![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
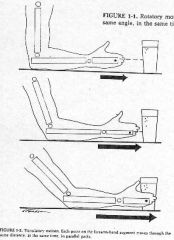
What type of motion?
|
linear/translatory
|
|
|
–
The number of independent movements allowed at a joint. – A joint can have up to three degrees of translatorymotions and three degrees of rotatorymotion. |
degrees of freedom
|
|
|
–
Describes the motion that occurs between the articular surfaces of the joints. – Three movements: roll, slide, & spin |
arthokinematics
|
|
|
For a convex-on-concave surface movement, the convex member rolls and slides in opposite direction
|
ArthrokinematicPrinciples of Movement
|
|
|
•
External Factors – Friction, air resistance, water resistance • Anatomic Factors:(modify motion of body segments) – Friction in joints – Tension of muscles, ligaments & fasciae – Anomalies of bones & joint structure – Presence of interfering soft tissue (fat) |
Factors that Modify Motion:
|
|
|
types of motion
|
Linear motionis the movement of all body parts in the same direction and at the same velocity.
• Angular motionprovides for the circular rotation of an object around an axis, • Curvilinear motionis the movement of an object along a curved but not circular path |
|
|
Joint Motionis described in degrees of freedom of independent movement.
• Jointsmove by rolling, sliding, spinning, and any combination of these motions. |
joint movement
|
|
|
Push & pull exerted by one object on another that can produce, arrest, or modify movement.
|
force
|
|
|
Two consequences of force
|
A force acting on a body has two effects, one to move it and two to rotate it.
|
|
|
Normal forces that push 2 surfaces together
|
comprehensive forces
|
|
|
Streching force
Normal forces that push 2 surfaces together |
tensile force
|
|
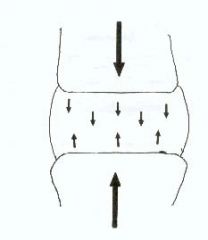
What type of force?
|
comprehensive
|
|
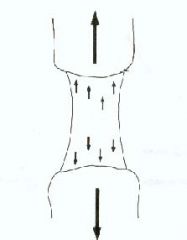
What type of force?
|
tensile forces
|
|
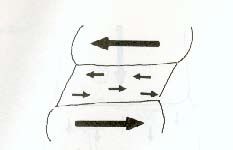
What type of force?
|
shear
|
|
|
Normal forces that act parallel to the surfaces
• a stress which is applied parallel or tangential to a face of a material, as opposed to a normal stress which is applied perpendicularly. Opposite directions |
shear/tangenital
|
|
|
Principal types of force acting to move or stabilize the musculoskeletal system can be:
|
–
Internal forces: produced from structures within the body – External forces: produced from structures outside the body |
|
|
What type of force?
Active: generated by muscles – Passive: generated by tension • |
•
Internal Force – |
|
|
what type of force?
– Gravity pulling on body mass – External load, such as weights – Physical contact |
types of external force
|
|
|
To describe force, you must know:
– |
To describe force, you must know:
– Magnitude(spatial quality/extent of the force being exerted) – Direction(pull toward or away from the source) – Point of application(point at which the force is applied to an object) |
|
|
a graphical representation of a force; straight line drawn to scale, with an arrow pointing the direction of the force
|
Vector –a graphical representation of a force; straight line drawn to scale, with an arrow pointing the direction of the force
|
|
|
2+ forces acting along the same line, in same or opposite direction
|
Linear Force
– |
|
|
Force action lines are parallel, in the same plane, and act at different points; same or opposite direction
• E.g., lever system or 3-point bracing system; 3rdforce between them = stabilizer (law of action-reaction) |
parallel forces
|
|
|
Two forces of different magnitudes & opposite direction applied simultaneously to an object
|
Force Systems
• |
|
|
•
2+ Forces acting at angles from a common point of application |
CONCURRENT FORCES
|
|
|
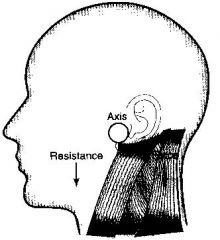
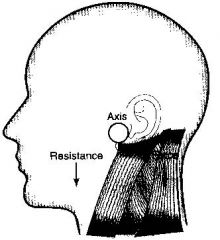
Example of Force Couple in the Body
|
:Movement of the scapula
|
|
|
•
____is not a standard term in mechanics. • ____is used to designate the ability to produce or resist a force. • Muscle______ maybe measured in terms of the ability to overcome a resistance, to resist forces, or to support a load. |
strength
|
|
|
is defined as the rate of doing work or work done per unit of time
= work / time |
power
|
|
|
is defined as the product of force and displacement of object in direction of the force as the force is applied
= weight x distance x repetition • |
Work
|
|
|
The human body moves because the musculoskeletal system is a system of _________
|
levers
|
|
|
a rigid bar acted upon at two different points by opposing forces
They allow us to either do something with less effort or to increase the speed or force of an object being moved.. |
lever
|
|
|
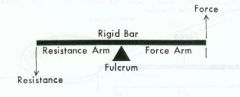
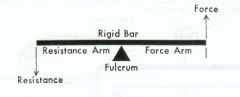
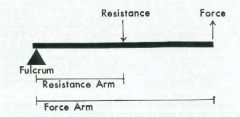
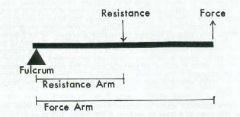
Lever Components
• |
Lever Components
• Fulcrum (axis) = A • Force Arm (force applied) = F • Resistance Arm (weight arm) = R |
|
|
What type of lever?
