protein coat called a capsid. Ex: HIV/AIDS
|
|
|
Fungi
|
one-celled or multi-celled organism. Plantlike organisms that have tiny filaments, that travel out from the cell to find and absorb nutrients. Ex: yeast, ringworm, rhizopus, aspergillus, cryptococcus |
|
|
Protozoa
|
one-celled animal-like organisms that can be found in water such as ponds and in soil. Ex: trypanosoma, plasmodium, amoeba. |
|
|
membranes
|
sheetlike structures throughout the body. |
|
|
pseudostratified
|
columnar epithelium, which looks stratified but is not. |
|
|
nervous tissue
|
acts as a rapid messenger service for the body and it's messages causes actions to occur |
|
|
Pituitary Gland
|
controls other glands; regulates growth and fluid balance |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Regulates water balance, body temperature, and appetite along with producing releasing hormones |
|
|
Thyroid Gland |
Controls tissue metabolic rate and regulates calcium levels |
|
|
Parathyroid gland |
regulates calcium levels (with thyroid) |
|
|
Thymus |
Controls white blood cell maturation |
|
|
Adrenal Glands |
adjust water balance, tissue metabolism, cardiovascular and respiratory activity |
|
|
pancreas |
regulates blood glucose levels |
|
|
gonads (testes) |
support male sexual characteristics and reproductive functions |
|
|
ovaries |
support female sexual characteristics and reproductive functions |
|
|
arteries
|
carry blood from heart to capillaries |
|
|
veins
|
return blood from capillaries to the heart |
|
|
septicemia |
sepsis aka blood poisoning |
|
|
bulimia |
a condition in which an individual goes on eating binges, overeats, and then attempts to get rid of the food by either vomiting or using laxatives to keep from gaining weight |
|
|
anorexia
|
the condition in which there is a progressive and severe weight loss even as the patient denies that there is a problem |
|
|
periosteum |
tough and fibrous connective tissue. contains blood vessels that transport blood and nutrients into the bone to nurture the bone cells. |
|
|
epiphysis |
the ends of long bones |
|
|
diaphysis (shaft) |
the region between or "running thru" the two ends of bones |
|
|
compact bone |
dense, hard tissue that normally forms the shafts of long bones and the outer layer of other bones |
|
|
medullary canal |
the hallow region in the diaphysis (shaft) |
|
|
red marrow |
makes blood cells |
|
|
yellow marrow |
has high fat content. can convert to red bone marrow to help in the production of red blood cells |
|
|
ossification/osteogenesis |
the formation of bone in the body |
|
|
osteoprogenitor cells |
non-specialized cells found in the periosteum, endosteum, and central canal of compact bones |
|
|
hemopoiesis |
the production of red blood cells |
|
|
epiphyseal plate
|
growth plate |
|
|
cartilage
|
special form of dense connective tissue that can withstand a fair amount of flexing, tension, and pressure. |
|
|
synovial fluid
|
protects the area between the bones, joints. |
|
|
articulation |
two or more bones joined together |
|
|
hinge joint
|
found in knees and elbow |
|
|
ball and socket
|
found in shoulders and hips |
|
|
pivot
|
found in neck and forearm |
|
|
extension
|
a movement that increases the angle of a joint |

