![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the stomata? |
Small pores on the underside of the leaf which allows for gases to be exchanged |
|
|
What is transpiration? |
The exchange of gases and the escape of water vapor through open stomata |
|
|
What is the transpirational pull? |
The force that pulls water from the roots all the way to the leaves via the xylem |
|
|
What is the purpose of the xylem? |
The lignified walls contribute to the plant's support |
|
|
What is cohesion? |
Water molecules are polar and stick to each other |
|
|
What is adhesion? |
Water molecules are polar and stick to the xylem vessels |
|
|
What is a xerophyte? |
A plant adapted to live in dry conditions |
|
|
What are the properties of a xerophyte? |
small leaves; stomata on the stem and not the leaf; stomata open at night to reduce water loss; waxy cuticles to reduce water loss |
|
|
Study the diagram of the xylem vessels. Draw and label afterwards. |
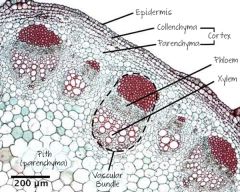
|
|
|
What is translocation? |
Transport of minerals, amino acids, and carbohydrates from one part of the plant to another through the phloem |
|
|
What is sap? |
Water containing carbohydrates, amino acids, and plant horomones. It acts similarly to the circulatory system of animals, ensuring that all parts of the plant can perform the functions of life |
|
|
What is the direction of the flow of sap? |
From source to sink |
|
|
Be Aware! |
Phloem: column of living cells with perforated walls between them. Xylem: column of dead cells, with cell end walls removed. Sap will flow from an area with high hydrostatic pressure to an area with low hydrostatic pressure. |
|
|
Distiguish between xylem and phloem. |
Xylem - columns of dead cells; continuous tube which allows unbroken column of water; thickened cell walls containing lignin; transport of water and minerals Phloem - columns of living cells; transport of organic compounds loaded by active transport; has companion cells for cell functions, with many mitochondria that provide the ATP for active transport; transports sugars, amino acids, and plant hormones |
|
|
Where is growth concentrated in plants? |
The meristems |
|
|
Define meristems. |
undifferentiated cells that divide and grow rapidly |
|
|
What is the apical meristem? |
the roots and tips of stems, where most of the growth occurs |
|
|
What is a tropism? |
A directional response caused by a directional external stimulus |
|
|
Define totipotent |
any plant cell can differentiate into all plant tissues |
|
|
Examine and draw this diagram. |
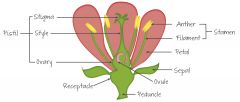
|

