![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Species |
Group of organisms that can reproduce to have fertile offspring |
|
|
Population |
Group of organisms of the same species living in the same place |
|
|
Community |
Formed by populations of different species living together and interacting with each other |
|
|
Ecosystem |
Formed by the interaction of a community with its abiotic environment |
|
|
Autotroph |
Organism that synthesizes organic molecules from simple inorganic substances obtained from the abiotic environment |
|
|
Heterotroph |
An organism that obtains organic molecules from other organisms |
|
|
Saprotroph |
A heterotrophic organism that lives on or in non-living organic matter, secreting digestive enzymes onto it and absorbing the products of digestion |
|
|
Consumer |
Heterotrophic organism that ingests other organic matter that is living or recently killed |
|
|
Detrivore |
Heterotroph that ingests detritus |
|
|
Food chain |
Shows linear relationship of one organism feeding on another, each organism is on a trophic level. |
|
|
Decomposers |
Dead organisms and waste products broken down by decomposers |
|
|
Food web |
Series of interlinking food chains |
|
|
Mesocosm |
- Small-scale investigations - Self-sustaining natural systems - Middle ground between controlled lab experiment and field experiment - Allow greater number of key variables to be controlled to evaluate how organisms would respond to a change in environment |
|
|
Energy in ecosystems |
- Enters as light, turned into chemical energy by photosynthesis - Stored in organic carbon compounds, flows through food chains by feeding. - Converted to heat energy during respiration and leaves the system as it cannot be converted. |
|
|
Efficiency of energy flow |
- Usually 10-20% - Restricts length of food chains when there is insufficient energy to support next trophic level - Biomass of higher trophic levels diminishes due to the loss of carbon dioxide and excretory compounds - Efficiency = Energy at next level/Energy at start of trophic level |
|
|
Ecosystem dynamics |
- Finite supply of nutrients - Sustainable if: sufficient energy input (sunlight), nutrients recycled or replenished, community not damaged - Death of organisms recycles nutrients |
|
|
Conversion of CO2 |
Autotrophs convert the gas into carbohydrates and other compounds |
|
|
Carbon in aquatic ecosystems |
Dissolved CO2 and hydrogen carbonate ions |
|
|
Methane |
Produced from organic matter in anaerobic conditions by methanogenic archaeans and diffuses into atmosphere or accumulates in the ground. Oxidized to form CO2 in atmosphere. |
|
|
Peat |
Forms when organic matter is not fully decomposed because of acidic or anaerobic conditions in waterlogged soils. |
|
|
Partially decomposed organic matter |
Accumulates and can be converted into coal or gas over time, with pressure due to layers of porous rock forming |
|
|
Production of CO2 |
- Combustion of biomass |
|
|
Fossilization |
Animals such as reef-building corals and mollusks have hard parts that are composed of calcium carbonate, become fossilized in limestone |
|
|
Construct diagram of carbon cycle |
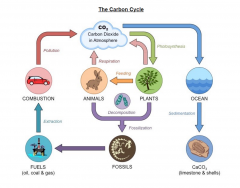
|
|
|
Carbon flux |
Flow of carbon from one carbon reservoir to another |
|
|
Four major carbon reservoirs |
- Atmosphere - Oceans - Earth crust - Terrestrial ecosystems |
|
|
Net flux |
The difference between the input to reservoirs and output from the reservoirs (measured in GT) |

