![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Force= |
mass x acceleration |
|
|
Potential energy
|
Energy of position
|
|
|
Energy |
the ability to do work. |
|
|
In order to do work, ______ _______ ________!
|
SOMETHING MUST MOVE!
|
|
|
Power
|
The rate at which work is done. |
|
|
Work
|
Applied energy; energy caused by forces.
|
|
|
Mechanical Energy?
|
energy created by the physical movement of rotation, revolution, ect. of an object.
|
|
|
Law of Conservation of Energy
|
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred and converted
|
|
|
Work
|
when a force acts on an object and the object moves in the direction of the force
|
|
|
Power
|
The rate at which work is done. |
|
|
Watt
|
The unit of power. (Joule/second)
|
|
|
Potential energy
|
Energy that is stored and held in readiness. ex: elastic, chemical, gravitational
|
|
|
Kinetic energy
|
The energy of motion.
|
|
|
Work energy theorem
|
States that whenever work is done, energy changes. |
|
|
Force unit
|
Newton
|
|
|
Work unit
|
Joule |
|
|
Force x distance
|
Work
|
|
|
Work / time
|
Power
|
|
|
number of supporting ropes
|
the mechanical advantage of a pulley
|
|
|
simple machine
|
a device with which you can do work in a way that is easier or more effective.
|
|
|
effort force
|
force you exert on the machine
|
|
|
resistance force
|
force exerted by the machine
|
|
|
wave
|
a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another
|
|
|
equilibrium
|
The natural position of a wave
|
|
|
pulse
|
A disturbance that moves through a wave
|
|
|
energy
|
What is actually transferred through a wave
|
|
|
interference
|
When two waves meet while traveling along the same medium
|
|
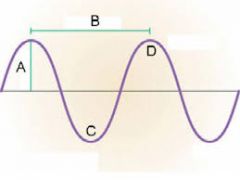
What is "A"? |
Amplitude
|
|
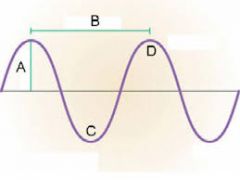
What is "B"?
|
Wavelength
|
|
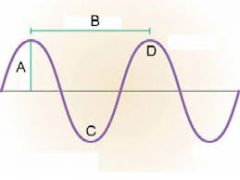
What is "C"?
|
Trough
|
|
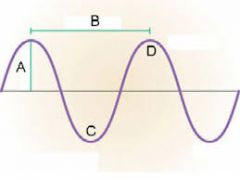
What is "D"?
|
Crest
|
|
|
The unit of weight
|
Newtons
|
|
|
The tendency of an object to resist change
|
inertia
|
|
|
mass in motion
|
momentum
|
|
|
the unit for momentum
|
kg m/s
|

