![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Provides support and protection to the abdominal organs.
Transmits forces from the head, arms, & trunk to the lower extremities. Receives the ground forces generated when the foot contacts the ground & transmits them upward toward the vertebral column. During walking, the pelvic girdle moves as a unit in all three planes. It provides attachment for muscles & makes up the bony portion of the birth canal in females. |
pelvic girdle
|
|
|
Bones of the Pelvic girdle
|
Sacrum
Coccyx Hip bones (ilium, ischium) pubis |
|
|
Bones are joined around the -------& tied together at the symphysis to form a single unit
|
sacrum
|
|
|
All mvmt. Of the pelvic girdle occurs around this joint
|
Lumbosacral
|
|
|
Nonaxial synovial joint
Mvmt. = Extremely limited & is never voluntary |
Sacroiliac (SI joint) (2)
|
|
|
Cartilaginous joint which joins the two pubes
Allows only slight movement (amphiarthroidal) |
pubic symphysis
|
|
|
Relaxed standing posture the angle is about
|
30 degrees
|
|
|
What does this show?
|
Forward tilt
|
|
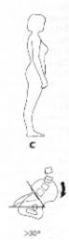
What does this show?
|
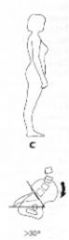
Forward tilt
|
|
|
Anterior tilt of the pelvis (i.e., iliac crest tilts forward; pubic symphysis tilts backwards. You may read some texts that talk about a posterior pelvic tilt, referring to the pubic symphysis.);
Hyperextension of the lumbosacral joint resulting in a downward & backward mvmt of the symphysis more than 30 degree tilt increased angle & lumbar lordosis |
forward tilt
|
|
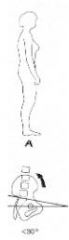
What type of tilt?
|
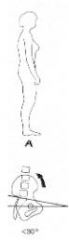
backward
|
|
|
Anterior tilt of the pelvis (i.e., iliac crest tilts forward; pubic symphysis tilts backwards. You may read some texts that talk about a posterior pelvic tilt, referring to the pubic symphysis.);
Hyperextension of the lumbosacral joint resulting in a downward & backward mvmt of the symphysis less 30 degree tilt =increased angle & lumbar lordosis |
backward tilt
|
|
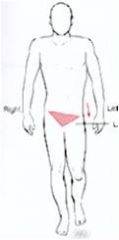
What type of tilt?
|
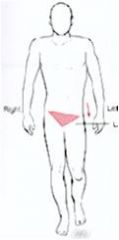
lateral tilt
|
|
|
Lateral flexion of the lumbosacral joint resulting in the raising or lowering of one iliac crest
Hip hiking |
lateral tilt
|
|
|
Movement to the right and left at the lumbosacral joint resulting in a pivoting motion of the hips around a vertical axis.
|
rotation
|
|
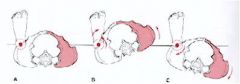
what motion?
|
rotation
Movement to the right and left at the lumbosacral joint resulting in a pivoting motion of the hips around a vertical axis. |
|
|
The first ---------degrees of spine flexion occurs in the lumbar area
|
50 to 60
|
|
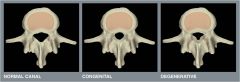
What pathology is show in the photo?
|
stenosis= narrowing of spinal canal
|
|
|
The first----------of spine flexion occurs in the lumbar area
|
The first 50 to 60 degrees of spine flexion occurs in the lumbar area
|
|
|
Additional ---------is accomplished through the forward tilting of the pelvis and weight of the upper body
|
Additional flexion is accomplished through the forward tilting of the pelvis and weight of the upper body
|
|
|
For the loads on the spine to be minimized during lifting, the distance between the trunk & the object lifted should be as ------------as possible
|
short
|
|
|
When a vertebra is subjected to compressive load that exceeds its failure point, the end-plate or the ---------- fractures before the disc is damaged
|
vertebral body
|
|
|
In what region?
Relaxed upright standing, the compressive load =2x the weight of the superimposed body e.g. holding 20 lbs. = compressive load of 40 lbs. |
Lumbar Region
|
|
|
Unsupported sitting--->------loads than standing.
Minimal load ---> ------position. Externally applied loads produced by lifting or carrying--->very high loads on the ------spine. Intrabdominal pressure may help to support the spine & thus reduce the load. |
Unsupported sitting--->higher loads than standing.
Minimal load ---> supine position. Externally applied loads produced by lifting or carrying--->ery high loads on the lumbar spine. Intrabdominal pressure may help to support the spine & thus reduce the load. |
|
|
ROM decreases up to ---% with old age
|
ROM decreases up to 50% with old age
|
|
|
Men have greater mobility in -------
|
flexion-extension.
|
|
|
Women are more mobile in --------
|
Women are more mobile in lateral flexion.
|
|
|
The ligaments and discs provide the intrinsic stability of the spine.
Most have a high ---------content which limits their extensibility during spine motion. |
The ligaments and discs provide the intrinsic stability of the spine.
Most have a high collagen content which limits their extensibility during spine motion. |
|
|
The amount of strain on the various ligaments differ with the spinal type of motion.
Flexion - Increases strain on ------------ligament Extension - increases strain on -------- ligament Lateral flexion - increases strain on --------------ligaments Rotation - increases strain on ---------ligament |
he amount of strain on the various ligaments differ with the spinal type of motion.
Flexion - Increases strain on interspinous ligament Extension - increases strain on anterior longitudinal ligament Lateral flexion - increases strain on contralateral transverse ligaments Rotation - increases strain on capsular ligaments |
|
|
Agonistic muscles -----------and carry out motion & antagonistic muscles ---------it.
|
Agonistic muscles initiate and carry out motion & antagonistic muscles control and modify it.
|
|
|
The orientation of the --------determines the type of motion possible at any level of the spine.
|
The orientation of the facets determines the type of motion possible at any level of the spine.
|
|
|
The facets may also sustain compressive loads, particularly during ----------
|
The facets may also sustain compressive loads, particularly during hyperextension.
|
|
|
The primary function of the facets is to ------ the motion of the moving segment.
|
The primary function of the facets is to guide the motion of the moving segment.
|
|
|
A joint is where two or more bones are joined. Joints allow motion (articulation). The joints in the spine are commonly called Facet Joints. Other names for these joints are ---------------
|
A joint is where two or more bones are joined. Joints allow motion (articulation). The joints in the spine are commonly called Facet Joints. Other names for these joints are Zygapophyseal or Apophyseal Joints.
|
|
|
Loads on the spine are produced primarily by
|
Body weight,
Muscle activity, Pre-stress exerted by the ligaments, & Externally applied loads. |
|
|
It is multi-axial
|
hip
|
|
|
Illiopsoas - located deep in the abdominal cavity
Tensor Fascia Latea & Erectus Femoris are assistive muscles Erectus Femoris is not a strong flexor Illiospsoas is made up of 2 muscles Illiacus – coming off of the Illium Psoas - comes from anterior part of vertebrae |
hip flexion
|
|
|
In the standing position, contracted -------muscles (which ride over the pubic crests) move the pubis backward; the ----------muscles move the pubis forward. (antagonists)
|
In the standing position, contracted psoas muscles (which ride over the pubic crests) move the pubis backward; the abdominal muscles move the pubis forward. (antagonists)
|
|
|
In walking, the ---------muscles of one side initiate movement of that leg forward, while the --------bring the same-side hip and pubis forward. (synergists)
|
In walking, the ilio-psoas muscles of one side initiate movement of that leg forward, while the abdominals bring the same-side hip and pubis forward. (synergists)
|

