![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3. Within what time frame must imaging be initiated following injection of 201 Tl chloride in exercise perfusion study?
a. within 5 minutes b. within 10-15 minutes c. within 20-30 minutes d. within 4 hours |
b
|
|
|
4.Of the choices offered, which is the best imaging view for calculating right ejection fraction?
a. RAO 60 deg b. RAO 30 deg c. anterior d. LAO 10 deg |
b
|
|
|
9. Which of the following cannot be evaluated by a MUGA scan?
a. wall motion b. wall thickness c. aneurysmal flow d. vessel patency |
b
|
|
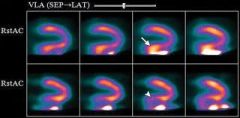
The images above represent:
a. short axis b. vertical long axis c. horizontal long axis d. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
15. The vertical long axis of the heart is most comparable to a:
a. coronal image b. sagittal image c. transverse |
b
|
|
|
17. In multigated analysis of the left ventricular, end systole is best described as:
a. the frame with the highest number of counts in the ROI around the left ventrical b. the frame with the lowest number of counts in the ROI around the right ventrical c. the frame with the lowest number of counts in the ROI around the left ventricle, plus the counts from the background ROI d. all of the above e. none of the above |
e
|
|
|
18. All of the following will negatively affect a myocardial study with 201 Tl chloride except:
a. wrong collimatior b. arrhythmia c. incorrect COR d. increased patient to detector distance e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
20. Which of the following does not describe correct preparation for an exercise myocardial study?
a. NPO at least 4 hours prior to radiopharmaceutical administration b. catheter placement for injection of radiopharmaceutical during exercise c. halt all medication 24 hours before study d. none of the above |
c
|
|
|
22. Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals is not used to study the heart?
a. 99mTc sestamibi b. 99mTc HSA c. 99mTc PYP d. 99mTc WBC's e. both b and d |
d
|
|
|
23. Which of the following is not a critical factor in obtaining a gated first pass study?
a. tracer bolus of small volume b. regular heartbeat c. use of multi-crystal gamma camera d. positioning heart in the center of the field of view |
c
|
|
|
24. The best collimator for use during a first pass study is:
a. LEAP b. high sensitivity c. high resoluton d. medium energy |
b
|
|
|
25. A neonatal first pass study is performed and the time activity curve for the ROI around the left ventricle shows a peak activity occuring before the activity peak on the lung ROI. This most likely indicates:
a. improperly drawn ROI b. interventricular shunt c. prolapsed mitral valve d. radiotracer contained in too high a volume |
b
|
|
|
26. A nuclear medicine physician prefers that static myocardial perfusion images be obtained according to the best septal visualization. If the septum is well visualized on LAO 45 deg, what other views should be obtained?
a. anterior, LAO 70 deg b. RAO 20 deg, LAO 60 deg c. anterior, LAO 60 deg d. RAO 5 deg, LAO 65 deg |
d
|
|
|
27. Cardiac contraction is initiated in the:
a. SI node b. AV node c. bundle of HIS d. P wave |
a
|
|
|
29. A high resolution collimator would be most appropriate for:
a. myocardial perfusion study with 201 Tl chloride b. myocardial perfusion with 99m Tc sestamibi c. first pass study with 99mTc DTPA d. myocardial imaging with 99mTc pyrophosphate |
b
|
|
|
31. Infarct-avid myocardial imaging with 99mTc PYP is usually interpreted by comparing cardiac activity in:
a. rib b. sternum c. kidneys d. all of the above e. a and b only |
e
|
|
|
33. Gated equilibrium cardiac blood pool images can be used to reliably determine:
a. hibernating myocardium b. LVEF c. interventricular shunt d. ischemia e. all of the above |
b
|
|
|
36. When labeling RBC's with 99mTc for radionuclide ventriculography, the highest labeling efficiency will be obtained by:
a. the invivo method b. the invitro method c. the modivied invivo/invitro method d. all result in the same labeling efficiency |
b
|
|
|
37. In which of the following cases must imaging be intiated as soon as possible after radiopharmaceutical injection?
a. radionuclide ventriculography with 99mTc labeled RBC's b. radionuclide ventriculography with 99mTc HSA c. myocardial prefusion imaging with 99mTc sestamibi d. resting myocardial perfusion with 201 Tl chloride |
b
|
|
|
38. A patient has an enlarged left atrium. When drawing an ROI for calculation of LVEF following radionuclide ventriculography, the technologist includes some activity from the left atrium. The resulting ejection fraction will be:
a. unchanged b. falsely elevated c. falsely lowered d. cannot be determined from the information given |
c
|
|
|
39. Gated blood pool ventriculography is often used to:
a. diagnose arrhythmia b. obtain a baseline measurement of cardiac function in potential radiation therapy patients c. detect hematologic spread of metastases d. determine effect of chemotherapy on cardiac fuction |
d
|
|
|
44. Choose the correct order in which the structures appear during a first pass study.
a. right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left ventricle b. right ventricle, pulmonary veins, lungs, pulmonary artery, left atrium c. left ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, right ventricle d. left ventricle, pulmonary veins, lungs, pulmonary artery, right ventricle e. right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium |
e
|
|
|
47. Why is it necessary to inject 2 doses of 99mTc Sestamibi for myocardial perfusion study including both stress and rest conditions?
a. because the physical half life of 99mTc is too short to obtain both image sets from one injection b. because there is no redistribution of the 99mTc sestamibi within the mycardium c. because the effective half life is too short d. because sestamibi is not retained by the myocardium for a sufficient time |
b
|
|
|
50. Differences between myocardial perfusion imaging with 201 Tl chloride and 99m Tc sestamibi include:
a. high resolution collimator can be used with 201 Tl b. less soft tissue attenuation with 201 Tl c. higher photon flux with 99mTc d. less respiratory motion with 201 Tl due to delay after exercise before imaging |
c
|
|
|
52. Following injection of 99mTc sestamibi, during a resting myocardial perfusion study, imaging is delayed for one hour because:
a. respiratory motion will decrease b. liver and lung activity is too high to allow high quality images of the myocardium c. until one hour after injection, sestamibi has not had sufficient time to be taken up by the myocardium d. the patient should be monitored for adverse reactions during the first hour |
b
|
|
|
57. During a MUGA study, data collection is stopped when:
a. a preset number of counts has been acquired b. a preset number of cardiac cycles has been reached c. a preset time has been reached d. when either a preset number of counts or a preset number of cardiac cycles has been reached e. when either a preset number of cardiac cycles or a preset time has been reached |
d
|
|
|
61. Relative to one another, 82 Rb and 82 Sr are:
a. isobars b. isotopes c. isotones d. none of the above |
a
|
|
|
62. Patient A and Patient B are injected with the same dose of 13N ammonia for a myocardial PET scan. The patients are the same height but Patient A weighs 120 lbs. and Patient B weighs 180 lbs. From which patient would more coincidence be detected?
|
b
|