FIRST CLASS LEVER – Fulcrum is between the weight (R) and force (F) arms • Lever characteristics – balanced movement • axis is midway between force and resistance • e.g.: seesaw – speed and range of motion • axis is close to force • e.g.: elbow extension – force • axis is close to resistance |
first class lever
|
|
|
•
This type of lever favors equilibrium. • This lever is used to gain either force or distance. • It is the most versatile of the three levers. • Frequently used for maintaining postures or balance. • Commonly used in orthotics, called a 3-point system for applying force. • Examples: seesaws, scissors, crowbars, & jacks |
first class lever
|
|
What type of lever?
|
first class lever
|
|
|
What type of lever?
Weight (R) is between the fulcrum and force (F) arm |
second class
|
|
What type of lever?
|
second class
|
|
|
lever provides a force advantage to support large weights or to be moved by a smaller force.
• This type of lever favors the force of effort. • Force arm is always greater (longer) than the resistance arm. • ROM is sacrificed to gain force. • In the human body, this type of lever is seen when gravity is the force and muscles are the resistance. • E.g. wheelbarrow,Nutcracker,Paddle, |
Second Class Lever
|
|
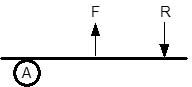
What type of lever?
Force (F) arm is between the fulcrum and weight (R) arm |
THIRD CLASS LEVER
|
|
|
lever used to produce speed & distance of the distal segment of the body
– What is gained in speed or distance is lost in force. – What is gained in force is lost in speed. • Force arm (FA) will always be shorter than the resistance arm (RA) • Designed to produce speed and distance of movement at the expense of force; allows minimal muscle shortening because the muscles insert near the joint • Most common lever type in the body. • Ex. Baseball bat, Boat paddle, Broom, Electric Gates, Fishing rod, Hockey stick, Mandible, Mousetrap (Spring-loaded bar type), Shovel (the action of picking or lifting up sand or dirt), Stapler, Tongs, Tweezers, Hammer, Tennis racket, The Human Arm |
third class lever
|
|
|
rigid bar which moves around a fulcrum (axis) for motion
|
bone
|
|
|
in a leverage system when does movement occur
|
Movement occurs when the force of muscle contraction is sufficient to overcome the resistance, which is at least the weight of the part being moved
|
|
|
F-----A------R
|
first class lever
|
|
|
A------R-------F
|
second class lever
|
|
|
A-----F-------R
|
third class lever
|
|
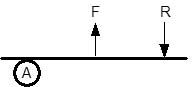
What type of Lever?
|
First Class Lever
|
|
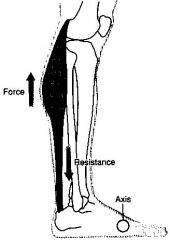
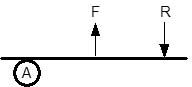
What type of lever?
|
2nd class
|
|
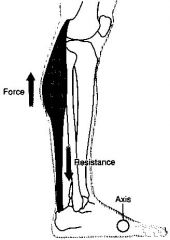
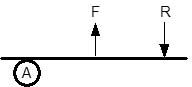
What type of lever?
|
third class
|
|
|
The principles of the ______are used to visualize the complex system of forces that produce rotary motion in the body –muscles, gravity, & physical contact.
|
levers
|
|
|
A lever is in balance or______ , when force x force arm = resistance x resistance arm
|
equilibrium
|
|
|
•
Refers to the efficiency of a lever. • Is the relationship between the length of the force arm (FA) and the length of the weight arm (RA) MA = FA / RA • When only a small effort of force is needed to overcome a larger resistance, the lever is efficient. |
mechanical advantage
|
|
|
: waste energy and force to gain speed and distance
|
3rdClass Levers
|
|
|
utilizes less force and energy to gain little speed or distance.
|
2ndClass Levers:
|
|
|
Majority of the human body levers are quite ________as far as force requirements are concerned, but they do provide a large amount of motion at the distal end.
• Goal of human function is the placement or relocation of the distal segments of the body. |
inefficient
|
|
|
the most constant force encountered by the body. It affects the stability of the body as well as the movement of the trunk, extremities & head.
|
GRAVITY
|
|
|
is enhanced by a low center of gravity, wide base of support, the gravity line at the center of the support, & heavy weight.
|
Stability
|
|
|
Any change in _____distribution results in a change in the center as well as line of gravity.
|
WEIGHT
|
|
|
•
is enhanced by a high center of gravity, narrow base of support, & light weight. • |
Mobility
|
|
|
--------can & does provide the force for motion.
|
GRAVITY
|
|
|
are easier to maintain when the base of support is increased or the center of gravity is lowered.
|
Balance & Stability
|
|
|
WHAT TYPE OF LEVER?
Used to gain force, distance, or stability |
FIRST CLASS
|
|
|
The human body uses a system of _______to move. The -------of a muscle pull directly effects the force it is capable of producing.
|
LEVER, EFFICIENCY
|
|
|
WHAT TYPE OF LEVER?
Allows for support of large weights or for the weights to be moved by a smaller force – Utilizes less force and energy to gain little speed or distance. |
2ND CLASS
|
|
|
WHAT TYPE OF LEVER?
– Produces speed & distance of distal segment – Wastes energy & force to gain speed & distance |
3RD CLASS
|
|
|
Changing the length of the force arm (FA) or resistance arm (RA) will make
|
–
Movement easier or harder and – Lever more or less efficient. |

