![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sagittal plane |
Long axis, right and left halves that are not always equal. |
|
|
Median Plane
|
Equal right and left halves .
|
|
|
Transverse plane
|
cross-section; cutting in half. perpendicular to the long axis. |
|
|
Dorsal plane in humans
|
called frontal plane, front and back halves.
|
|
|
Dorsal plane in animals
|
upper and lower halves. dorsal and central
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity
|
close to the spine or vertebral column. includes cranial and spinal cavity.
|
|
|
Ventral cavity
|
close to the belly. includes thoratic cavity, pleural cavity, pericardial cavity. abdominal cavity
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity
|
Chest cavity, Part of the ventral cavity.
|
|
|
Pleural cavity
|
Lungs, in the central cavity
|
|
|
Pericardial cavity
|
The heart, ventral cavity.
|
|
|
abdominal cavity |
the pelvic cavity, in the ventral cavity. |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Organic molecules that give energy, store, contribute to cell structures. Includes sugar, starch and cellulose |
|
|
Lipids |
Organic molecules that store energy, give physical protection, contributes to hormone through cell communication. Includes triglycerides, steroids, elcosanoids and phospholipids. Hydrophilic tail, hydrophobic head. |
|
|
Starch |
Type of carbohydrate, the storage form of sugars. |
|
|
Cellulose |
Type of carbohydrate that gives you fiber. |
|
|
Proteins |
Organic molecule that builds everything, and is most abundant. made up of amino acids and peptide bonds. Physical shape is important. |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Organic molecule, and the largest in the body. Includes DNA and RNA and codes for proteins. |
|
|
Amino acids |
Make up proteins, 100 make one protein. 20 biologically active ones in the body, the rest are obtained through the essential ones. |
|
|
Form determines ________ which determines ______ and ________. Surface area determines _________ |
Shape/function/form/ cell size |
|
|
Cell membrane |
Barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell, and includes the phospholipid bilayer. It is selectively permeable |
|
|
Integral protein |
Membrane protein in the phospholipid bilayer. + and - Pores. Embedded within and pass through the membrane without going through the lipid bilayer. |
|
|
Peripheral protein |
Membrane protein on the outside of both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. Can attach things to the surface of the cell and include glycoproteins |
|
|
Integral glycoproteins |
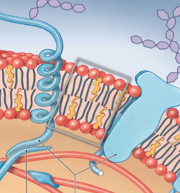
|
|
|
Peripheral proteins |
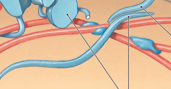
|
|
|
Sperm |
The only flagellated cell in the mammalian body. |
|
|
Cytosol |
Part of the cytoplasm that gives form and structure to the cell, consists of dissolved molecules, suspended proteins, and mostly water. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Part of the cytoplasm that is flexible. It includes microtubules, intermediate fibers, and microfilaments. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Organelle that is the powerhouse, breaks down molecules for fuel, contains ATP, and more of these equals a more active cell. Have their own nucleic acids and DNA, and has a double membrane. |
|
|
Mitochondria |

|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Have their own RNA, site of protein synthesis, may be free or attached. |
|
|
Ribosome |
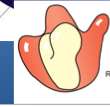
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Flat tubes with a lot of surface area. Connected with the Golgi apparatus and the nucleus. |
|
|
Rough ER |
Has ribosomes, and is involved in protein production. Sends things to the golgi apparatus to be sent out of the cell. |
|
|
Smooth ER |
Involved in the production and storage of lipids, Glycogen breakdown, and detoxification. |
|
|
Rough ER |

|
|
|
Smooth ER |

|
|
|
Nucleus |
Surrounded by a double lipid bilayer membrane that is porous for transportation, contains the DNA and is filled with nucleoplasm. |
|
|
Nucleus |
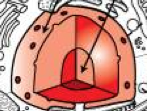
|
|
|
Chromatin |
The strand-like areas of the nucleus, includes DNA wrapped around histone proteins that condense into chromosomes during cell division. |
|
|
Nucleoli |
Part of the nucleus that has ribosome synthesis and makes rRNA |
|
|
Chromatin |

|
|
|
Simple diffusion |
Passive process that moves a molecule from an area of high concentration, down the concentration gradient, and into an area of low concentration. Speed depends on the amount of kinetic energy. |
|
|
Ability of a molecule to diffuse across the cell membrane |
- Cell size (must be small) - Lipid solubility - Molecular charge (must be neutral and ions need pores)
|
|
|
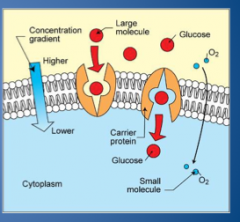
Faciliated diffusion |
Passive process that is used by small, non-lipid molecules. Binds to a carrier protein that transports it. Rate is limited by the number of carrier proteins, but can be affected by other things (insulin) |
|
|
Faciliated diffusion |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Passive process that moves only water across a semipermeable membrane. Continues until equilibrium and same solute is reached. |
|
|
Importance of osmosis to cells |
Determines the movement of fluids into and out of the cell. They want all concentrations to be leveled to prevent osmosis. |
|
|
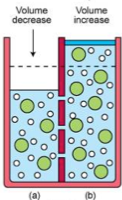
Crenate |
When cells shrink in a hypertonic solution |
|
|
Lice |
Cell bursting from being placed in a hypotonic solution |
|
|
Osmotic pressure |
Weight of water against the membrane. |
|
|
Osmosis |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
|
|
|
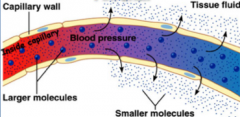
Filtration |
Hydrostatic pressure forcing fluid across the membrane, the pushing force. This pressure is provided by the heart in mammals. Fluid can move down or against a pressure membrane. |
|
|
Filtration |
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
An active process that where materials are engulfed by cell membrane extensions, and are taken in as membrane-bound vesicles. Include phagocytosis and pinocytosis. |
|
|
Receptor-mediated endocytosis |
A ligand binds specific receptors on cell surface, and only takes what binds. |
|
|
Macrophage |
Acts as a cleanup around the cells through endocytosis. |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Takes materials out of the cell through membrane-bound vesicles. Helps during an allergic reaction. |
|
|
Active transport |
Uses a carrier molecule with a specific binding site. ATP is used as an energy source in case molecules are moved against a concentration gradient. |
|
|
Symport |
Carrier in active transport that takes two things in the same direction |
|
|
Antiport |
Carrier in active transport that takes one thing in and one thing out. |
|
|
Na+/K+ Pump |
Resting membrane potential. Active transport. Keeps normal ion concentrations in the cell. |
|
|
Resting membrane potential |
Maintains the normal difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane. |
|
|
ATP |
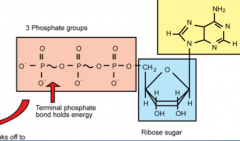
|
|
|
Na+/K+ in normal resting cell |
Inside: Low Na+/ high K+ Outside: High Na+/low K+ |
|
|
Na+/K+ Pump |
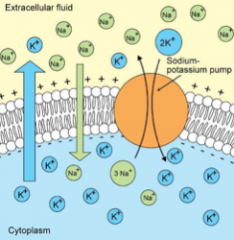
|

